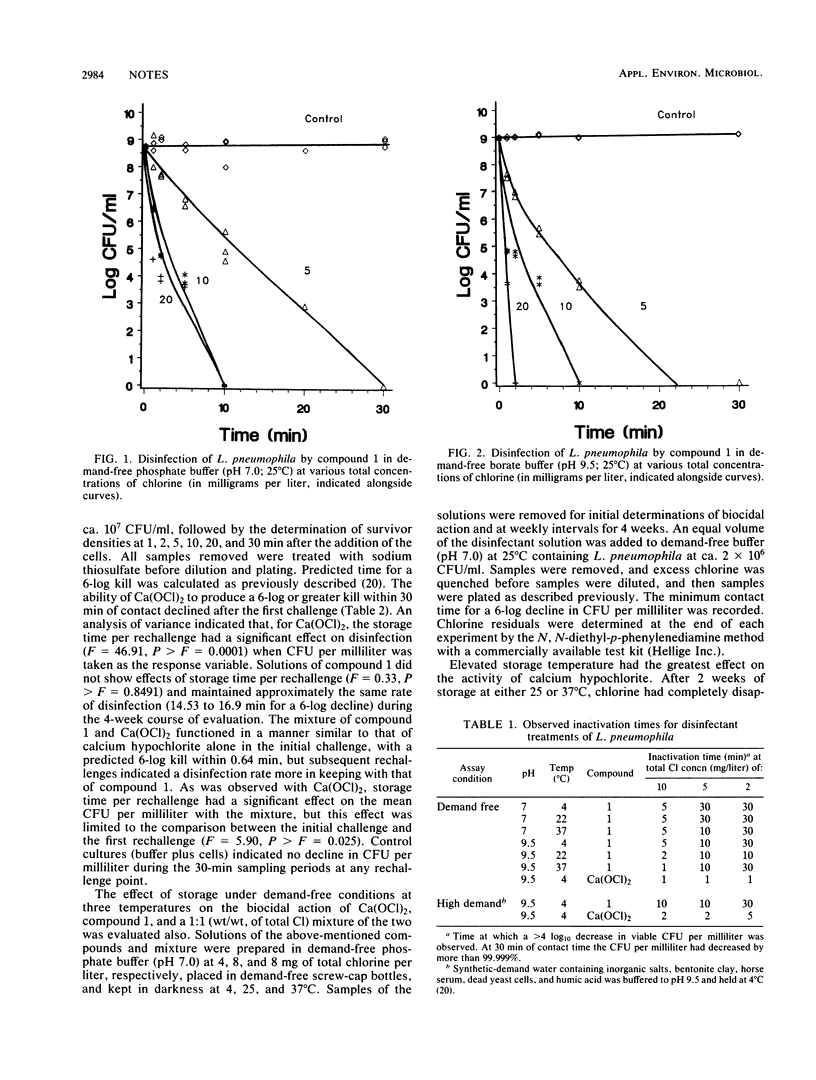
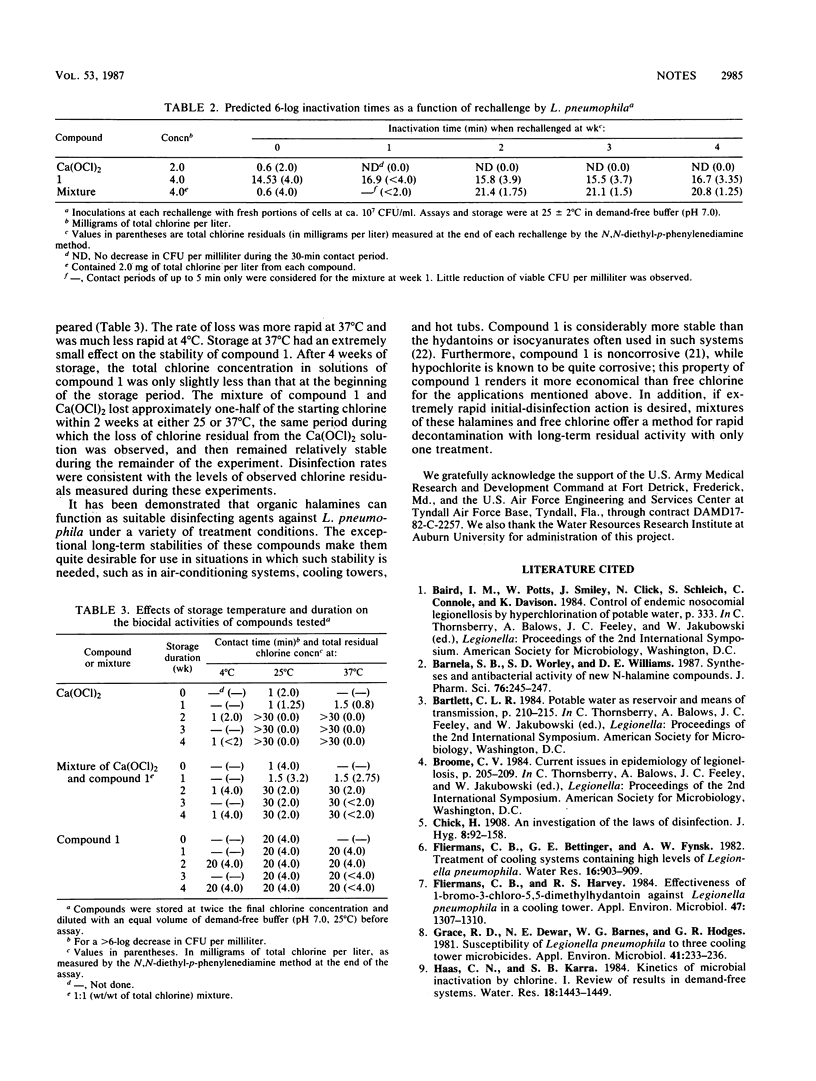
Abstract
The susceptibility of a strain of Legionella pneumophila to disinfection by an organic halamine, free chlorine, and a mixture of the organic halamine and free chlorine was assessed. The organic halamine was found to have superior stability in solution and to exhibit adequate disinfectant potential over a period of 1 month of repeated reinoculations of fresh bacteria. The combined halamine exhibited great potential for use in maintaining closed-cycle cooling water systems free of L. pneumophila.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnela S. B., Worley S. D., Williams D. E. Syntheses and antibacterial activity of new N-halamine compounds. J Pharm Sci. 1987 Mar;76(3):245–247. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600760314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Harvey R. S. Effectiveness of 1-bromo-3-chloro-5,5-dimethylhydantoin against Legionella pneumophila in a cooling tower. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jun;47(6):1307–1310. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.6.1307-1310.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grace R. D., Dewar N. E., Barnes W. G., Hodges G. R. Susceptibility of Legionella pneumophila to three cooling tower microbicides. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):233–236. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.233-236.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchta J. M., States S. J., McNamara A. M., Wadowsky R. M., Yee R. B. Susceptibility of Legionella pneumophila to chlorine in tap water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1134–1139. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1134-1139.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muraca P., Stout J. E., Yu V. L. Comparative assessment of chlorine, heat, ozone, and UV light for killing Legionella pneumophila within a model plumbing system. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Feb;53(2):447–453. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.2.447-453.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands K. N., Ho J. L., Meyer R. D., Gorman G. W., Edelstein P. H., Mallison G. F., Finegold S. M., Fraser D. W. Potable water as a source of Legionnaires' disease. JAMA. 1985 Mar 8;253(10):1412–1416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skaliy P., Thompson T. A., Gorman G. W., Morris G. K., McEachern H. V., Mackel D. C. Laboratory studies of disinfectants against Legionella pneumophila. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Oct;40(4):697–700. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.4.697-700.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soracco R. J., Gill H. K., Fliermans C. B., Pope D. H. Susceptibilities of algae and Legionella pneumophila to cooling tower biocides. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Apr;45(4):1254–1260. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.4.1254-1260.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- States S. J., Conley L. F., Kuchta J. M., Oleck B. M., Lipovich M. J., Wolford R. S., Wadowsky R. M., McNamara A. M., Sykora J. L., Keleti G. Survival and multiplication of Legionella pneumophila in municipal drinking water systems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):979–986. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.979-986.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- States S. J., Conley L. F., Towner S. G., Wolford R. S., Stephenson T. E., McNamara A. M., Wadowsky R. M., Yee R. B. An alkaline approach to treating cooling towers for control of Legionella pneumophila. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Aug;53(8):1775–1779. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.8.1775-1779.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadowsky R. M., Yee R. B., Mezmar L., Wing E. J., Dowling J. N. Hot water systems as sources of Legionella pneumophila in hospital and nonhospital plumbing fixtures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1104–1110. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1104-1110.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. E., Worley S. D., Wheatley W. B., Swango L. J. Bactericidal properties of a new water disinfectant. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Mar;49(3):637–643. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.3.637-643.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


