Abstract
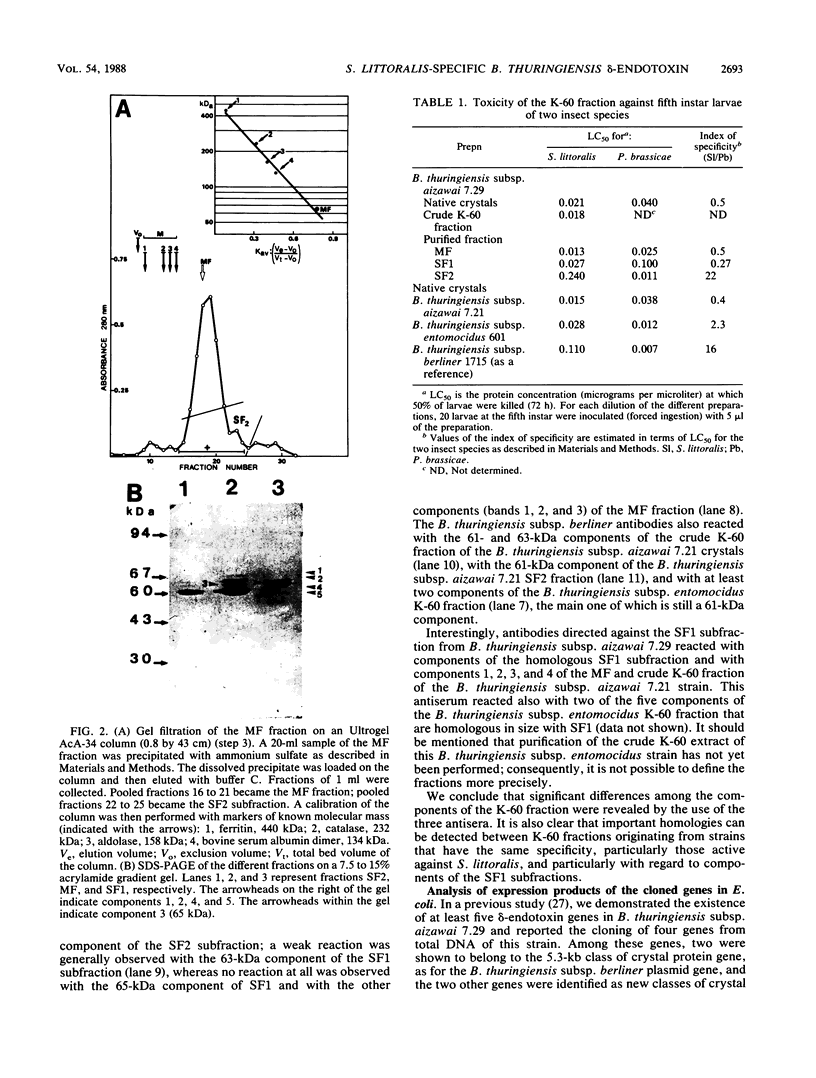
At least three different insecticidal crystal protein genes were shown to be expressed in Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. aizawai 7.29, a strain that is potentially active against the cotton leafworm Spodoptera littoralis Bdv. Among crude K-60 fractions (60- to 70-kilodalton [kDa] molecules) that were products of proteolysed crystals containing the active domains of the protoxin molecules, we were able to distinguish several distinct components on the basis of their antigenic relationship and their larvicidal properties. A purified fraction designated SF2 was a 61-kDa component specifically active against Pieris brassicae L. and homologous to the B. thuringiensis subsp. berliner 1715 plasmid-encoded crystal protein. A second fraction designated SF1 was composed of 63- and 65-kDa polypeptides and was specifically active against S. littoralis. The SF1 fraction and particularly the 65-kDa component were not antigenically related to the 61-kDa component. The purified fractions were compared with the products of three different crystal protein genes we previously cloned from total DNA of B. thuringiensis subsp. aizawai, among them a new type of crystal protein gene encoding a protein that is specifically active against S. littoralis and other insects of the Noctuidae family. This approach led us to consider the 65-kDa component as a minimum active part of a δ-endotoxin that is encoded by this new gene. Products of the two other cloned genes can be correlated with the 61- and 63-kDa components, respectively. Thus, in B. thuringiensis subsp. aizawai 7.29, multiple δ-endotoxin genes of different structural types direct the synthesis of several δ-endotoxins with different host specificities which were identified as components of the insecticidal crystals.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adang M. J., Staver M. J., Rocheleau T. A., Leighton J., Barker R. F., Thompson D. V. Characterized full-length and truncated plasmid clones of the crystal protein of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki HD-73 and their toxicity to Manduca sexta. Gene. 1985;36(3):289–300. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90184-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews R. E., Jr, Bibilos M. M., Bulla L. A., Jr Protease activation of the entomocidal protoxin of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Oct;50(4):737–742. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.737-742.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews R. E., Jr, Faust R. M., Wabiko H., Raymond K. C., Bulla L. A., Jr The biotechnology of Bacillus thuringiensis. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 1987;6(2):163–232. doi: 10.3109/07388558709113596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson A. I., Beckman W., Dunn P. Bacillus thuringiensis and related insect pathogens. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Mar;50(1):1–24. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.1.1-24.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulla L. A., Jr, Davidson L. I., Kramer K. J., Jones B. L. Purification of the insecticidal toxin from the parasporal crystal of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Dec 14;91(3):1123–1130. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91997-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese D. M., Nickerson K. W., Lane L. C. A comparison of protein crystal subunit sizes in Bacillus thuringiensis. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Aug;26(8):1006–1010. doi: 10.1139/m80-170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chak K. F., Ellar D. J. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of an insecticidal crystal protein gene from Bacillus thuringiensis var. aizawai HD-133. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Oct;133(10):2921–2931. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-10-2921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haider M. Z., Ellar D. J. Characterization of the toxicity and cytopathic specificity of a cloned Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein using insect cell culture. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Jul;1(1):59–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb00527.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haider M. Z., Ward E. S., Ellar D. J. Cloning and heterologous expression of an insecticidal delta-endotoxin gene from Bacillus thuringiensis var. aizawai IC1 toxic to both lepidoptera and diptera. Gene. 1987;52(2-3):285–290. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höfte H., de Greve H., Seurinck J., Jansens S., Mahillon J., Ampe C., Vandekerckhove J., Vanderbruggen H., van Montagu M., Zabeau M. Structural and functional analysis of a cloned delta endotoxin of Bacillus thuringiensis berliner 1715. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Dec 1;161(2):273–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10443.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaquet F., Hütter R., Lüthy P. Specificity of Bacillus thuringiensis Delta-Endotoxin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Mar;53(3):500–504. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.3.500-504.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. H., Ohba M., Aizawa K. Purification of the toxic protein from Bacillus thuringiensis serotype 10 isolate demonstrating a preferential larvicidal activity to the mosquito. J Invertebr Pathol. 1984 Sep;44(2):214–219. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(84)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klier A., Fargette F., Ribier J., Rapoport G. Cloning and expression of the crystal protein genes from Bacillus thuringiensis strain berliner 1715. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):791–799. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01249.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. H., Ellar D. J. Differential specificity of two insecticidal toxins from Bacillus thuringiensis var. aizawai. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Jan;2(1):153–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronstad J. W., Whiteley H. R. Three classes of homologous Bacillus thuringiensis crystal-protein genes. Gene. 1986;43(1-2):29–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecadet M. M., Dedonder R. Biogenesis of the crystalline inclusion of Bacillus thuringiensis during sporulation. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Nov 11;23(2):282–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lereclus D., Lecadet M. M., Klier A., Ribier J., Rapoport G., Dedonder R. Recent aspects of genetic manipulation in Bacillus thuringiensis. Biochimie. 1985 Jan;67(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(85)80234-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oeda K., Oshie K., Shimizu M., Nakamura K., Yamamoto H., Nakayama I., Ohkawa H. Nucleotide sequence of the insecticidal protein gene of Bacillus thuringiensis strain aizawai IPL7 and its high-level expression in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;53(1):113–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchis V., Lereclus D., Menou G., Chaufaux J., Lecadet M. M. Multiplicity of delta-endotoxin genes with different insecticidal specificities in Bacillus thuringiensis aizawai 7.29. Mol Microbiol. 1988 May;2(3):393–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00044.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnepf H. E., Whiteley H. R. Delineation of a toxin-encoding segment of a Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6273–6280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley H. R., Schnepf H. E. The molecular biology of parasporal crystal body formation in Bacillus thuringiensis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:549–576. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]