Abstract
1 The effects of pretreatment with various inhibitors of anaphylactic mediators on antigen-induced bronchoconstriction were studied in anaesthetized guinea-pigs, actively sensitized according to two different regimens (one producing IgE- and IgG-like antibodies and the other producing exclusively IgG antibodies).
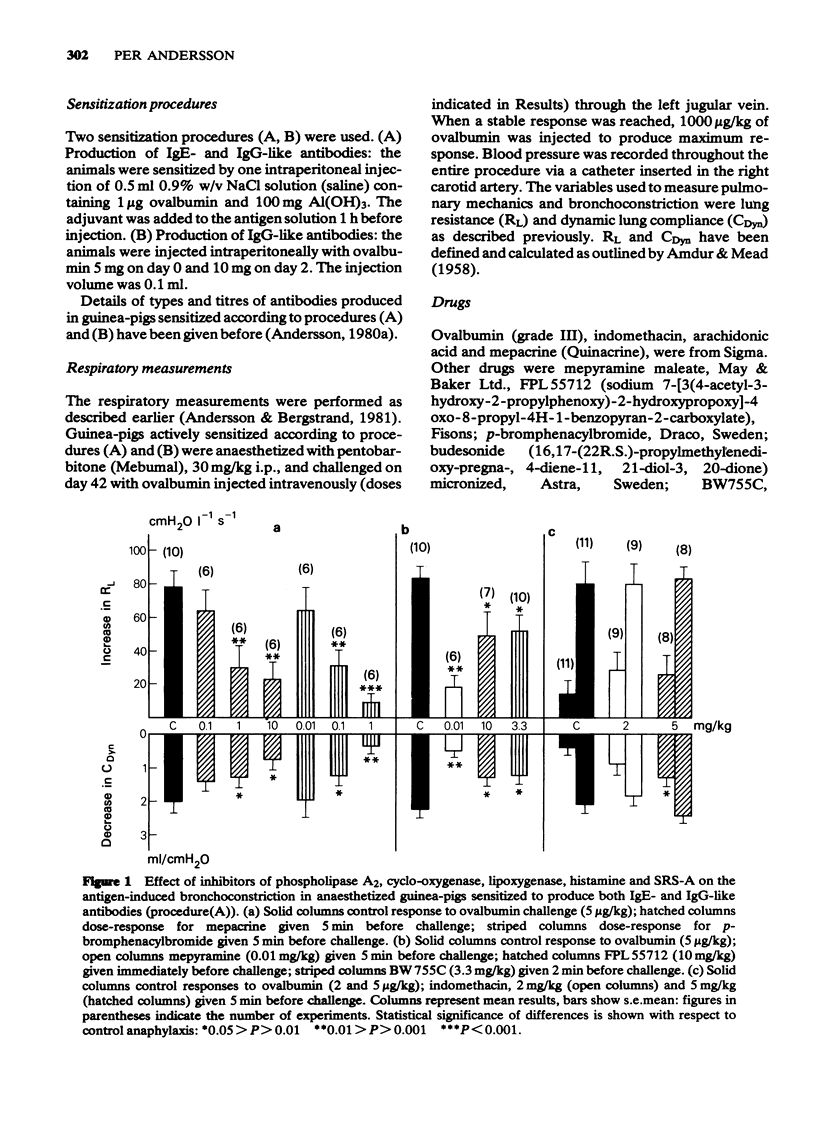
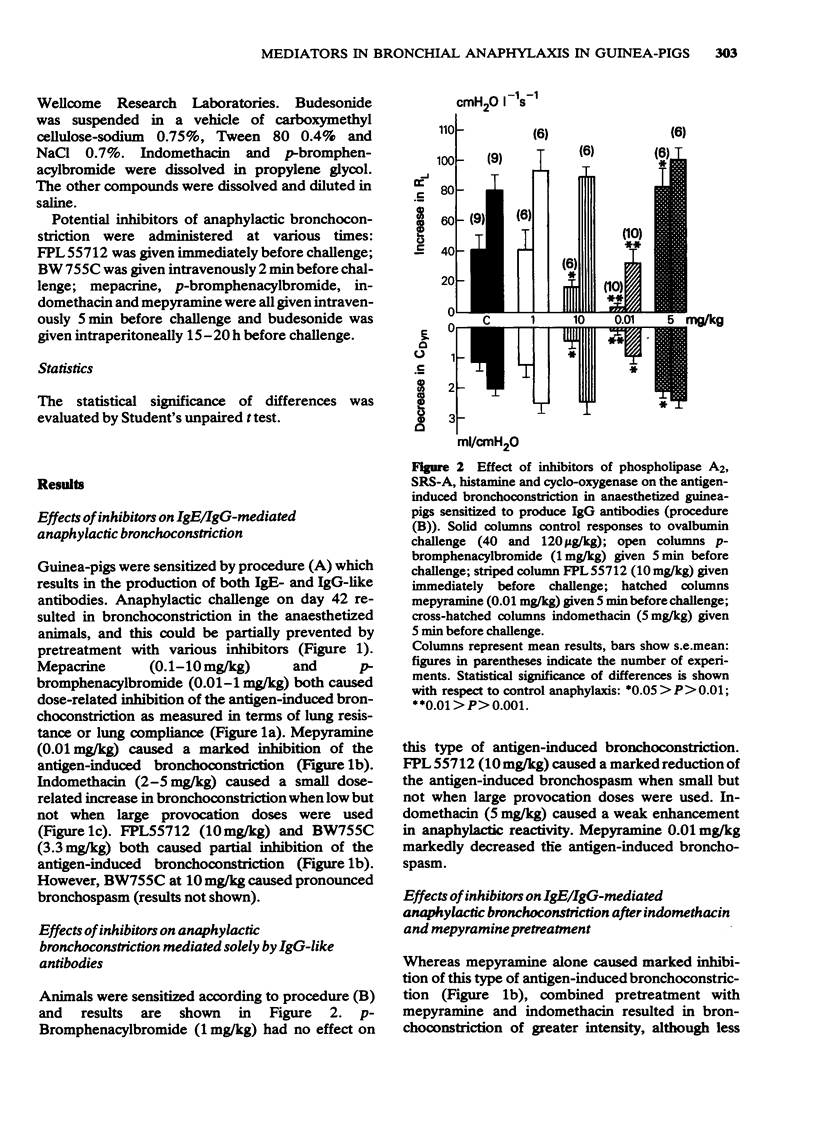
2 The phospholipase A2-inhibitors mepacrine and p-bromphenacylbromide caused a dose-dependent inhibition of the antigen-induced bronchoconstriction in guinea-pigs sensitized to produce both IgE and IgG antibodies. No effect was seen in those sensitized to produce only IgG antibodies.
3 In both models indomethacin pretreatment led to an increased anaphylactic bronchoreactivity, whereas mepyramine and FPL 55712 reduced it.
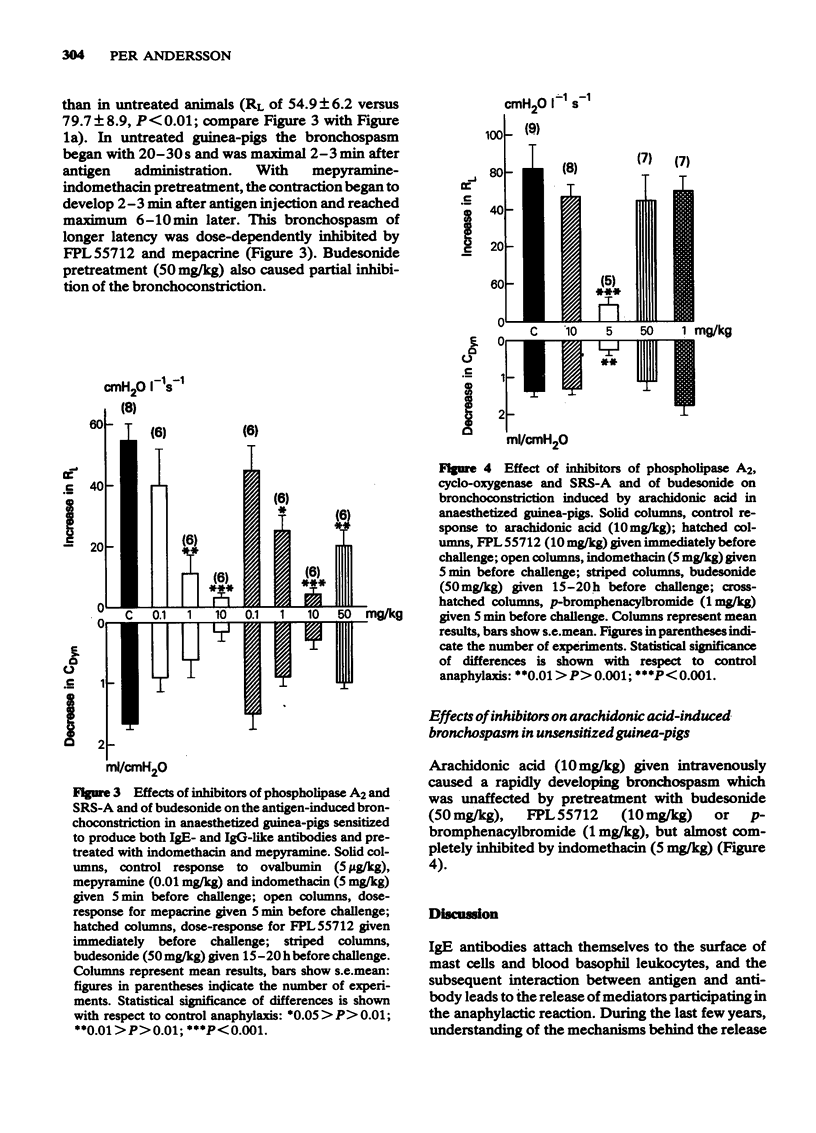
4 BW 755C significantly reduced antigen-induced bronchoconstriction in guinea-pigs sensitized to produce both IgE and IgG antibodies. In this model, the residual bronchoconstriction evident after combined pretreatment with indomethacin and mepyramine was prevented by additional pretreatment with mepacrine, FPL 55712 or budesonide.
5 Arachidonic acid given intravenously caused a marked bronchoconstriction that was prevented by indomethacin but not by budesonide, FPL 55712 or p-bromphenacylbromide.
6 Although the same pattern of anaphylactic mediators is released in the two models of anaphylactic bronchoconstriction, a different activation mechanism is indicated by the results obtained with phospholipase A2 inhibitors.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMDUR M. O., MEAD J. Mechanics of respiration in unanesthetized guinea pigs. Am J Physiol. 1958 Feb;192(2):364–368. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.192.2.364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ubaidi F., Bakhle Y. S. Differences in biological activation of arachidonic acid in perfused lungs from guinea pig, rat and man. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Mar 7;62(1):89–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90484-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson P. Antigen-induced bronchial anaphylaxis in actively sensitized guinea-pigs. Pattern of response in relation to immunization regimen. Allergy. 1980 Jan;35(1):65–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1980.tb01718.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson P. Antigen-induced bronchial anaphylaxis in actively sensitized guinea-pigs: anti-anaphylactic effects of sodium cromoglycate and aminophylline. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Jul;69(3):467–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb07036.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson P., Bergstrand H. Antigen-induced bronchial anaphylaxis in actively sensitized guinea-pigs: effect of long-term treatment with sodium cromoglycate and aminophylline. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Nov;74(3):601–609. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb10470.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson P., Brattsand R. Protective effects of the glucocorticoid, budesonide, on lung anaphylaxis in actively sensitized guinea-pigs: inhibition of IgE-but not of IgG-mediated anaphylaxis. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 May;76(1):139–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09199.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach M. K., Brashler J. R., Hammarström S., Samuelsson B. Identification of a component of rat mononuclear cell SRS as leukotriene D. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Apr 29;93(4):1121–1126. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90605-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell G. J., Flower R. J., Nijkamp F. P., Vane J. R. Phospholipase A2 activity of guinea-pig isolated perfused lungs: stimulation, and inhibition by anti-inflammatory steroids. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Jan;62(1):79–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb07009.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgeat P., Sirois P. Leukotrienes: a major step in the understanding of immediate hypersensitivity reactions. J Med Chem. 1981 Feb;24(2):121–126. doi: 10.1021/jm00134a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant D. H., Burns M. W., Lazarus L. Identification of IgG antibody as a carrier of reaginic activity in asthmatic patients. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1975 Dec;56(6):417–428. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(75)90060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant D. H., Burns M. W., Lazarus L. New type of allergic asthma due to IgG "reaginic" antibody. Br Med J. 1973 Dec 8;4(5892):589–592. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5892.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chand N. FPL 55712 -- an antagonist of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS-A): a review. Agents Actions. 1979 Jun;9(2):133–140. doi: 10.1007/BF02024724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daëron M., Prouvost-Danon A., Voisin G. A. Mast cell membrane antigens and Fc receptors in anaphylaxis. II. Functionally distinct receptors for IgG and for IgE on mouse mast cells. Cell Immunol. 1980 Jan;49(1):178–189. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engineer D. M., Jose P. J., Piper P. J., Tippins J. R. Modulation of slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis and histamine release by prostacyclin and thromboxanes [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:42P–42P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg K., Sörenby L. The influence of a new corticosteroid, budesonide, on anaphylactic bronchoconstriction and SRS-A release in the guinea pig. Agents Actions. 1981 Jul;11(4):391–395. doi: 10.1007/BF01982476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M. On the formation of thromboxane B2 and 12l-hydroxy-5,8,10,14-eicosatetraenoic acid (12 ho-20:4) in tissues from the guinea pig. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 22;431(3):651–654. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs G. A., Flower R. J., Vane J. R. A new approach to anti-inflammatory drugs. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Jun 15;28(12):1959–1961. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90651-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Axelrod J. Phospholipid methylation and biological signal transmission. Science. 1980 Sep 5;209(4461):1082–1090. doi: 10.1126/science.6157192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holroyde M. C., Altounyan R. E., Cole M., Dixon M., Elliott E. V. Bronchoconstriction produced in man by leukotrienes C and D. Lancet. 1981 Jul 4;2(8236):17–18. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90254-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T. The Robert A. Cooke memorial lecture. Analysis of triggering events in mast cells for immunoglobulin E-mediated histamine release. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1981 Feb;67(2):90–96. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(81)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Austen K. F. Mediation of local homeostasis and inflammation by leukotrienes and other mast cell-dependent compounds. Nature. 1981 Sep 10;293(5828):103–108. doi: 10.1038/293103a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marone G., Kagey-Sobotka A., Lichtenstein L. M. Possible role of phospholipase A2 in triggering histamine secretion from human basophils in vitro. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 Aug;20(2):231–239. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(81)90181-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGivney A., Morita Y., Crews F. T., Hirata F., Axelrod J., Siraganian R. P. Phospholipase activation in the IgE-mediated and Ca2+ ionophore A23187-induced release of histamine from rat basophilic leukemia cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Dec;212(2):572–580. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90400-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michoud M. C., Fraser R. S., Pare P. D., Hogg J. C. Effect of indomethacin and atropine in experimental asthma in conscious guinea pigs. J Appl Physiol. 1976 Jun;40(6):889–894. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.40.6.889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moodley I., Mongar J. L. IgG receptors on the mast cells. Agents Actions. 1981 Apr;11(1-2):77–83. doi: 10.1007/BF01991464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris H. R., Piper P. J., Taylor G. W., Tippins J. R. The role of arachidonate lipoxygenase in the release of SRS-A from guinea-pig chopped lung. Prostaglandins. 1980 Mar;19(3):371–383. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(80)90071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orehek J., Douglas J. S., Lewis A. J., Bouhuys A. Prostaglandin regulation of airway smooth muscle tone. Nat New Biol. 1973 Sep 19;245(142):84–85. doi: 10.1038/newbio245084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson R., Pruzansky J. J., Harris K. E. An agent that releases basophil and mast cell histamine but blocks cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase metabolism of arachidonic acid inhibits immunoglobulin E-mediated asthma in rhesus monkeys. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1981 Jun;67(6):444–449. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(81)90097-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters S. P., Siegel M. I., Kagey-Sobotka A., Lichtenstein L. M. Lipoxygenase products modulate histamine release in human basophils. Nature. 1981 Jul 30;292(5822):455–457. doi: 10.1038/292455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper P. J. Anaphylaxis and the release of active substances in the lungs. Pharmacol Ther B. 1977;3(1):75–98. doi: 10.1016/0306-039x(77)90005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper P. J., Tippins J. R., Morris H. R., Taylor G. W. Arachidonic acid metabolism and SRS-A. Agents Actions Suppl. 1979;(4):37–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheard P., Lee T. B., Tattersall M. L. Further studies on the SRS-A antagonist FPL 55712. Monogr Allergy. 1977;12:245–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. P. Effect of indomethacin in asthma: evidence against a role for prostaglandins in its pathogenesis. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1975 Aug;2(4):307–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1975.tb02775.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spannhake E. W., Hyman A. L., Kadowitz P. J. Bronchoactive metabolites of arachidonic acid and their role in airway function. Prostaglandins. 1981 Dec;22(6):1013–1026. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(81)90028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauber A. I., Kaliner M., Stechschulte D. J., Austen K. F. Immunologic release of histamine and slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis from human lung. V. Effects of prostaglandins on release of histamine. J Immunol. 1973 Jul;111(1):27–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargaftig B. B. Carrageenan and thrombin trigger prostaglandin synthetase-independent aggregation of rabbit platelets: inhibition by phospholipase A2 inhibitors. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1977 Apr;29(4):222–228. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1977.tb11293.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volwerk J. J., Pieterson W. A., de Haas G. H. Histidine at the active site of phospholipase A2. Biochemistry. 1974 Mar 26;13(7):1446–1454. doi: 10.1021/bi00704a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


