Abstract
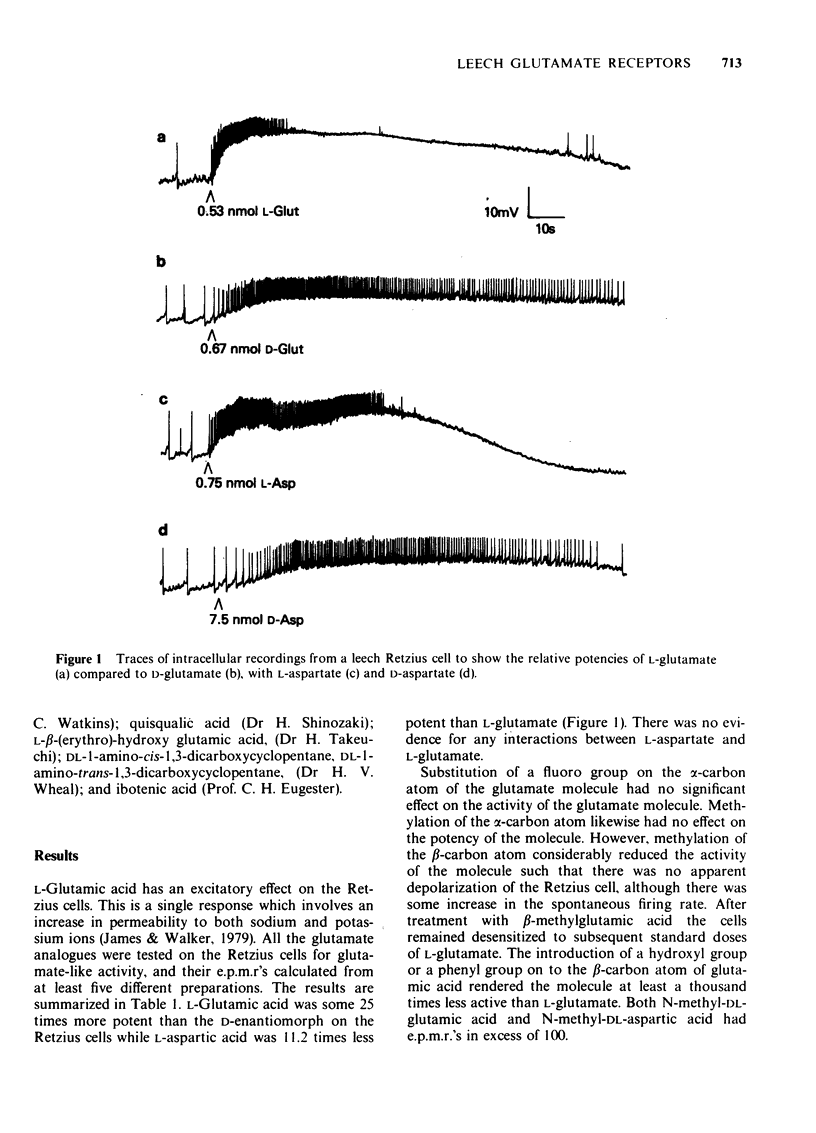
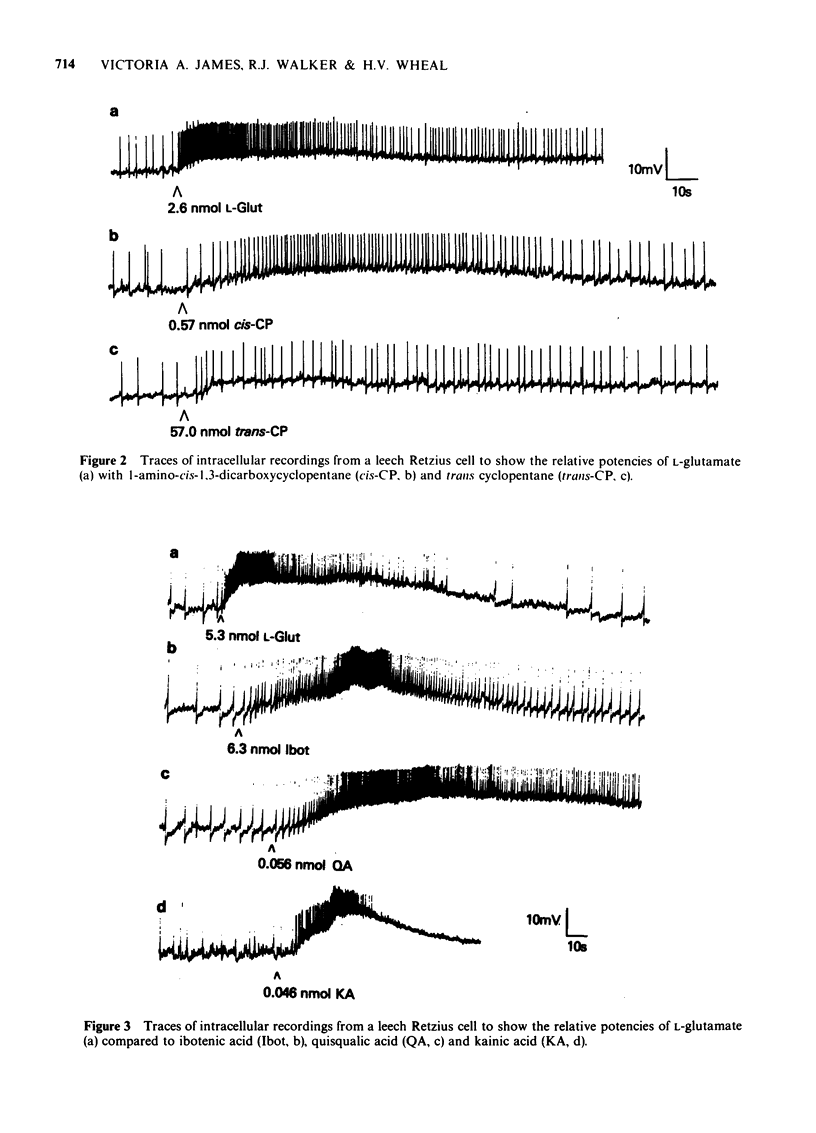
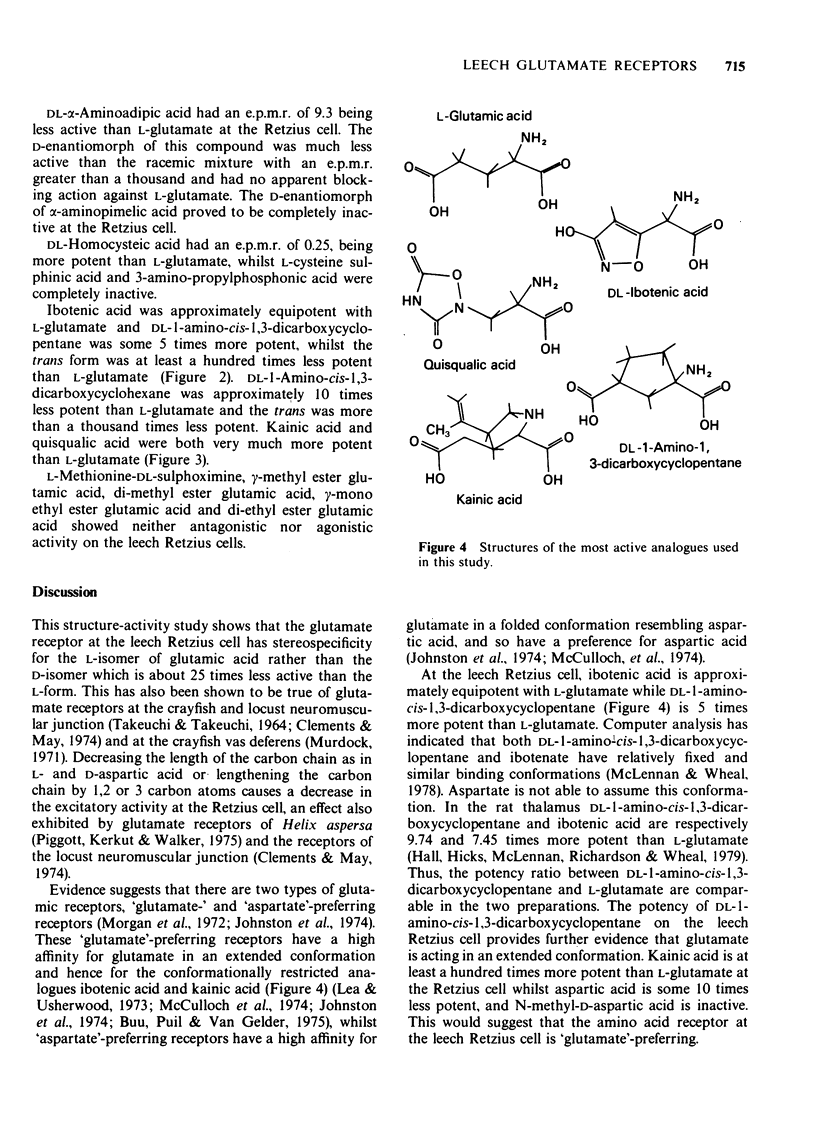
1 Intracellular recordings were made from Retzius cells from the segmental ganglia of Hirudo medicinalis and Haemopis sanguisuga. Glutamate had a direct excitatory effect on the leech Retzius cells. 2 L-Glutamate was 25 times more potent than D-glutamate. 3 L-Glutamate was approximately equipotent with ibotenic acid and 11.2 times more potent than L-aspartic acid. 4 Quisqualic acid and kainic acid were both approximately 100 times more potent than L-glutamate. DL-1-Amino-cis-1-3-dicarboxyclyclopentane was approximately 5 times more potent than L-glutamate, while the trans isomer was 105 times less potent. 5 alpha-NH2-pimelic acid and beta-CH3-glutamic acid reduced the response to L-glutamate. 6 It is suggested that glutamic acid may interact with the Retzius cell glutamate receptor in an extended conformation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biscoe T. J., Davies J., Dray A., Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Martin M. R., Watkins J. C. Depression of synaptic excitation and of amino acid induced excitatory responses of spinal neurones by D-alpha-aminoadipate, alpha,epsilon-diaminopimelic acid and HA-966. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Oct 1;45(3):315–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biscoe T. J., Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Martin M. R., Watkins J. C., Davies J., Dray A. D-alpha-Aminoadipate as a selective antagonist of amino acid-induced and synaptic excitation of mammalian spinal neurones. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):743–745. doi: 10.1038/270743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buu N. T., Puil E., van Gelder N. M. Receptors for amino acids in excitable tissues. Gen Pharmacol. 1976;7(1):5–14. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(76)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements A. N., May T. E. Pharmacological studies on a locust neuromuscular preparation. J Exp Biol. 1974 Oct;61(2):421–442. doi: 10.1242/jeb.61.2.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Johnston G. A. Amino acid transmitters in the mammalian central nervous system. Ergeb Physiol. 1974;69(0):97–188. doi: 10.1007/3-540-06498-2_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerschenfeld H. M. Chemical transmission in invertebrate central nervous systems and neuromuscular junctions. Physiol Rev. 1973 Jan;53(1):1–119. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1973.53.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldeman S., McLennan H. The antagonistic action of glutamic acid diethylester towards amino acid-induced and synaptic excitations of central neurones. Brain Res. 1972 Oct 27;45(2):393–400. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90470-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James V. A., Walker R. J. Structure-activity studies on an excitatory glutamate receptor of leech neurones [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Mar;62(3):432P–433P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston G. A., Curtis D. R., Davies J., McCulloch R. M. Spinal interneurone excitation by conformationally restricted analogues of L-glutamic acid. Nature. 1974 Apr 26;248(5451):804–805. doi: 10.1038/248804a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerkut G. A., Piggott S. M., Walker R. J. The antagonist effect of alpha-amino-pimelic acid on glutamate-induced inhibitions of Helix neurones. Brain Res. 1975 Mar 14;86(1):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90646-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lea T. J., Usherwood P. N. The site of action of ibotenic acid and the identification of two populations of glutamate receptors on insect muscle-fibres. Comp Gen Pharmacol. 1973 Dec;4(16):333–350. doi: 10.1016/0010-4035(73)90045-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowagie C., Gerschenfeld H. M. Glutamate antagonists at a crayfish neuromuscular junction. Nature. 1974 Apr 5;248(448):533–535. doi: 10.1038/248533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald J. F., Nistri A. Actions of microiontophoretically applied ibotenate on cat spinal interneurones. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1977 Aug;55(4):965–967. doi: 10.1139/y77-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCulloch R. M., Johnston G. A., Game C. J., Curtis D. R. The differential sensitivity of spinal interneurones and Renshaw cells to Kainate and N-methyl-D-aspartate. Exp Brain Res. 1974;21(5):515–518. doi: 10.1007/BF00237169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan R., Vrbová G., Wolstencroft J. H. Correlation between the retinal input to lateral geniculate neurones and their relative response to glutamate and aspartate. J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(1):41P–42P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murdock L. L. Crayfish vas deferens: contractions in response to L-glutamate and gamma-aminobutyrate. Comp Gen Pharmacol. 1971 Mar;2(5):93–98. doi: 10.1016/0010-4035(71)90073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOLLS J. G., KUFFLER S. W. EXTRACELLULAR SPACE AS A PATHWAY FOR EXCHANGE BETWEEN BLOOD AND NEURONS IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM OF THE LEECH: IONIC COMPOSITION OF GLIAL CELLS AND NEURONS. J Neurophysiol. 1964 Jul;27:645–671. doi: 10.1152/jn.1964.27.4.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggott S. M., Kerkut G. A., Walker R. J. Structure-activity studies on glutamate receptor sites of three identifiable neurones in the sub-oesophageal ganglia of Helix aspersa. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1975 Jun 1;51(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0306-4492(75)90044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki H., Shibuya I. A new potent excitant, quisqualic acid: effects on crayfish neuromuscular junction. Neuropharmacology. 1974 Jul;13(7):665–672. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(74)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A., TAKEUCHI N. THE EFFECT ON CRAYFISH MUSCLE OF IONTOPHORETICALLY APPLIED GLUTAMATE. J Physiol. 1964 Mar;170:296–317. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usherwood P. N. Amino acids as neurotransmitters. Adv Comp Physiol Biochem. 1978;7:227–309. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-011507-5.50009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. J. The action of kainic acid and quisqualic acid on the glutamate receptors of three identifiable neurones from the brain of the snail, Helix aspersa. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1976;55(1):61–67. doi: 10.1016/0306-4492(76)90013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


