Abstract
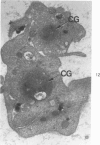
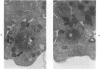
Blood platelets contain a variety of contractile protein species, including the glycoprotein alpha-actinin, which is found at the Z disc in skeletal muscle cells. In the present study, we have considered the possibility that alpha-actinin might be one of several previously described platelet surface glycoproteins. Purified anti-alpha-actinin antibody was found to react strongly with partially purified platelet glycoprotein III, weakly with platelet glycoprotein IIb, and not at all with platelet glycoproteins Ib and IV. Platelets from three siblings with thrombasthenia, a disorder characterized by severe deficiency of platelet glycoproteins IIb and III, were found also to be equally deficient in alpha-actinin. These findings indicate that alpha-actinin and glycoprotein III are identical and suggest that this protein may be an anchor point for actin on the inside of the membrane. Combined with ultrastructural studies of normal and thrombasthenic platelets, the new findings provide a clearer understanding of contraction in single cells and small aggregates.
Full text
PDF



















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arakawa N., Robson R. M., Goll D. E. An improved method for the preparation of alpha-actinin from rabbit striated muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 17;200(2):284–295. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90172-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettex-Galland M., Lüscher E. F. Thrombosthenin, the contractile protein from blood platelets and its relation to other contractile proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1965;20:1–35. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60387-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch W. A., Stromer M. H., Goll D. E., Suzuki A. Ca 2+ -specific removal of Z lines from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1972 Feb;52(2):367–381. doi: 10.1083/jcb.52.2.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I., Cohen C. A tropomyosin-like protein from human platelets. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 21;68(2):383–387. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I., Kaminski E., De Vries A. Actin-linked regulation of the human platelet contractile system. FEBS Lett. 1973 Aug 15;34(2):315–317. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80820-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton W. R., Goll D. E., Zeece M. G., Robson R. M., Reville W. J. A Ca2+-activated protease possibly involved in myofibrillar protein turnover. Purification from porcine muscle. Biochemistry. 1976 May 18;15(10):2150–2158. doi: 10.1021/bi00655a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton W. R., Reville W. J., Goll D. E., Stromer M. H. A Ca2+-activated protease possibly involved in myofibrillar protein turnover. Partial characterization of the purified enzyme. Biochemistry. 1976 May 18;15(10):2159–2167. doi: 10.1021/bi00655a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller G. M., Brinkley B. R., Boughter J. M. Immunofluorescence of mitotic spindles by using monospecific antibody against bovine brain tubulin. Science. 1975 Mar 14;187(4180):948–950. doi: 10.1126/science.1096300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J. N., Potterf R. D., Lewis P. C., Sears D. A. Studies on platelet plasma membranes. I. Characterization of surface proteins of human platelets labeled with diazotized (125i)-diiodosulfanilic acid. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Aug;88(2):232–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. M., Rao G. H., White J. G. The influence of reserpine and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) on serotonin storage organelles of blood platelets. Am J Pathol. 1977 Jun;87(3):633–646. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. M., White J. G., Rao G. H. Effects of the lonophore A23187 on the blood platelets II. Influence on ultrastructure. Am J Pathol. 1974 Nov;77(2):151–166. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. M., White J. G., Rao G. H., Krivit W., Witkop C. J., Jr Labile aggregation stimulating substance (LASS): the factor from storage pool deficient platelets correcting defective aggregation and release of aspirin treated normal platelets. Br J Haematol. 1975 Apr;29(4):657–665. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb02751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. M., White J. G., Rao G. H., Townsend D. Localization of platelet prostaglandin production in the platelet dense tubular system. Am J Pathol. 1976 May;83(2):283–298. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. M., White J. G. The influence of aspirin and indomethacin on the platelet contractile wave. Am J Pathol. 1976 Mar;82(3):513–526. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. M., White J. G. The influence of prostaglandin endoperoxides on platelet ultrastructure. Am J Pathol. 1975 Aug;80(2):189–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. M., White J. G. The structure and function of platelets, with emphasis on their contractile nature. Pathobiol Annu. 1976;6:31–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDISTY R. M., DORMANDY K. M., HUTTON R. A. THROMBASTHENIA. STUDIES ON THREE CASES. Br J Haematol. 1964 Jul;10:371–387. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1964.tb00714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowey S., Steiner L. A. An immunochemical approach to the structure of myosin and the thick filament. J Mol Biol. 1972 Mar 14;65(1):111–126. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90495-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masaki T., Endo M., Ebashi S. Localization of 6S component of a alpha-actinin at Z-band. J Biochem. 1967 Nov;62(5):630–632. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Needleman P., Bunting S., Vane J. R. Prostaglandin endoperoxide and thromboxane generating systems and their selective inhibition. Prostaglandins. 1976 Sep;12(3):323–335. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(76)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooseker M. S., Tilney L. G. Organization of an actin filament-membrane complex. Filament polarity and membrane attachment in the microvilli of intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):725–743. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurden A. T., Caen J. P. An abnormal platelet glycoprotein pattern in three cases of Glanzmann's thrombasthenia. Br J Haematol. 1974 Oct;28(2):253–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb06660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okumura T., Jamieson G. A. Platelet glycocalicin. I. Orientation of glycoproteins of the human platelet surface. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):5944–5949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Agin P. P. Platelet membrane defects in Glanzmann's thrombasthenia. Evidence for decreased amounts of two major glycoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1977 Sep;60(3):535–545. doi: 10.1172/JCI108805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Agin P. P. Platelet plasma membrane glycoproteins. Evidence for the presence of nonequivalent disulfide bonds using nonreduced-reduced two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):2121–2126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Agin P. P. Thrombin substrates and the proteolytic site of thrombin action on human-platelet plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jun 13;352(2):218–227. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Jakábová M. Ca2+-dependent protease in human platelets. Specific cleavage of platelet polypeptides in the presence of added Ca2+. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5602–5605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Jenkins C. S., Lüscher E. F., Larrieu M. Molecular differences of exposed surface proteins on thrombasthenic platelet plasma membranes. Nature. 1975 Oct 16;257(5527):599–600. doi: 10.1038/257599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy M. K., Etlinger J. D., Rabinowitz M., Fischman D. A., Zak R. Removal of Z-lines and alpha-actinin from isolated myofibrils by a calcium-activated neutral protease. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4278–4284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson R. M., Goll D. E., Arakawa N., Stromer M. H. Purification and properties of alpha-actinin from rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 17;200(2):296–318. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90173-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stromer M. H., Hartshorne D. J., Mueller H., Rice R. V. The effect of various protein fractions on Z- and M-line reconstitution. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jan;40(1):167–178. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki A., Goll D. E., Singh I., Allen R. E., Robson R. M., Stromer M. H. Some properties of purified skeletal muscle alpha-actinin. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6860–6870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE J. G., YUNIS E., COLLIANDER M., KRIVIT W. THE CORRECTION OF PROLONGED BLEEDING TIMES IN TWO BROTHERS BY PLATELET TRANSFUSIONS DESPITE NORMAL IN VITRO PLATELET TESTS. Pediatrics. 1964 Apr;33:579–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Fine structural alterations induced in platelets by adenosine diphosphate. Blood. 1968 May;31(5):604–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]