Abstract
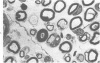
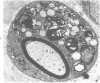
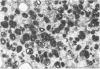
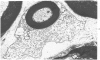
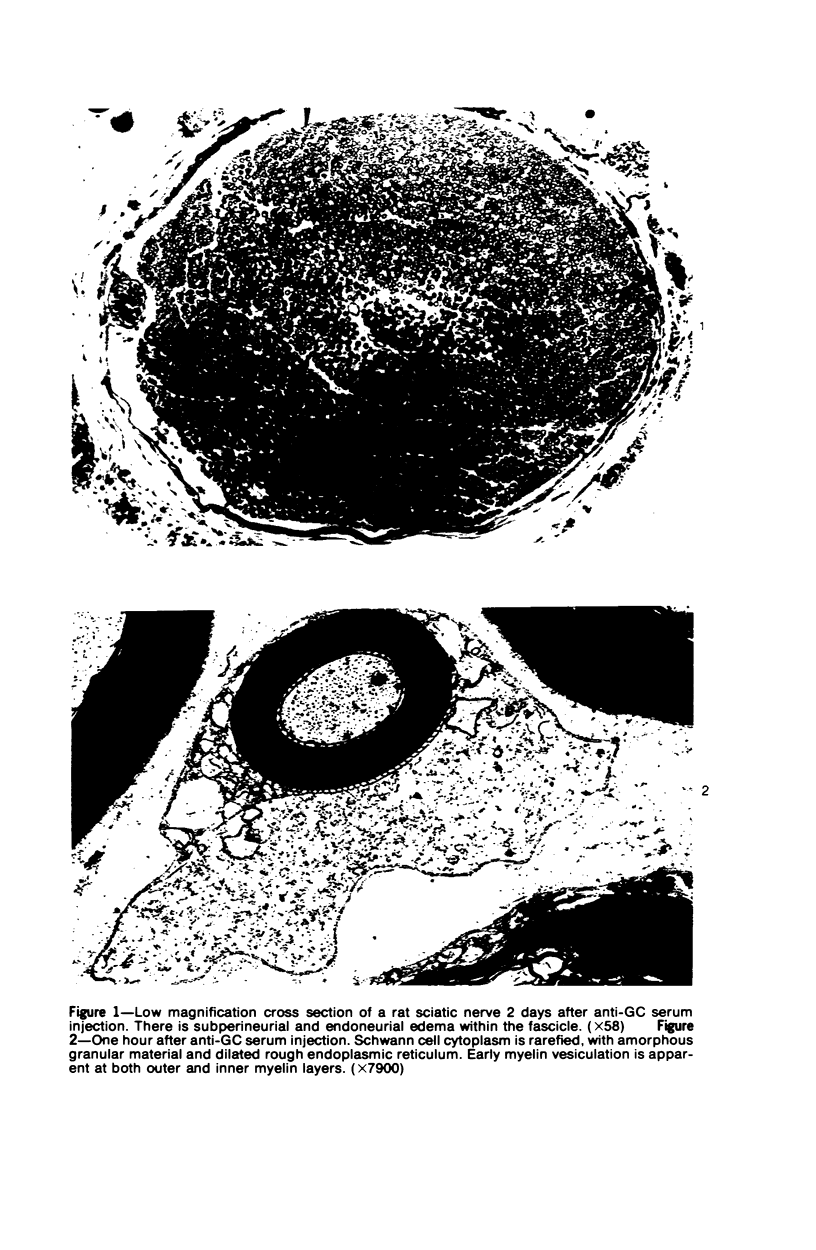
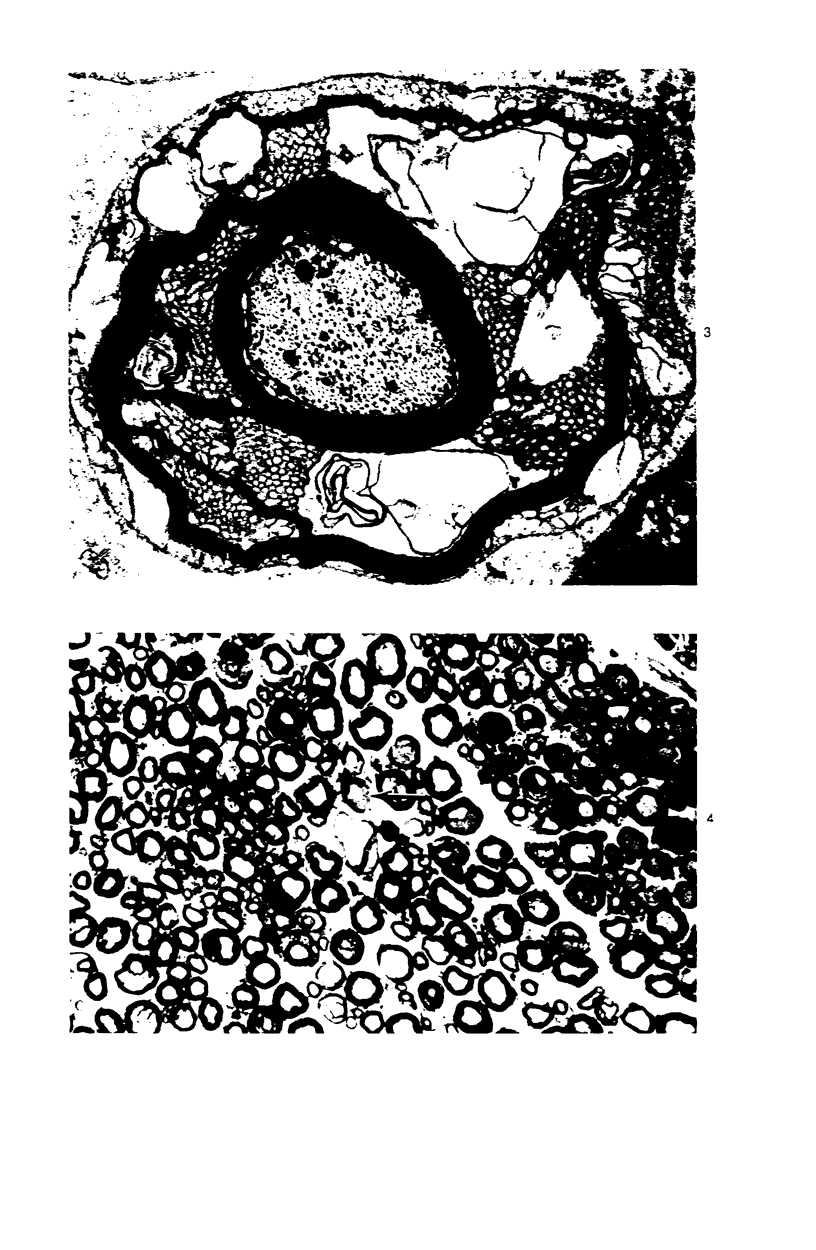
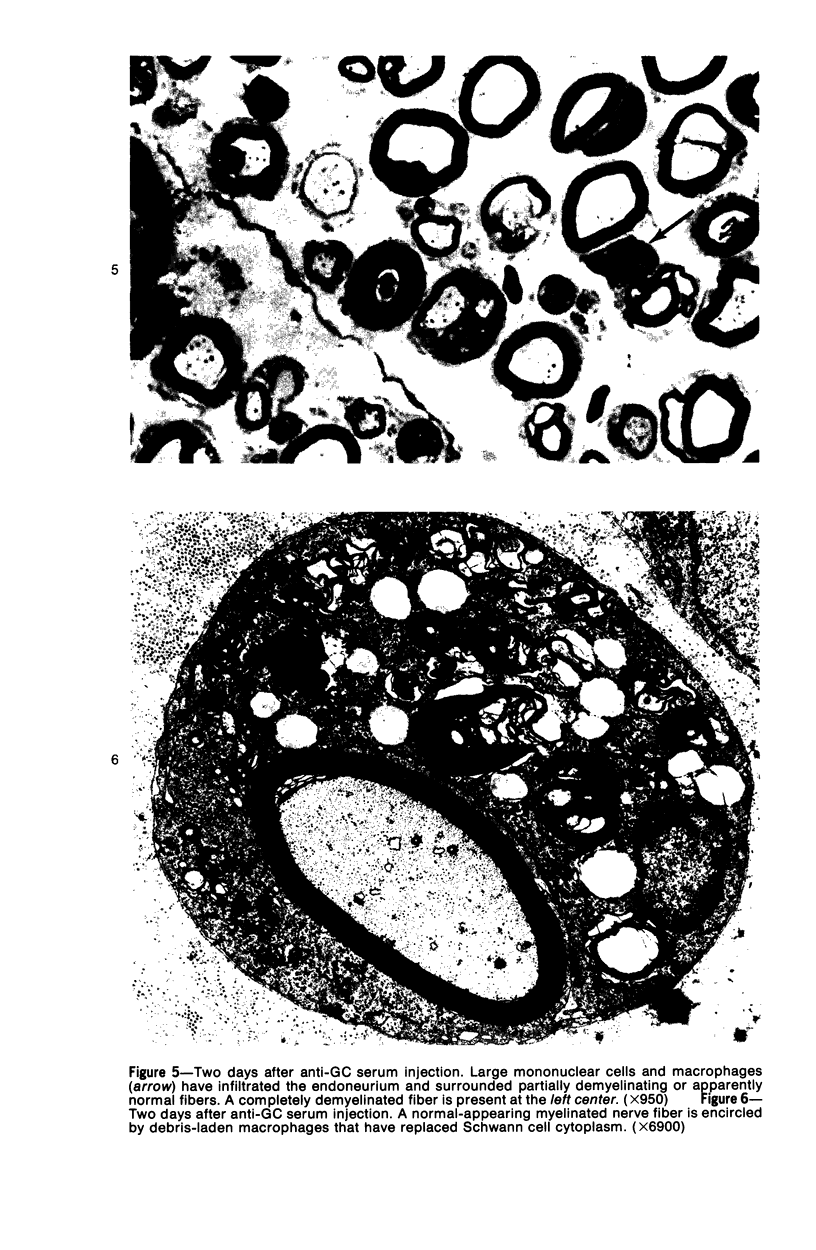
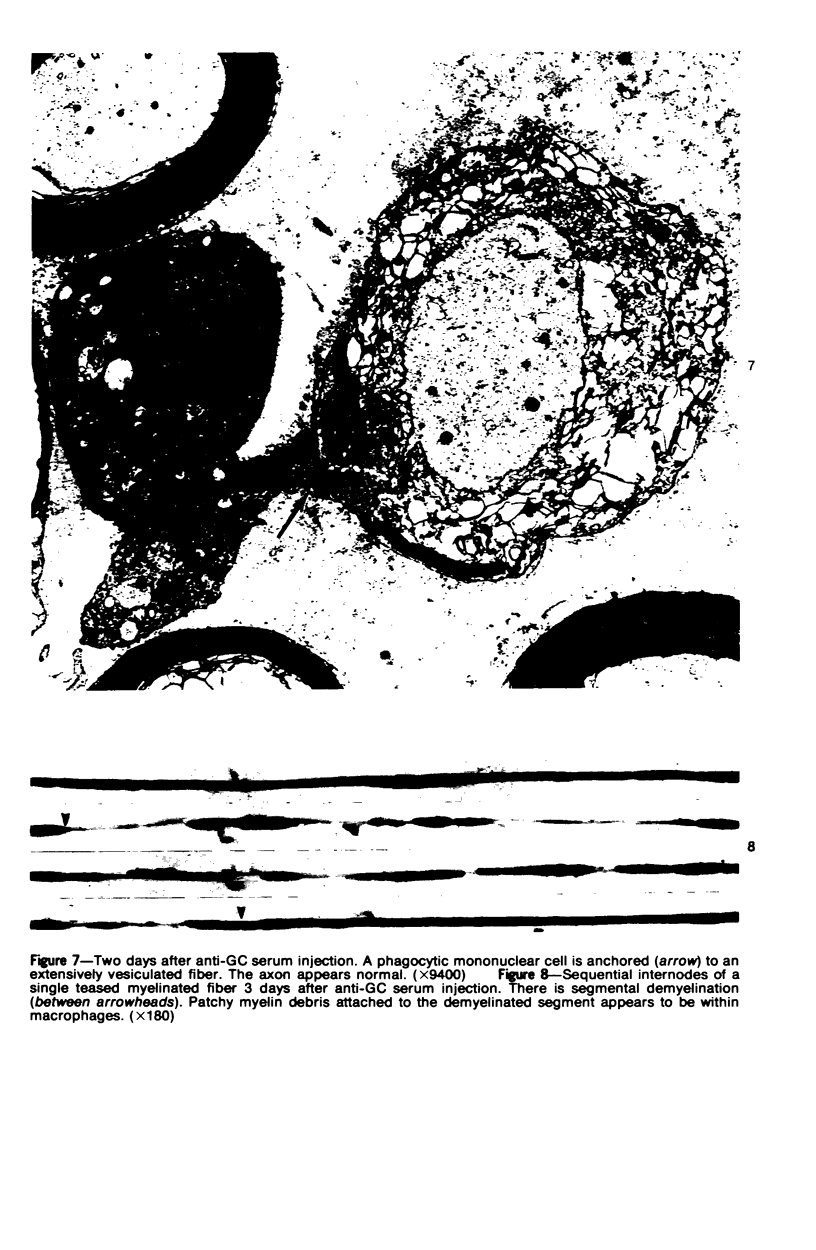
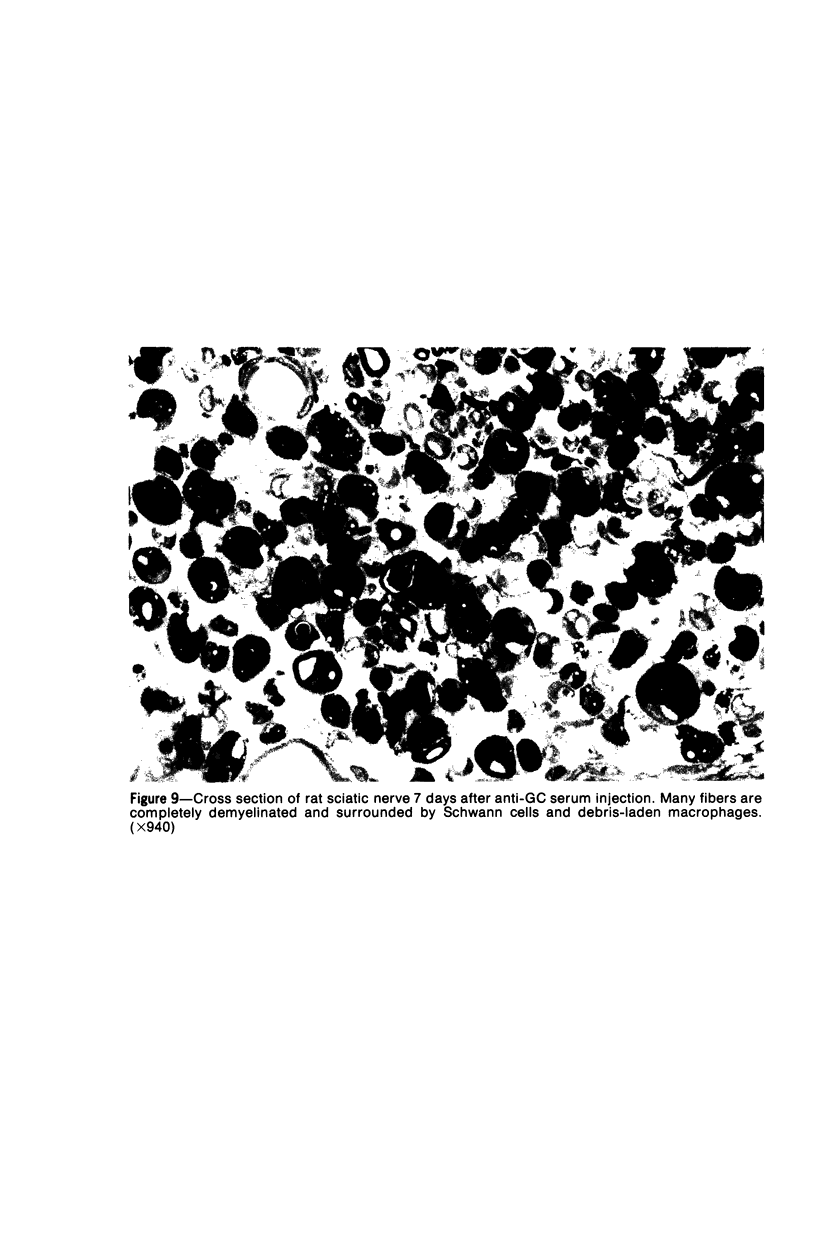
Intraneural injection of rabbit anti-galactocerebroside (anti-GC) serum produced focaldemyelinative lesions in rat sciatic nerves. Recipient rats developed a sensory motordeficit of the toes and feet on the side injected with anti-GC serum. Schwann cellabnormalities in recipient nerves were apparent by 20 minutes, followed by myelinsplitting and vesiculation over the next 8 hours. Macrophages first appeared in moder-ate numbers by 15 hours, and degraded myelin was completely phagocvtized by 5 days.An acute inflammatory reaction consisting of endoneurial edema, polymorphonuclearcell infiltration, and fibrin extravasation also was prominent. In vivo demyelinativeactivity of rabbit anti-GC serums was removed by pre-incubation with GC or central orperipheral nervous system myelin and was also lost when the serums were heated at 56C for 30 minutes and injected into nerves of rats previously injected with cobra venomfactor. Anti-GC antibodies are present in the serum of rabbits with experimentalallergic neuritis (WNV-EAN) and encephalomyelitis (WM-EAE) produced, respectively,by immunization with whole peripheral nerve or brain white matter and may play arole in the pathogenesis of demyelination in GC-induced EAN, WN-EAN, or WM-EAE.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramsky O., Teitelbaum D., Webb C., Arnon R. Neuritogenic and encephalitogenic properties of the peripheral nerve basic proteins. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1975 Jan;34(1):36–45. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197501000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agamanolis D. P., Victor M., Harris J. W., Hines J. D., Chester E. M., Kark J. A. An ultrastructural study of subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord in vitamin B12-deficient rhesus monkeys. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1978 May;37(3):273–299. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197805000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allt G., Evans E. M., Evans D. H. The vulnerability of immature rabbits to experimental allergic neuritis: a light and electron microscope study. Brain Res. 1971 Jun 18;29(2):271–291. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbury A. K., Arnason B. G., Adams R. D. The inflammatory lesion in idiopathic polyneuritis. Its role in pathogenesis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1969 May;48(3):173–215. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196905000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballin R. H., Thomas P. K. Electron microscope observations on demyelination and remyelination in experimental allergic neuritis. I. Demyelination. J Neurol Sci. 1969 Jan-Feb;8(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(69)90037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakemore W. F. Observations on remyelination in the rabbit spinal cord following demyelination induced by lysolecithin. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1978 Jan-Feb;4(1):47–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1978.tb00528.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein M. B., Raines C. S. The initial structural lesion in serum-induced demyelination in vitro. Lab Invest. 1976 Oct;35(4):391–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostoff S. W., Levit S., Powers J. M. Induction of experimental allergic neuritis with a peptide from myelin P2 basic protein. Nature. 1977 Aug 25;268(5622):752–753. doi: 10.1038/268752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalcanto M. C., Wiśniewski H. M., Johnson A. B., Brostoff S. W., Raine C. S. Vesicular disruption of myelin in autoimmune demyelination. J Neurol Sci. 1975 Mar;24(3):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(75)90251-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorfman S. H., Fry J. M., Silberberg D. H., Grose C., Manning M. C. Cerebroside antibody titers in antisera capable of myelination inhibition and demyelination. Brain Res. 1978 May 26;147(2):410–415. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90854-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois-Dalcq M., Niedieck B., Buyse M. Action of anti-cerebroside sera on myelinated nervous tissue cultures. Pathol Eur. 1970;5(3):331–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry J. M., Lisak R. P., Manning M. C., Silberberg D. H. Serological techniques for detection of antibody to galactocerebroside. J Immunol Methods. 1976;11(2):185–193. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry J. M., Weissbarth S., Lehrer G. M., Bornstein M. B. Cerebroside antibody inhibits sulfatide synthesis and myelination and demyelinates in cord tissue cultures. Science. 1974 Feb 8;183(4124):540–542. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4124.540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E. Bee and wasp venoms. Science. 1972 Jul 28;177(4046):314–322. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4046.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall S. M., Gregson N. A. The in vivo and ultrastructural effects of injection of lysophosphatidyl choline into myelinated peripheral nerve fibres of the adult mouse. J Cell Sci. 1971 Nov;9(3):769–789. doi: 10.1242/jcs.9.3.769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano A., Cook S. D., Whitaker J. N., Dowling P. C., Murray M. R. Fine structural aspects of demyelination in vitro. The effects of Guillain-Barré serum. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1971 Apr;30(2):249–265. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197104000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruger L., Maxwell D. S. Wallerian degeneration in the optic nerve of a reptile: an electron microscopic study. Am J Anat. 1969 Jul;125(3):247–269. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001250302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P. W., Kies M. W. Mechanism of demyelination in allergic encephalomyelitis of guinea pigs. An electron microscopic study. Exp Neurol. 1967 Jun;18(2):210–223. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(67)90042-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P. W. Mechanism of demyelination in experimental allergic neuritis. Electron microscopic studies. Lab Invest. 1969 Feb;20(2):127–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisak R. P., Heinze R. G., Kies M. W. Relationships between antibodies and experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. 3. Coprecipitation and radioautography of 125I-labeled antigen-antibody complexes for detection of antibodies to myelin basic protein. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;37(6):621–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masurovsky E. B., Bunge M. B., Bunge R. P. Cytological studies of organotypic cultures of rat dorsal root ganglia following X-irradiation in vitro. II. Changes in Schwann cells, myelin sheaths, and nerve fibers. J Cell Biol. 1967 Feb;32(2):497–518. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.2.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIEDIECK B. ZUR FRAGE DER LIPIDHAPTENE DES NERVENSYSTEMS. Z Immunitats Allergieforsch. 1964 Mar;126:40–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson Y. Studies on vascular permeability in peripheral nerves. IV. Distribution of intravenously injected protein tracers in the peripheral nervous system of various species. Acta Neuropathol. 1971;17(2):114–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00687487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prineas J. W. Acute idiopathic polyneuritis. An electron microscope study. Lab Invest. 1972 Feb;26(2):133–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raine C. S., Bornstein M. B. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: an ultrastructural study of experimental demyelination in vitro. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1970 Apr;29(2):177–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raine C. S., Snyder D. H., Valsamis M. P., Stone S. H. Chronic experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in inbred guinea pigs. An ultrastructural study. Lab Invest. 1974 Oct;31(4):369–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saida K., Mendell J. R., Sahenk Z. Peripheral nerve changes induced by local application of bee venom. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1977 Sep-Oct;36(5):783–796. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197709000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saida K., Saida T., Brown M. J., Silberberg D. H., Asbury A. K. Antiserum-mediated demyelination in vivo: a sequential study using intraneural injection of experimental allergic neuritis serum. Lab Invest. 1978 Nov;39(5):449–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saida T., Saida K., Silberberg D. H., Brown M. J. Transfer of demyelination by intraneural injection of experimental allergic neuritis serum. Nature. 1978 Apr 13;272(5654):639–641. doi: 10.1038/272639a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaepfer W. W. Vesicular disruption of myelin simulated by exposure of nerve to calcium ionophore. Nature. 1977 Feb 24;265(5596):734–736. doi: 10.1038/265734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seil F. J., Falk G. A., Kies M. W., Alvord E. C., Jr The in vitro demyelinating activity of sera from guinea pigs sensitized with whole CNS and with purified encephalitogen. Exp Neurol. 1968 Dec;22(4):545–555. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(68)90148-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAKSMAN B. H. Experimental study of diphtheritic polyneuritis in the rabbit and guinea pig. III. The bloodnerve barrier in the rabbit. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1961 Jan;20:35–77. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196101000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski H., Prineas J., Raine C. S. An ultrastructural study of experimental demyelination and remyelination. I. Acute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the peripheral nervous system. Lab Invest. 1969 Aug;21(2):105–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski H., Terry R. D., Whitaker J. N., Cook S. D., Dowling P. C. Landry-Guillain-Barré syndrome. A primary demyelinating disease. Arch Neurol. 1969 Sep;21(3):269–276. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1969.00480150059008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]