Abstract
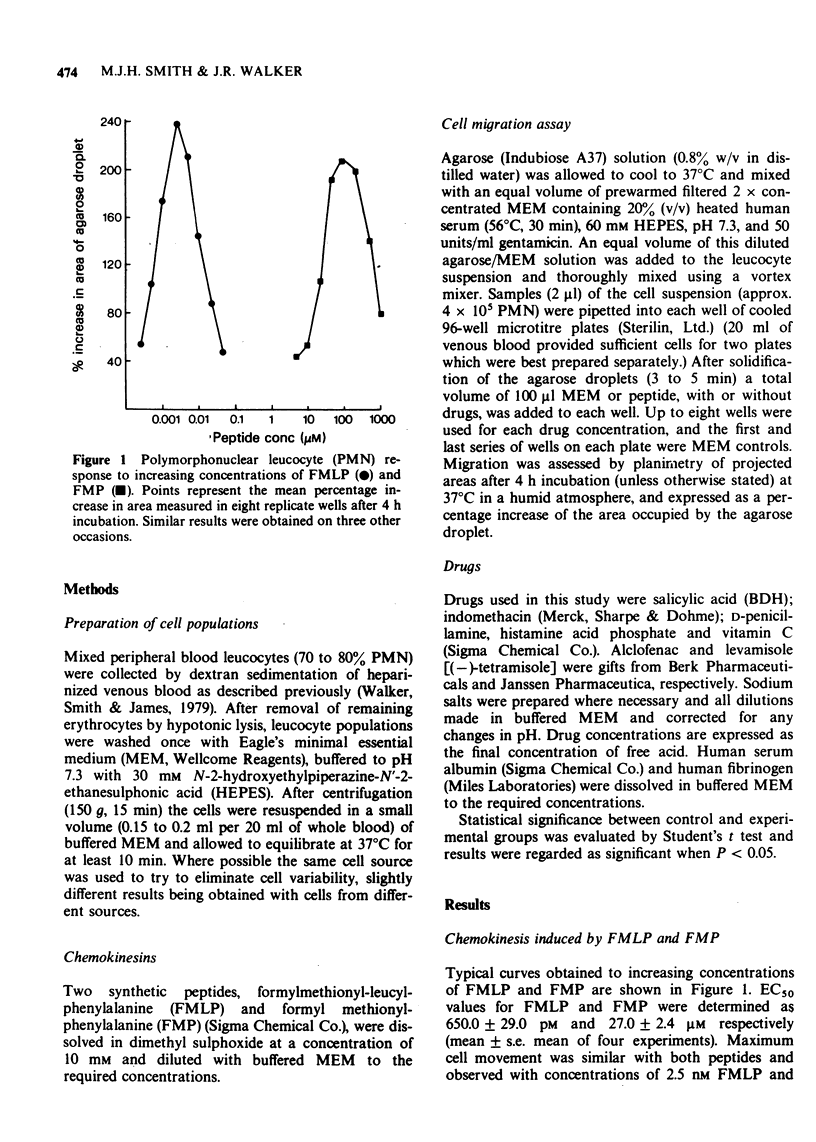
1 A rapid, reproducible in vitro assay for studying the chemokinetic movement of human polymorphonuclear leucocytes (PMNs) is described. Two synthetic peptides, formyl methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (FMLP) and formyl methionyl-phenylalanine (FMP), were used as a standard chemokinesins. 2 Maximal chemokinetic movement was observed with peptide concentrations of 2.5 nM (FMLP) and 100 muM (FMP). EC50 values of 650.0 +/- 60.0 pM and 27.0 +/- 3.5 muM respectively are similar to those reported for chemotactic activity of the peptides in micropore filter assays. 3 The PMN chemokinetic response to FMLP was enhanced by histamine (100 nM) and vitamin C (2.5 muM). 4 Human serum albumin was shown to induce chemokinesis but to antagonize the response to FMLP in a dose-related fashion. Fibrinogen similarly antagonized the cell response to peptide. 5 Levamisole (250 nM to 2.5 muM) significantly potentiated the chemokinetic responses to FMLP and FMP in a dose-related manner. The chemokinetic response to FMLP was unaffected by D-penicillamine (250 muM to 10 mM) while alclofenac (500 muM to 1 mM), salicylic acid (250 muM to 10 mM) and indomethacin (100 muM to 1 mM) caused dose-related inhibition.
Full text
PDF
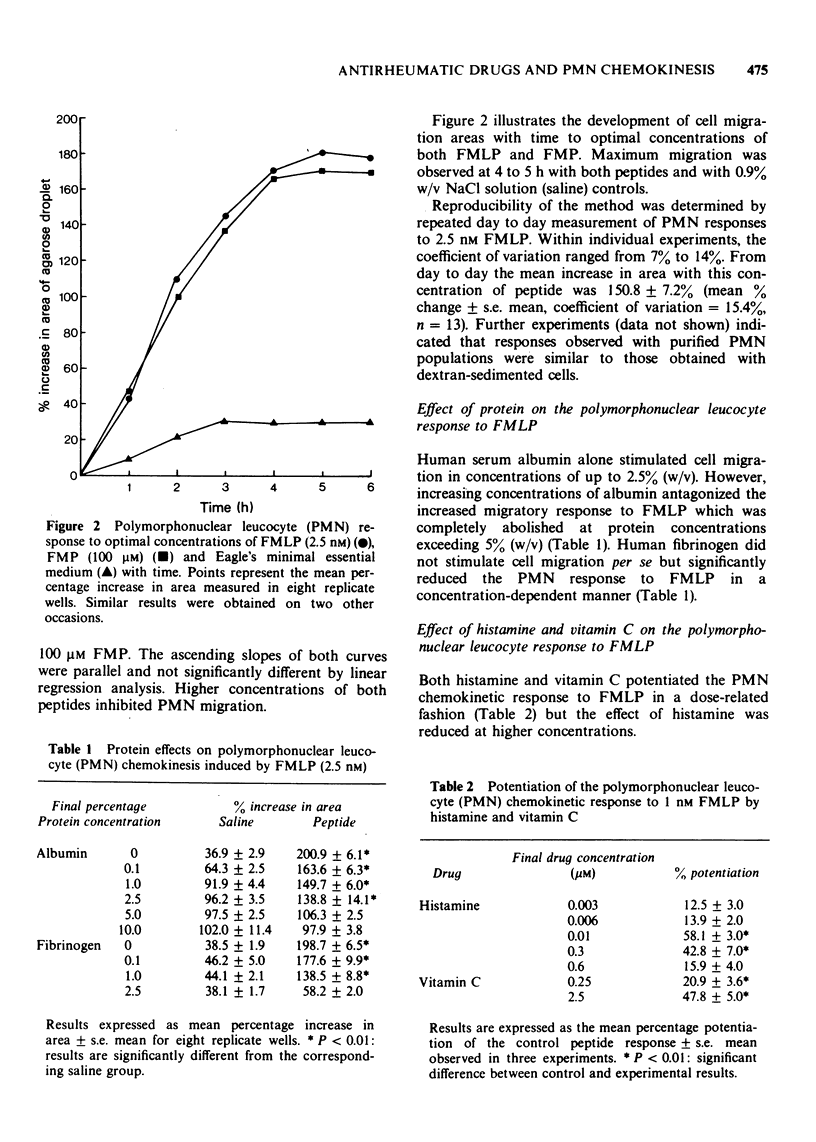


Selected References
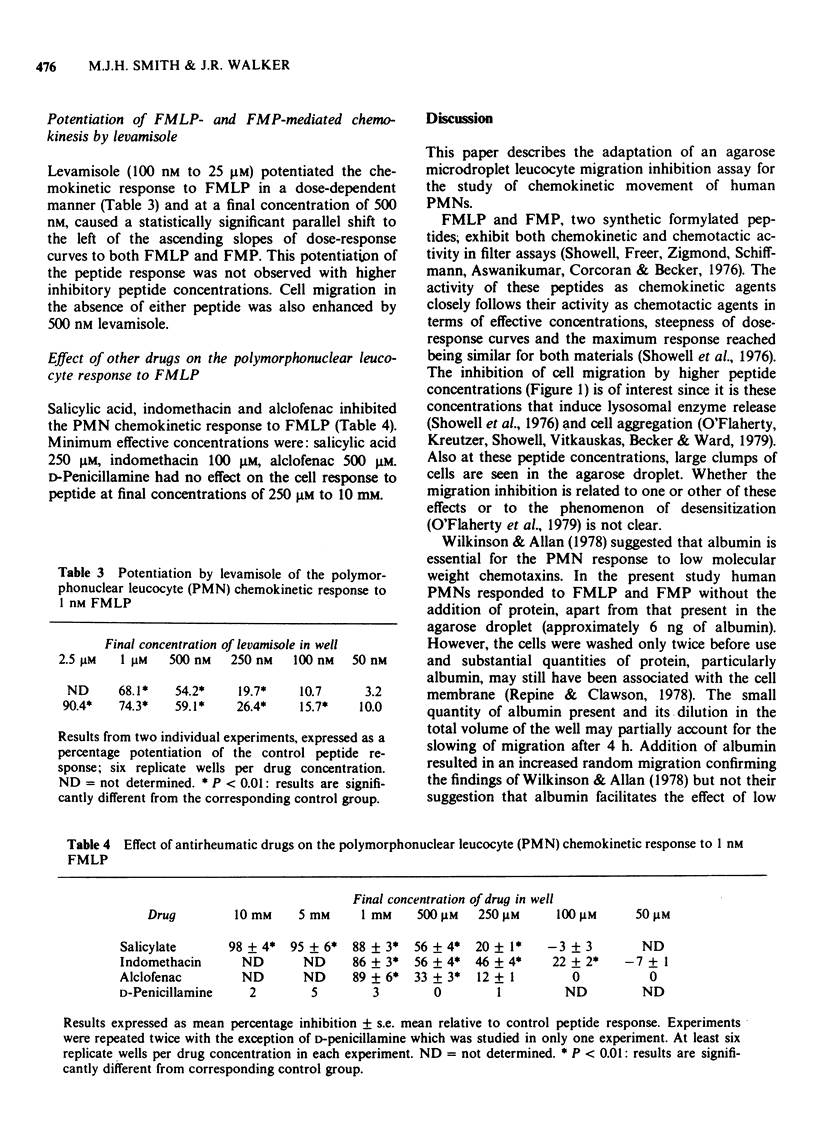
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R., Glover A., Koornhof H. J., Rabson A. R. In vitro stimulation of neutrophil motility by levamisole: maintenance of cgmp levels in chemotactically stimulated levamisole-treated neutrophils. J Immunol. 1976 Aug;117(2):428–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R., Glover A., Rabson A. R. The in vitro effects of histamine and metiamide on neutrophil motility and their relationship to intracellular cyclic nucleotide levels. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1690–1696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borel J. F. Effect of some drugs on the chemotaxis of rabbit neutrophils in vitro. Experientia. 1973 Jun 15;29(6):676–678. doi: 10.1007/BF01944767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. A., Collins A. J. Action of nonsteroidal, anti-inflammatory drugs on human and rat peripheral leucocyte migration in vitro. Ann Rheum Dis. 1977 Jun;36(3):239–243. doi: 10.1136/ard.36.3.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. A., Collins A. J. In vitro effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on human polymorphonuclear cells and lymphocyte migration. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Nov;64(3):347–352. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chwalinska-Sadowska H., Baum J. The effect of D-penicillamine on polymorphonuclear leukocyte function. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):871–879. doi: 10.1172/JCI108540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham F. M., Ford-Hutchinson A. W., Oliver A. M., Smith M. J., Walker J. R. The effects of D-pencillamine and levamisole on leucocyte chemotaxis in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 May;63(1):119–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb07781.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEORGE M., VAUGHAN J. H. In vitro cell migration as a model for delayed hypersensitivity. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Nov;111:514–521. doi: 10.3181/00379727-111-27841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Wasserman S. I., Gigli I., Austen K. F. Enhancement of random migration and chemotactic response of human leukocytes by ascorbic acid. J Clin Invest. 1974 Mar;53(3):813–818. doi: 10.1172/JCI107620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington J. T., Jr, Stastny P. Macrophage migration from an agarose droplet: development of a micromethod for assay of delayed hypersensitivity. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):752–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambelin G., Roba J., Gillet C., Buu-Hoï N. P. Pharmacology of a new analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory agent, 4-allyloxy-3-chlorophenylacetic acid. Arzneimittelforschung. 1970 May;20(5):610–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maderazo E. G., Woronick C. L. Micropore filter assay of human granulocyte locomotion: problems and solutions. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1978 Oct;11(2):196–211. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(78)90044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meacock S. C., Kitchen E. A. Some effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on leucocyte migration. Agents Actions. 1976 Feb;6(1-3):320–325. doi: 10.1007/BF01972249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat A. G. Neutrophil chemotaxis in rheumatoid arthritis. Effect of D-penicillamine, gold salts, and levamisole. Ann Rheum Dis. 1978 Feb;37(1):1–8. doi: 10.1136/ard.37.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee C., Lynn W. S. Role of ions and extracellular protein in leukocyte motility and membrane ruffling. Am J Pathol. 1978 Nov;93(2):369–381. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Kreutzer D. L., Showell H. J., Vitkauskas G., Becker E. L., Ward P. A. Selective neutrophil desensitization to chemotactic factors. J Cell Biol. 1979 Mar;80(3):564–572. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.3.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repine J. E., Clawson C. C. Influence of surface proteins and separation techniques on neutrophil unstimulated and stimulated locomotion in vitro. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1978 Sep;24(3):217–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivkin I., Foschi G. V., Rosen C. H. Inhibition of in vitro neutrophil chemotaxis and spontaneous motility by anti-inflammatory agents. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Nov;153(2):236–240. doi: 10.3181/00379727-153-39518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivkin I. The effect of bovine serum albumin on the in vitro inhibition of chemotaxis by anti-inflammatory agents. Agents Actions. 1977 Oct;7(4):465–468. doi: 10.1007/BF01966854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showell H. J., Freer R. J., Zigmond S. H., Schiffmann E., Aswanikumar S., Corcoran B., Becker E. L. The structure-activity relations of synthetic peptides as chemotactic factors and inducers of lysosomal secretion for neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1154–1169. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. R., James D. W., Smith M. J. Directed migration of circulating polymorphonuclear leucocytes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a defect in the plasma. Ann Rheum Dis. 1979 Jun;38(3):215–218. doi: 10.1136/ard.38.3.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weese J. L., McCoy J. L., Dean J. H., Ortaldo J. R., Burk K. R., Herberman R. B. Brief communication: technical modifications of the human agarose microdroplet leukocyte migration inhibition assay. J Immunol Methods. 1978;24(3-4):363–370. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90139-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. G., Kirkpatrick C. H., Gallin J. I. Effects of levamisole on normal and abnormal leukocyte locomotion. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):941–950. doi: 10.1172/JCI108716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Hirsch J. G. Leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis. New methods for evaluation, and demonstration of a cell-derived chemotactic factor. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):387–410. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


