Abstract
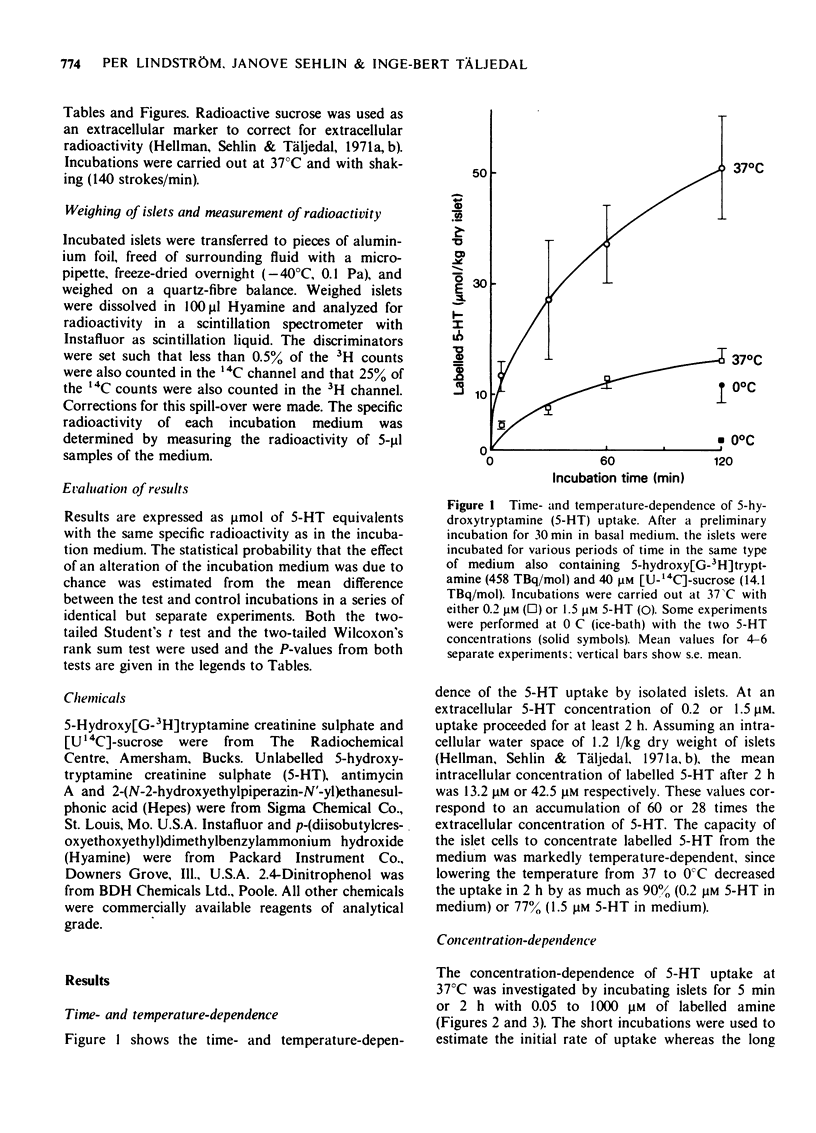
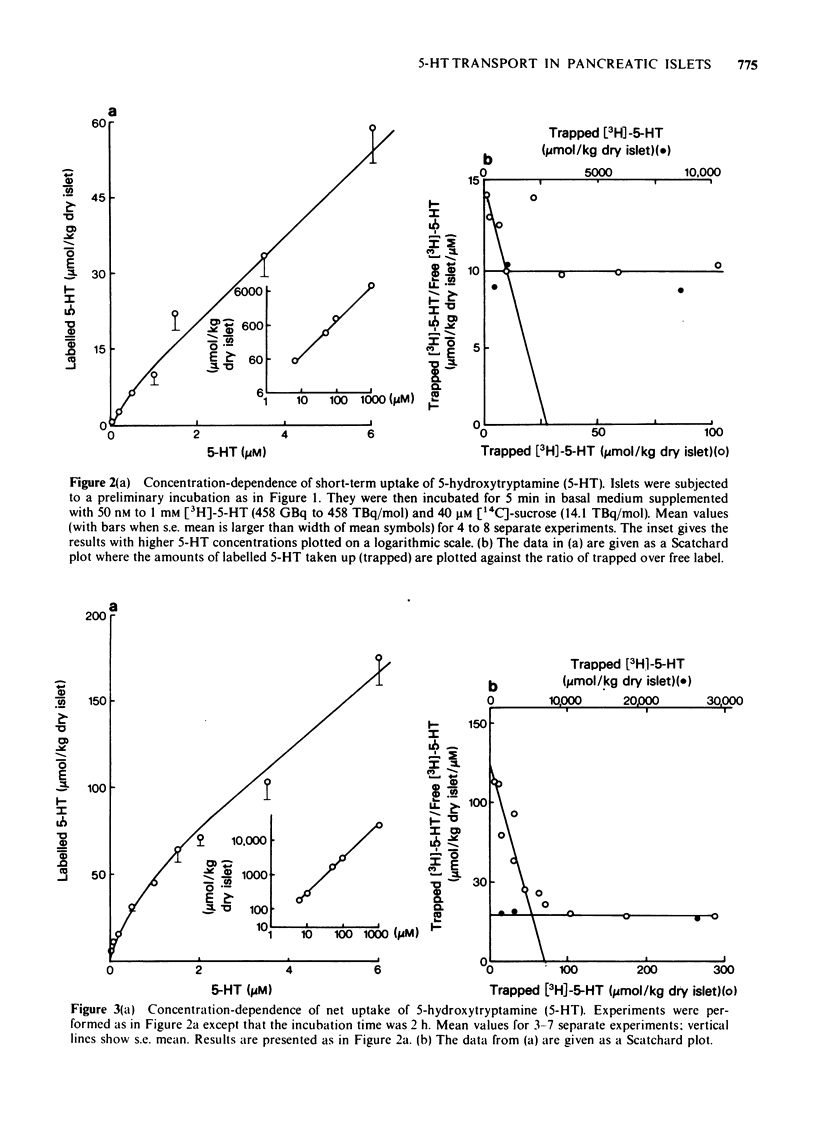
1 Transmembrane transport of 3H-labelled 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) by isolated pancreatic islets of non-inbred ob/ob mice was studied. 2 5-HT was vigorously accumulated in a temperature-dependent way by the islet cells. 3 Studies of the concentration-dependence of [3H]-5-HT uptake revealed complex kinetics with one component being saturated at 1 to 3 microM 5-HT (apparent association constant 0.6 x 10(6) M(-1) and the other non-saturated up to 1 mM 5-HT. 4 The saturable uptake was inhibited by Na+-deficiency and metabolic poisoning with 2,4-dinitrophenol and antimycin A, whereas the non-saturable component was not affected. 5 Omission of K+, Ca2+ or Mg2+ did not affect the uptake rate. 6 It is concluded that 5-HT is taken up by pancreatic beta-cells by mechanisms very similar to those observed in thrombocytes and neurones.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams W. B., Solomon H. M. The human platelet as a pharmacologic model for the adrenergic neuron. The uptake and release of norepinephrine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1969 Sep-Oct;10(5):702–709. doi: 10.1002/cpt1969105702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn K. J., French P. C., Merrills R. J. 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake by rat brain in vitro. Life Sci. 1967 Aug 1;6(15):1653–1663. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90176-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogdanski D. F., Brodie B. B. Role of sodium and potassium ions in storage of norepinephrine by sympathetic nerve endings. Life Sci. 1966 Sep;5(17):1563–1569. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(66)91025-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekholm R., Ericson L. E., Lundquist I. Monoamines in the pancreatic islets of the mouse. Subcellular localization of 5-hydroxytryptamine by electron microscopic autoradiography. Diabetologia. 1971 Oct;7(5):339–348. doi: 10.1007/BF01219468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman J. M., Chapman B. Characterization of pancreatic islet monoamine oxidase. Metabolism. 1975 May;24(5):581–588. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90138-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman J. M., Lebovitz H. E. Specificity of serotonin inhibition of insulin release from golden hamster pancreas. Diabetes. 1970 Jul;19(7):475–479. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.7.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagliardino J. J., Nierle C., Pfeiffer E. F. The effect of serotonin on in vitro insulin secretion and biosynthesis in mice. Diabetologia. 1974 Oct;10(5):411–414. doi: 10.1007/BF01221630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gylfe E. Association between 5-hydroxytryptamine release and insulin secretion. J Endocrinol. 1978 Aug;78(2):239–248. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0780239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gylfe E., Hellman B., Sehlin J., Taljedal I. B. Amino acid conversion into 5-hydroxytryptamine in pancreatic beta-cells. Endocrinology. 1973 Oct;93(4):932–937. doi: 10.1210/endo-93-4-932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Lernmark A., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Transport and storage of 5-hydroxytryptamine in pancreatic -cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 Mar 1;21(5):695–706. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Evidence for mediated transport of glucose in mammalian pancreatic -cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jul 6;241(1):147–154. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90312-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Transport of -aminoisobutyric acid in mammalian pancretic -cells. Diabetologia. 1971 Aug;7(4):256–265. doi: 10.1007/BF01211878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B. Studies in obese-hyperglycemic mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Oct 8;131(1):541–558. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb34819.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebovitz H. E., Feldman J. M. Pancreatic biogenic amines and insulin secretion in health and disease. Fed Proc. 1973 Jul;32(7):1797–1802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lernmark A. The significance of 5-hydroxytryptamine for insulin secretion in the mouse. Horm Metab Res. 1971 Sep;3(5):305–309. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1094131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahony C., Feldman J. M. Species variation in pancreatic islet monoamine uptake and action. Diabetes. 1977 Apr;26(4):257–261. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.4.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pletscher A. Metabolism, transfer and storage of 5-hydroxytryptamine in blood platelets. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Jan;32(1):1–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00423.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross S. B., Renyi A. L. Tricyclic antidepressant agents. I. Comparison of the inhibition of the uptake of 3-H-noradrenaline and 14-C-5-hydroxytryptamine in slices and crude synaptosome preparations of the midbrain-hypothalamus region of the rat brain. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1975;36(Suppl 5):382–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1975.tb00806.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaskan E. G., Snyder S. H. Kinetics of serotonin accumulation into slices from rat brain: relationship to catecholamine uptake. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 Nov;175(2):404–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon J. M. Blood platelets as a model for monoamine-containing neurones. Prog Neurobiol. 1973;1(2):151–198. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(73)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon J. M. Sodium-dependent accumulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine by rat blood platelets. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Nov;37(3):680–688. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb08506.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl S. M., Meltzer H. Y. A kinetic and pharmacologic analysis of 5-hydroxytryptamine transport by human platelets and platelet storage granules: comparison with central serotonergic neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1978 Apr;205(1):118–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. P., Downs R. W., Jr, Feldman J. M., Lebovitz H. E. Beta cell monoamines: further evidence for their role in modulating insulin secretion. Am J Physiol. 1974 Aug;227(2):305–312. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.2.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Leiva A., Tanenberg R. J., Anderson G., Greenberg B., Senske B., Goetz F. C. Serotoninergic activation and inhibition: effects on carbohydrate tolerance and plasma insulin and glucagon. Metabolism. 1978 May;27(5):511–520. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(78)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


