Abstract
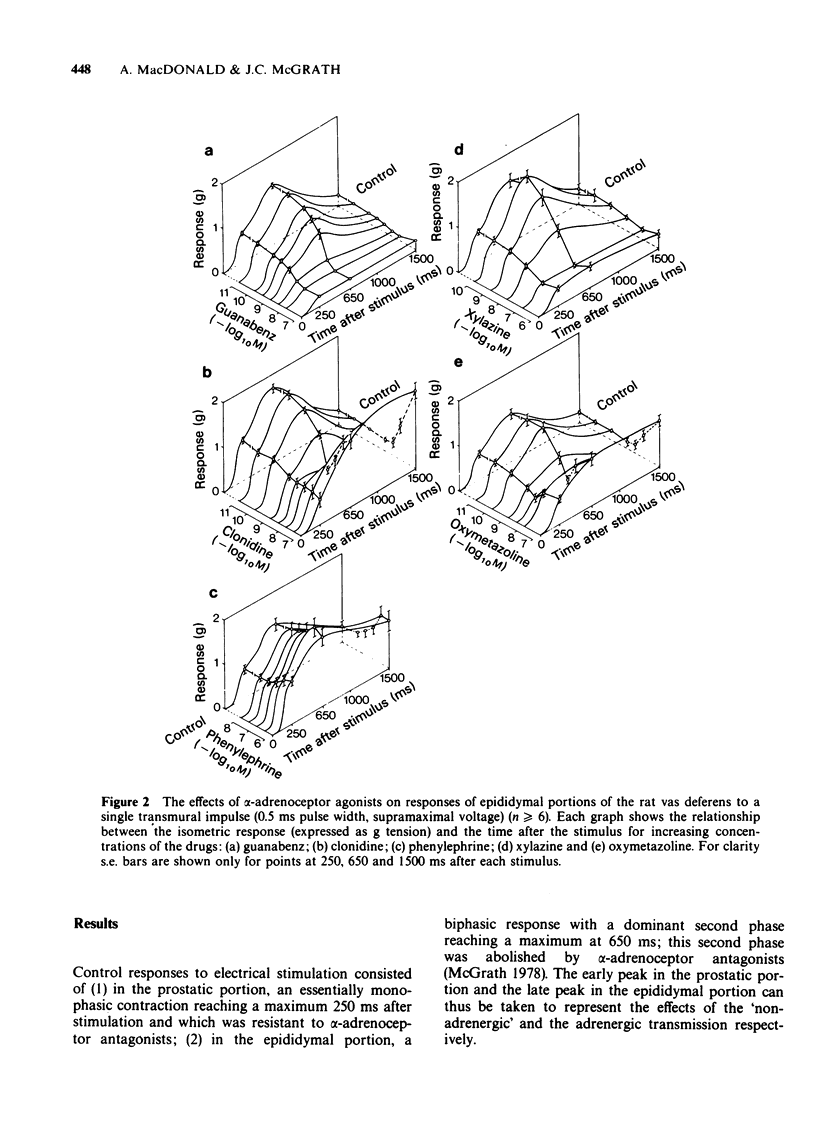
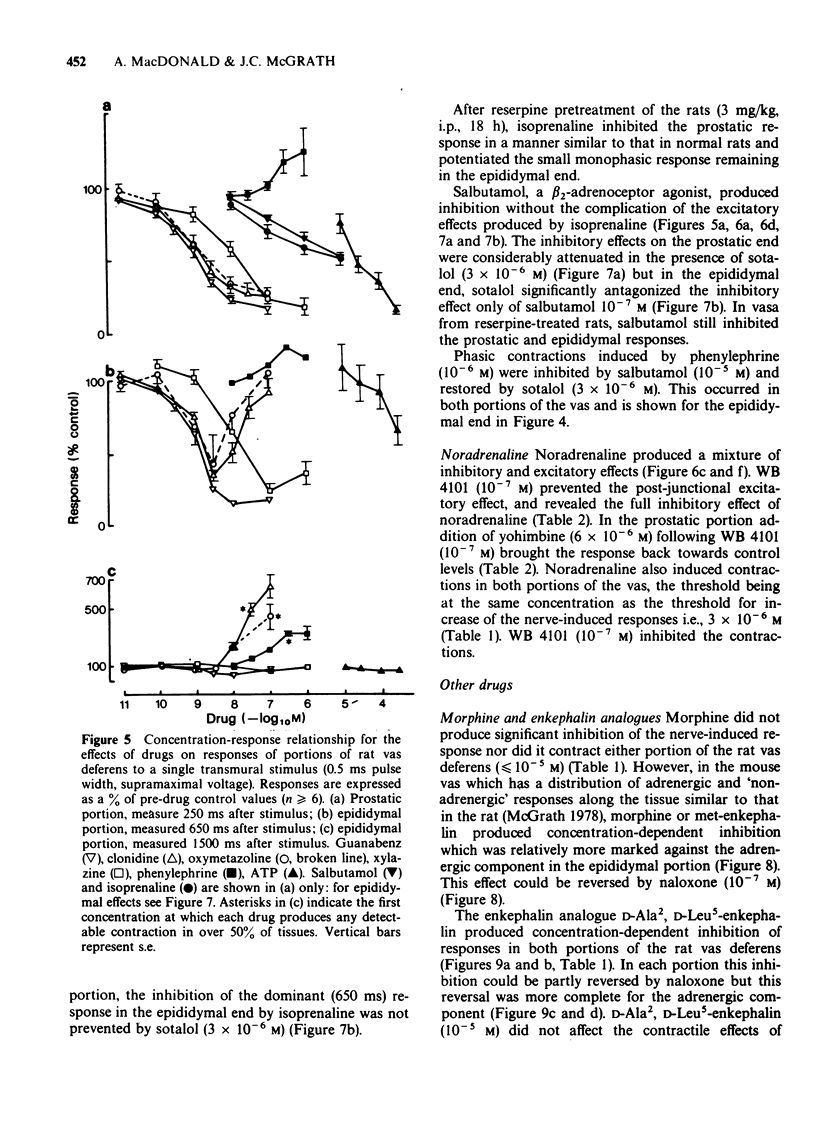
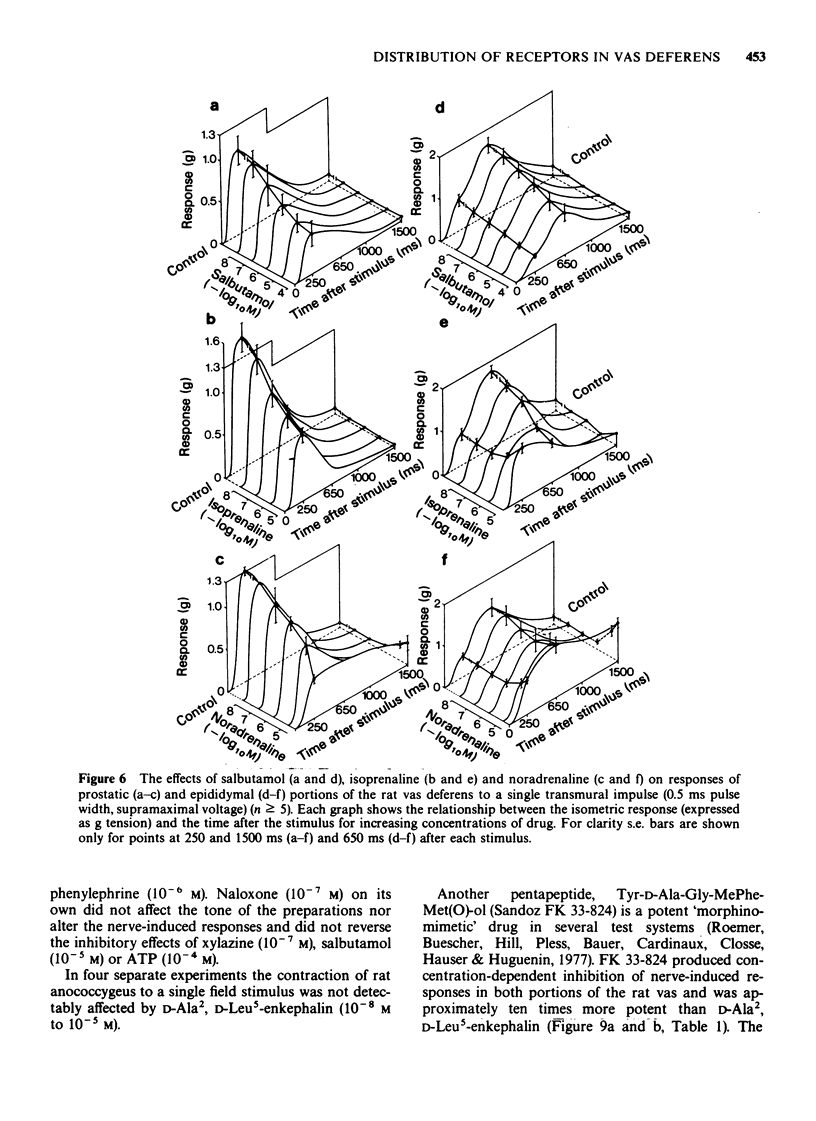
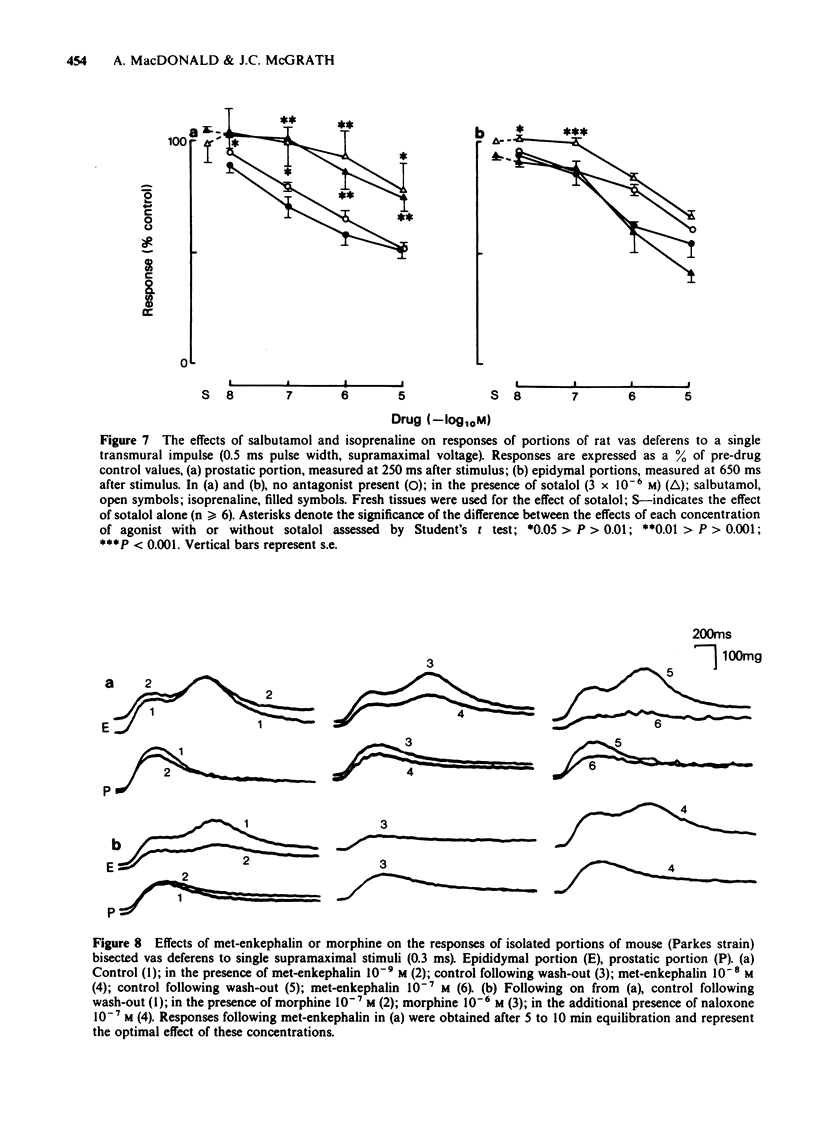
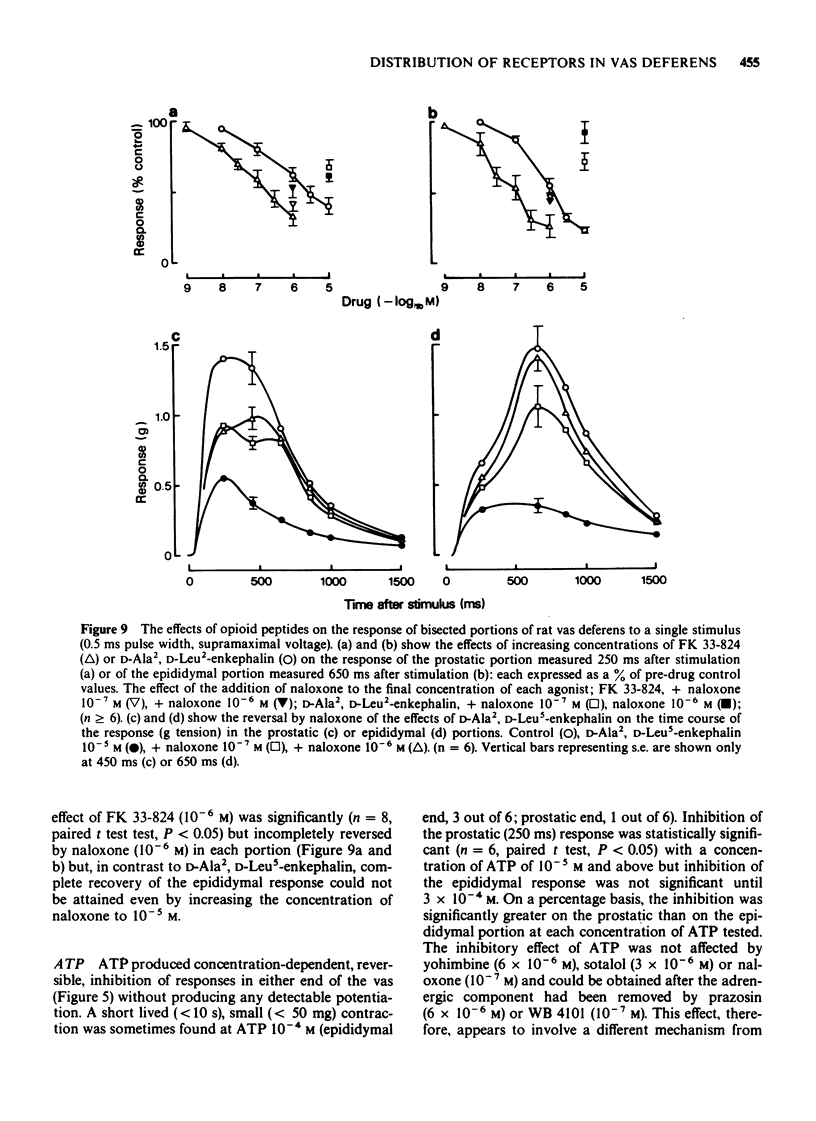
1. The effects of adrenoceptor agonists and other agonists on the contractile responses of the prostatic and epididymal portions of the rat isolated vas deferens to single pulse field stimulation were investigated. 2. alpha-Adrenoceptor agonists produced prejunctional alpha 2-mediated inhibition and post-junctional alpha 1-mediated potentiation of the nerve-induced responses. Guanabenz and xylazine produced mainly inhibitory effects, xylazine being 10 times less potent. Clonidine and oxymetazoline produced inhibition with similar potency to guanabenz but at higher concentrations excitatory effects were present, particularly in the epididymal portion. Phenylephrine produced only potentiation of the nerve-induced response in both portions. Potentiation of nerve-induced responses was a more sensitive and quantitative index of excitation than was direct contraction of the tissue. 3. Isoprenaline and salbutamol both gave beta 2-mediated inhibition of the nerve-induced responses in both portions of tissue. At least part of the effect was post-junctional since phenylephrine contractions were inhibited. Isoprenaline also produced a post-junctional alpha 1-mediated excitation. 4. Noradrenaline produced effects qualitatively similar to those of the other alpha-adrenoceptor agonists, inhibition and excitation predominating in the prostatic and epididymal ends respectively. 5. Morphine produced inhibition in the mouse but not in the rat vas deferens. In rat vas, however, enkephalin analogues produced pre-junctional inhibition of responses in both portions which could be partly reversed by naloxone; restoration of the adrenergic component was more complete. Rat anococcygeus showed no equivalent effect. 6. Adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) inhibited nerve-induced responses in each portion with a greater effect on the prostatic portion.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anton P. G., Duncan M. E., McGrath J. C. An analysis of the anatomical basis for the mechanical response to motor nerve stimulation of the rat vas deferens. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(1):23–43. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum T., Shropshire A. T., Rowles G., Van Pelt R., Fernandez S. P., Eckfeld D. K., Gluckman M. I. General pharmacologic actions of the antihypertensive agent 2,6-dichlorobenzylidene aminoguanidine acetate (WY-8678). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 Feb;171(2):276–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth F. J., Connell G. J., Docherty J. R., McGrath J. C. Isolation of the 'non-adrenergic' motor nerve response in rat vas deferens by elimination of the adrenergic motor component [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:19P–20P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. M., McGrath J. C., Summers R. J. The effects of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists on responses of transmurally stimulated prostatic and epididymal portions of the isolated vas deferens of the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Aug;66(4):553–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb13694.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler M., Jenkinson D. H. Blockade by WB 4101 of alpha-adrenoceptors in the rat vas deferens and guinea-pig taenia caeci. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Dec 1;52(3-4):303–311. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90283-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clanachan A. S., Johns A., Paton D. M. Presynaptic inhibitory actions of adenine nucleotides and adenosine on neurotransmission in the rat vas deferens. Neuroscience. 1977;2(4):597–602. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. R., MacDonald A., McGrath J. C. Further sub-classification of alpha-adrenoceptors in the cardiovascular system, vas deferens and anococcygeus of the rat [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;67(3):421P–422P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. R., McGrath J. C. A comparison of pre- and post-junctional potencies of several alpha-adrenoceptor agonists in the cardiovascular system and anococcygeus muscle of the rat. Evidence for two types of post-junctional alpha-adrenoceptor. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Jun;312(2):107–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00569718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxey J. C., Smith C. F., Walker J. M. Selectivity of blocking agents for pre-and postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 May;60(1):91–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb16752.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M. Pharmacological characterisation of the presynaptic alpha-adrenoceptor in the rat vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Mar 21;42(2):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90351-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M., Whiting S. B. Evidence for two distinct types of postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptor in vascular smooth muscle in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Oct;67(2):207–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb08668.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly D. K., Bhattacharya B. B. Adrenergic beta receptors in vas deferens. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1970 Jun;185(2):406–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., McGrath J. C. The effect of pithing and of nerve stimulation on the depletion of noradrenaline by reserpine in the rat anococcygeus muscle and vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Dec;52(4):585–590. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09727.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., McGrath J. C. The response of the cat anococcygeus muscle to nerve or drug stimulation and a comparison with the rat anococcygeus. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Jan;50(1):109–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09597.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S. The rat anococcygeus muscle and its response to nerve stimulation and to some drugs. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Jul;45(3):404–416. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb08097.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedqvist P., Von Euler U. S. Inhibition by alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors of the twitch response to transmural stimulation in the guinea-pig vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;40(1):153–162. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(76)90365-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. A new example of a morphine-sensitive neuro-effector junction: adrenergic transmission in the mouse vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Dec;46(4):764–766. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb06901.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins D. A., Marshall I., Nasmyth P. A. An inhibitory role for noradrenaline in the mouse vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Dec;61(4):649–655. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07558.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapur H., Mottram D. R. A comparative study on the pre- and post-synaptic alpha blocking activity of a series of benzodioxanes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;27(14):1879–1880. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Lord J. A., Paterson S. J., Waterfield A. A. Effects of changes in the structure of enkephalins and of narcotic analgesic drugs on their interactions with mu- and delta-receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Feb;68(2):333–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10422.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARGE B. J. SYMPATHETIC BETA-RECEPTORS AND THE GUINEA-PIG VAS DEFERENS. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1965 Feb;24:194–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1965.tb02095.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z. Presynaptic regulation of catecholamine release. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Jul 1;23(13):1793–1800. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90187-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lish P. M., Weikel J. H., Dungan K. W. Pharmacological and toxicological properties of two new beta-adrenergic receptor antagonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 Aug;149(2):161–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald A., McGrath J. C. The effects of castration on neurotransmission in the rat vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 May;69(1):49–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10882.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. C. Adrenergic and 'non-adrenergic' components in the contractile response of the vas deferens to a single indirect stimulus. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:23–39. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris H. R., Piper P. J., Taylor G. W., Tippins J. R. Comparative studies on immunologically and non-immunologically produced slow-reacting substances from man, guinea-pig and rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Oct;67(2):179–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb08664.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roemer D., Buescher H. H., Hill R. C., Pless J., Bauer W., Cardinaux F., Closse A., Hauser D., Huguenin R. A synthetic enkephalin analogue with prolonged parenteral and oral analgesic activity. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):547–549. doi: 10.1038/268547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöstrand N. O. Effects of acetylcholine and some other smooth muscle stimulants on the electrical and mechanical responses of the guinea-pig vas deferens to nerve stimulation. Acta Physiol Scand. 1973 Sep;89(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1973.tb05491.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöstrand N. O., Swedin G. Potentiation by smooth muscle stimulants of the hypogastric nerve--vas deferens preparation from normal and castrated guinea-pigs. Acta Physiol Scand. 1968 Nov;74(3):472–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1968.tb04255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Endo T., Taube H. D. Relative pre- and postsynaptic potencies of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists in the rabbit pulmonary artery. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1975;291(1):55–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00510821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner U., Starke K., Schümann H. J. Actions of clonidine and 2-(2-methyl-6-ethyl-cyclohexylamino)-2-oxazoline on postganglionic autonomic nerves. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1972 Feb;195(2):282–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


