Abstract
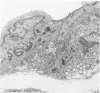
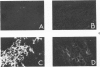
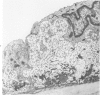
The morphology and permeability to horseradish peroxidase of the rat aortic intima have been investigated in three experimental models of hypertension having different values of plasma renin content and plasma aldosterone level. During hypertension the aortic endothelium shows three main changes: 1) increased arithmetic mean thickness, with prominent rough endoplasmic reticulum and polyribosomes; 2) the appearance of actin microfilament bundles; and 3) increased permeability to horseradish peroxidase. These changes are not present in all models, do not appear to depend on hypertension per se, and are independent of each other. The subendothelial layer of hypertensive animals shows an increased thickness that appears to be correlated with an increase of endothelial cell volume. Our results suggest that: 1) the aortic intima reacts differently to different types of hypertension, and 2) factors other than hypertension per se play a role in the development of vascular changes observed in animals with elevated blood pressure.
Full text
PDF




















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benditt E. P., Benditt J. M. Evidence for a monoclonal origin of human atherosclerotic plaques. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1753–1756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettex-Galland M., Lüscher E. F., Weibel E. R. Thrombosthenin--electron microscopical studies on its localization in human blood platelets and some properties of its subunits. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1969 Dec 31;22(3):431–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner H. R., Laragh J. H., Baer L., Newton M. A., Goodwin F. T., Krakoff L. R., Bard R. H., Bühler F. R. Essential hypertension: renin and aldosterone, heart attack and stroke. N Engl J Med. 1972 Mar 2;286(9):441–449. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197203022860901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner H. R., Sealey J. E., Laragh J. H. Renin as a risk factor in essential hypertension: more evidence. Am J Med. 1973 Sep;55(3):295–302. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90131-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carretero O. A., Kuk P., Piwonska S., Houle J. A., Marin-Grez M. Role of the renin-angiotensin system in the pathogenesis of severe hypertension in rats. Circ Res. 1971 Dec;29(6):654–663. doi: 10.1161/01.res.29.6.654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaponnier C., Kohler L., Gabbiani G. Fixation of human anti-actin autoantibodies on skeletal muscle fibres. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Feb;27(2):278–284. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHL L. K. Effects of chronic excess salt feeding. Induction of self-sustaining hypertension in rats. J Exp Med. 1961 Aug 1;114:231–236. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.2.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle A. E., Jerums G., Johnston C. I., Louis W. J. Plasma renin levels and vascular complications in hypertension. Br Med J. 1973 Apr 28;2(5860):206–207. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5860.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes M., Onesti G., Weder A., Dykyj R., Gould A. B., Kim K. E., Swartz C. Experimental model of severe renal hypertension. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Apr;87(4):561–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIESE J. ACUTE HYPERTENSIVE VASCULAR DISEASE. 2. STUDIES ON VASCULAR REACTION PATTERNS AND PERMEABILITY CHANGES BY MEANS OF VITAL MICROSCOPY AND COLLOIDAL TRACER TECHNIQUE. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1964;62:497–515. doi: 10.1111/apm.1964.62.4.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Badonnel M. C. Contractile apparatus in aortic endothelium of hypertensive rat. Recent Adv Stud Cardiac Struct Metab. 1975;10:591–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Badonnel M. C., Rona G. Cytoplasmic contractile apparatus in aortic endothelial cells of hypertensive rats. Lab Invest. 1975 Feb;32(2):227–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Hirschel B. J., Ryan G. B., Statkov P. R., Majno G. Granulation tissue as a contractile organ. A study of structure and function. J Exp Med. 1972 Apr 1;135(4):719–734. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.4.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Ryan G. B., Lamelin J. P., Vassalli P., Majno G., Bouvier C. A., Cruchaud A., Lüscher E. F. Human smooth muscle autoantibody. Its identification as antiactin antibody and a study of its binding to "nonmuscular" cells. Am J Pathol. 1973 Sep;72(3):473–488. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genest J., Boucher R., Kuchel O., Rojo-Ortega J. M., Nowaczynski W. Jeremiah Metzger lecture, 1974: The renin-angiotensin system. Some new aspects. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 1975;86:139–162. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacomelli F., Anversa P., Wiener J. Effect of angiotensin-induced hypertension on rat coronary arteries and myocardium. Am J Pathol. 1976 Jul;84(1):111–138. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacomelli F., Juechter K. B., Wiener J. The cellular pathology of experimental hypertension. VI. Alterations in retinal vasculature. Am J Pathol. 1972 Jul;68(1):81–96. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacomelli F., Wiener J., Spiro D. Cross-striated arrays of filaments in endothelium. J Cell Biol. 1970 Apr;45(1):188–192. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacomelli F., Wiener J., Spiro D. The cellular pathology of experimental hypertension. V. Increased permeability of cerebral arterial vessels. Am J Pathol. 1970 Apr;59(1):133–160. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese J. Renin, angiotensin and hypertensive vascular damage: a review. Am J Med. 1973 Sep;55(3):315–332. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hüttner I., Boutet M., More R. H. Studies on protein passage through arterial endothelium. I. Structural correlates of permeability in rat arterial endothelium. Lab Invest. 1973 Jun;28(6):672–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hüttner I., Boutet M., More R. H. Studies on protein passage through arterial endothelium. II. Regional differences in permeability to fine structural protein tracers in arterial endothelium of normotensive rat. Lab Invest. 1973 Jun;28(6):678–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnovsky M. J. The ultrastructural basis of capillary permeability studied with peroxidase as a tracer. J Cell Biol. 1967 Oct;35(1):213–236. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Howell S. L., Young D. A., Fink C. J. New hypothesis of insulin secretion. Nature. 1968 Sep 14;219(5159):1177–1179. doi: 10.1038/2191177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mroczek W. J., Finnerty F. A., Catt K. J. Lack of association between plasma-renin and history of heart-attack or stroke in patients with essential hypertension. Lancet. 1973 Sep 1;2(7827):464–468. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92069-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Gabbay K. H., Malaisse W. J. Pancreatic beta-cell web: its possible role in insulin secretion. Science. 1972 Mar 10;175(4026):1128–1130. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4026.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettinger W. A., Marchelle M., Augusto L. Renin suppression by DOC and NaCl in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1971 Oct;221(4):1071–1074. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.4.1071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettinger W. A., Tanaka K., Keeton K., Campbell W. B., Brooks S. N. Renin release, an artifact of anesthesia and its implications in rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Mar;148(3):625–630. doi: 10.3181/00379727-148-38597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen K., Jorgensen J. An easy radioimmunological microassay of renin activity, concentration and substrate in human and animal plasma and tissues based on angiotensin I trapping by antibody. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Nov;39(5):816–825. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-5-816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodin J. A. The ultrastructure of mammalian arterioles and precapillary sphincters. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 Apr;18(1):181–223. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80239-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson A. L., Khairallah P. A. Effects of angiotensin II and some analogues on vascular permeability in the rabbit. Circ Res. 1972 Dec;31(6):923–931. doi: 10.1161/01.res.31.6.923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Harker L. Hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis. Science. 1976 Sep 17;193(4258):1094–1100. doi: 10.1126/science.822515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röhlich P., Oláh I. Cross-striated fibrils in the endothelium of the rat myometral arterioles. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 Jun;18(5):667–676. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80212-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ J., BLOCH R., VELLY J. RELATIONS BETWEEN RENIN, ALDOSTERONE AND EXPERIMENTAL HYPERTENSION IN RATS. Can Med Assoc J. 1964 Jan 25;90:243–244. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKEGGS L. T., Jr, KAHN J. R., LENTZ K., SHUMWAY N. P. The preparation, purification, and amino acid sequence of a polypeptide renin substrate. J Exp Med. 1957 Sep 1;106(3):439–453. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.3.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. M., Benditt E. P. Aortic endothelial cell replication. I. Effects of age and hypertension in the rat. Circ Res. 1977 Aug;41(2):248–255. doi: 10.1161/01.res.41.2.248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. M., Benditt E. P. Postnatal development of the aortic subendothelium in rats. Lab Invest. 1972 Jun;26(6):778–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. M., Benditt E. P. Studies on aortic intima. I. Structure and permeability of rat thoracic aortic intima. Am J Pathol. 1972 Feb;66(2):241–264. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skeggs L. T., Lentz K. E., Kahn J. R., Dorer F. E., Levine M. Pseudorenin. A new angiotensin-forming enzyme. Circ Res. 1969 Oct;25(4):451–462. doi: 10.1161/01.res.25.4.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Still W. J., Dennison S. The arterial endothelium of the hypertensive rat: a scanning and transmission electron microscopical study. Arch Pathol. 1974 Jun;97(6):337–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallotton M. B. Relationship between chemical structure and antigenicity of angiotensin analogues. Immunochemistry. 1970 Jun;7(6):529–542. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90274-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vracko R., Benditt E. P. Basal lamina: the scaffold for orderly cell replacement. Observations on regeneration of injured skeletal muscle fibers and capillaries. J Cell Biol. 1972 Nov;55(2):406–419. doi: 10.1083/jcb.55.2.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBEL E. R., KNIGHT B. W. A MORPHOMETRIC STUDY ON THE THICKNESS OF THE PULMONARY AIR-BLOOD BARRIER. J Cell Biol. 1964 Jun;21:367–396. doi: 10.1083/jcb.21.3.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren B. A. A method for the production of "en face" preparations one cell in thickness. J R Microsc Soc. 1965 Dec;85(4):407–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1965.tb02141.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yohro T., Burnstock G. Filament bundles and contractility of endothelial cells in coronary arteries. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1973 Mar 21;138(1):85–95. doi: 10.1007/BF00307080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong W. Release of renin by rat kidney slices; relationship to plasma renin after desoxycorticosterone and renal hypertension. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jan;130(1):85–88. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]