Abstract
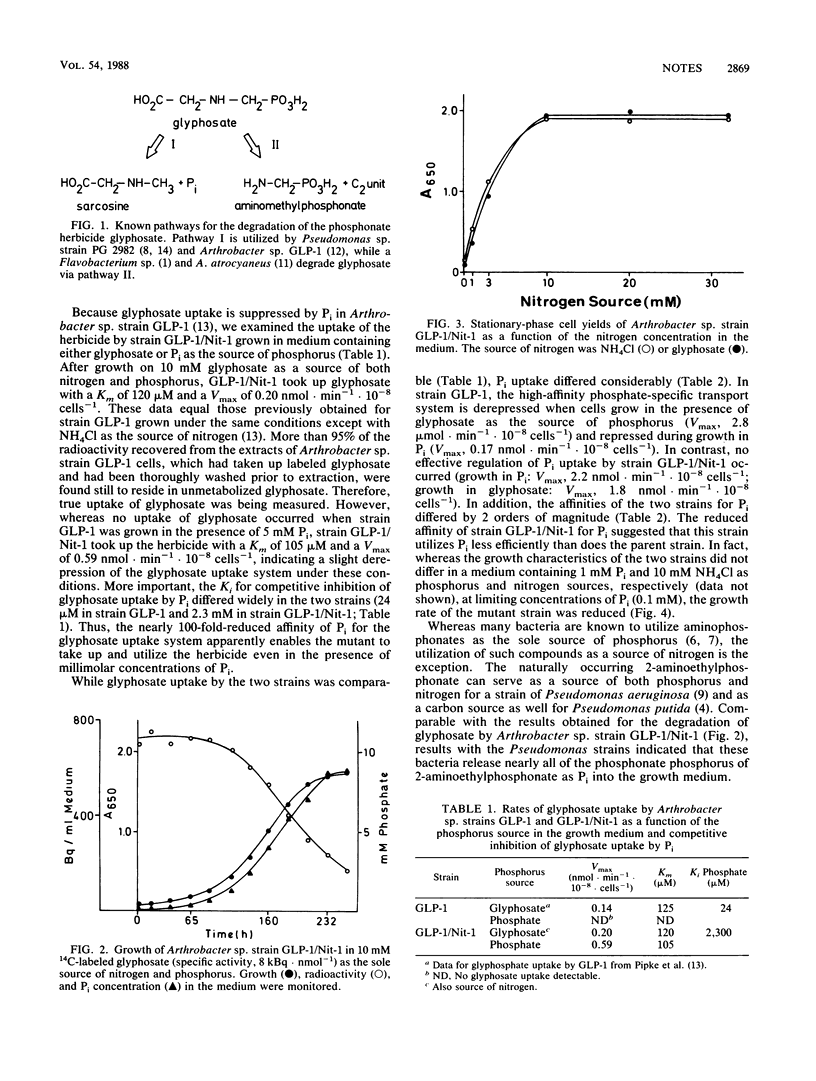
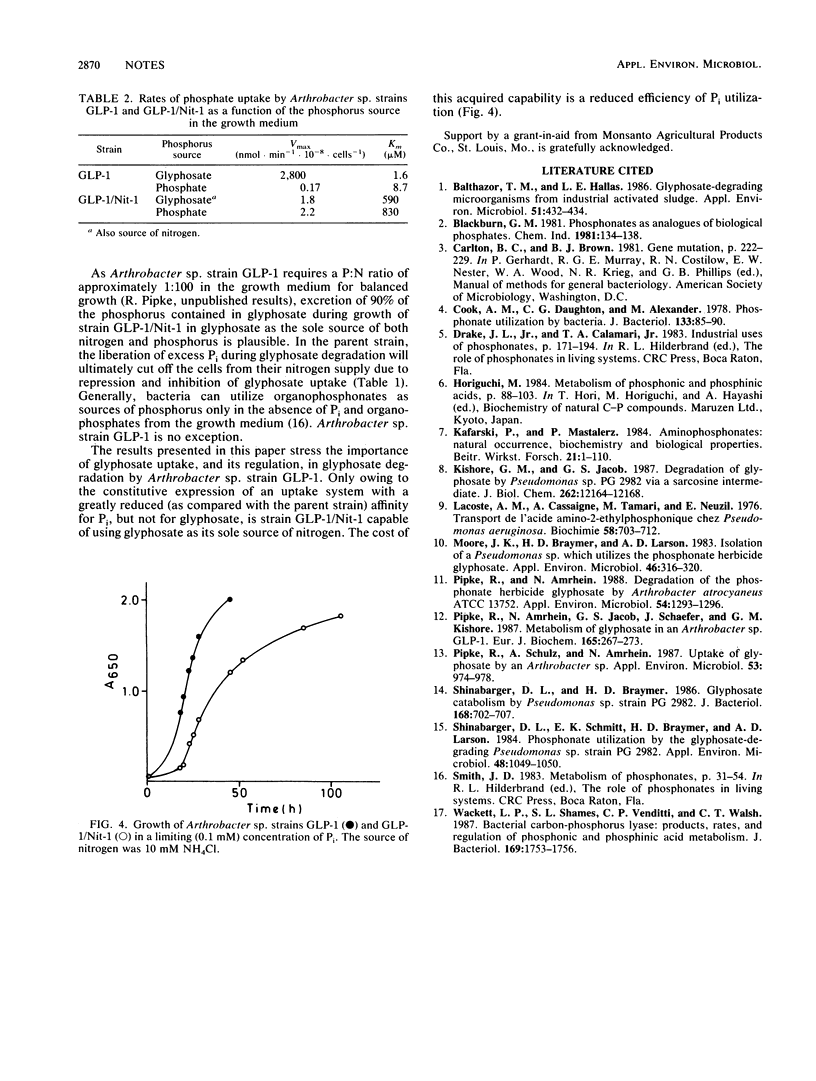
Arthrobacter sp. strain GLP-1, grown on glucose as a carbon source, utilizes the herbicide glyphosate [N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine] as its sole source of phosphorus as well as its sole source of nitrogen. The mutant strain GLP-1/Nit-1 utilizes glyphosate as its sole source of nitrogen as well. In strain GLP-1, Pi was a potent competitive inhibitor of glyphosate uptake (Ki, 24 μM), while the affinity of Pi for the uptake system of strain GLP-1/Nit-1 was reduced by 2 orders of magnitude (Ki, 2.3 mM). It is concluded that the inability of strain GLP-1 to utilize glyphosate as a source of nitrogen is due to the stringent control of glyphosate uptake by excess phosphate released during the degradation of the herbicide.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balthazor T. M., Hallas L. E. Glyphosate-degrading microorganisms from industrial activated sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Feb;51(2):432–434. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.2.432-434.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook A. M., Daughton C. G., Alexander M. Phosphonate utilization by bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):85–90. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.85-90.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishore G. M., Jacob G. S. Degradation of glyphosate by Pseudomonas sp. PG2982 via a sarcosine intermediate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12164–12168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacoste A. M., Cassaigne A., Tamari M., Neuzil E. Transport de l'acide amino-2-éthylphosphonique chez Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochimie. 1976;58(6):703–712. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(76)80395-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. K., Braymer H. D., Larson A. D. Isolation of a Pseudomonas sp. Which Utilizes the Phosphonate Herbicide Glyphosate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Aug;46(2):316–320. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.2.316-320.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipke R., Amrhein N. Degradation of the Phosphonate Herbicide Glyphosate by Arthrobacter atrocyaneus ATCC 13752. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 May;54(5):1293–1296. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.5.1293-1296.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipke R., Amrhein N., Jacob G. S., Schaefer J., Kishore G. M. Metabolism of glyphosate in an Arthrobacter sp. GLP-1. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jun 1;165(2):267–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipke R., Schulz A., Amrhein N. Uptake of Glyphosate by an Arthrobacter sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):974–978. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.974-978.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinabarger D. L., Braymer H. D. Glyphosate catabolism by Pseudomonas sp. strain PG2982. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):702–707. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.702-707.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinabarger D. L., Schmitt E. K., Braymer H. D., Larson A. D. Phosphonate Utilization by the Glyphosate-Degrading Pseudomonas sp. Strain PG2982. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Nov;48(5):1049–1050. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.5.1049-1050.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wackett L. P., Wanner B. L., Venditti C. P., Walsh C. T. Involvement of the phosphate regulon and the psiD locus in carbon-phosphorus lyase activity of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1753–1756. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1753-1756.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


