Abstract
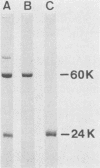
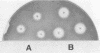
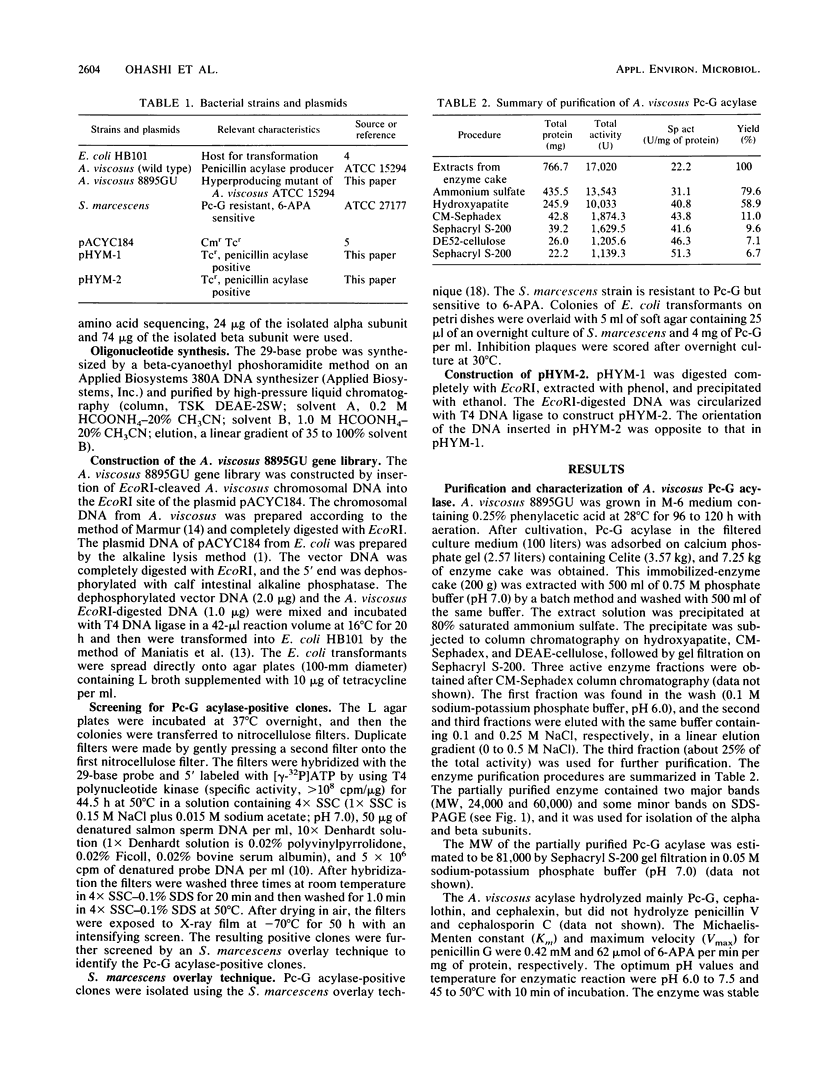
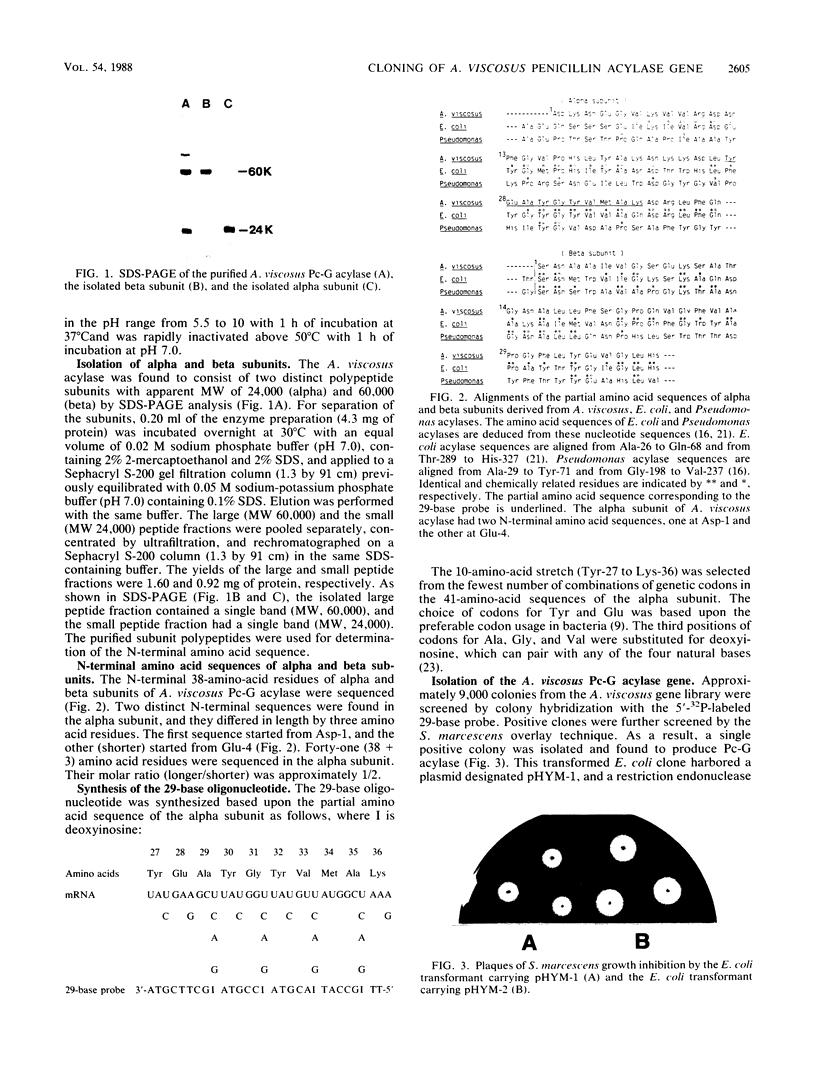
Penicillin G acylase was purified from the cultured filtrate of Arthrobacter viscosus 8895GU and was found to consist of two distinct subunits with apparent molecular weights of 24,000 (alpha) and 60,000 (beta). The partial N-terminal amino acid sequences of the alpha and beta subunits were determined with a protein gas phase sequencer, and a 29-base oligonucleotide corresponding to the partial amino acid sequence of the alpha subunit was synthesized. An Escherichia coli transformant having the penicillin G acylase gene was isolated from an A. viscosus gene library by hybridization with the 29-base probe. The resulting positive clone was further screened by the Serratia marcescens overlay technique. E. coli carrying a plasmid designated pHYM-1 was found to produce penicillin G acylase in the cells. This plasmid had an 8.0-kilobase pair DNA fragment inserted in the EcoRI site of pACYC184.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daumy G. O., Danley D., McColl A. S. Role of protein subunits in Proteus rettgeri penicillin G acylase. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1279–1281. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1279-1281.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daumy G. O., Williams J. A., McColl A. S., Zuzel T. J., Danley D. Expression and regulation of the penicillin G acylase gene from Proteus rettgeri cloned in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):431–433. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.431-433.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouy M., Gautier C. Codon usage in bacteria: correlation with gene expressivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7055–7074. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:333–342. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrelli L. P. Colorimetric method for determination of 7-aminocephalosporanic acid (7-ACA) and related compounds. J Pharm Sci. 1968 Dec;57(12):2172–2173. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600571234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda A., Komatsu K. I. Molecular cloning and structure of the gene for 7 beta-(4-carboxybutanamido)cephalosporanic acid acylase from a Pseudomonas strain. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1222–1228. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1222-1228.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meevootisom V., Somsuk P., Prachaktam R., Flegel T. W. Simple screening method for isolation of penicillin acylase-producing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1227–1229. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1227-1229.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson A., Hagström T., Nilsson B., Uhlén M., Gatenbeck S. Molecular cloning of Bacillus sphaericus penicillin V amidase gene and its expression in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1084–1089. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1084-1089.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savidge T. A., Cole M. Penicillin acylase (bacterial). Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:705–721. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43136-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher G., Sizmann D., Haug H., Buckel P., Böck A. Penicillin acylase from E. coli: unique gene-protein relation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 25;14(14):5713–5727. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.14.5713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi Y., Kato K., Hayashizaki Y., Wakabayashi T., Ohtsuka E., Matsuki S., Ikehara M., Matsubara K. Molecular cloning of the human cholecystokinin gene by use of a synthetic probe containing deoxyinosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1931–1935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandamme E. J., Voets J. P. Microbial penicillin acylases. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1974;17(0):311–369. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70563-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]