Abstract
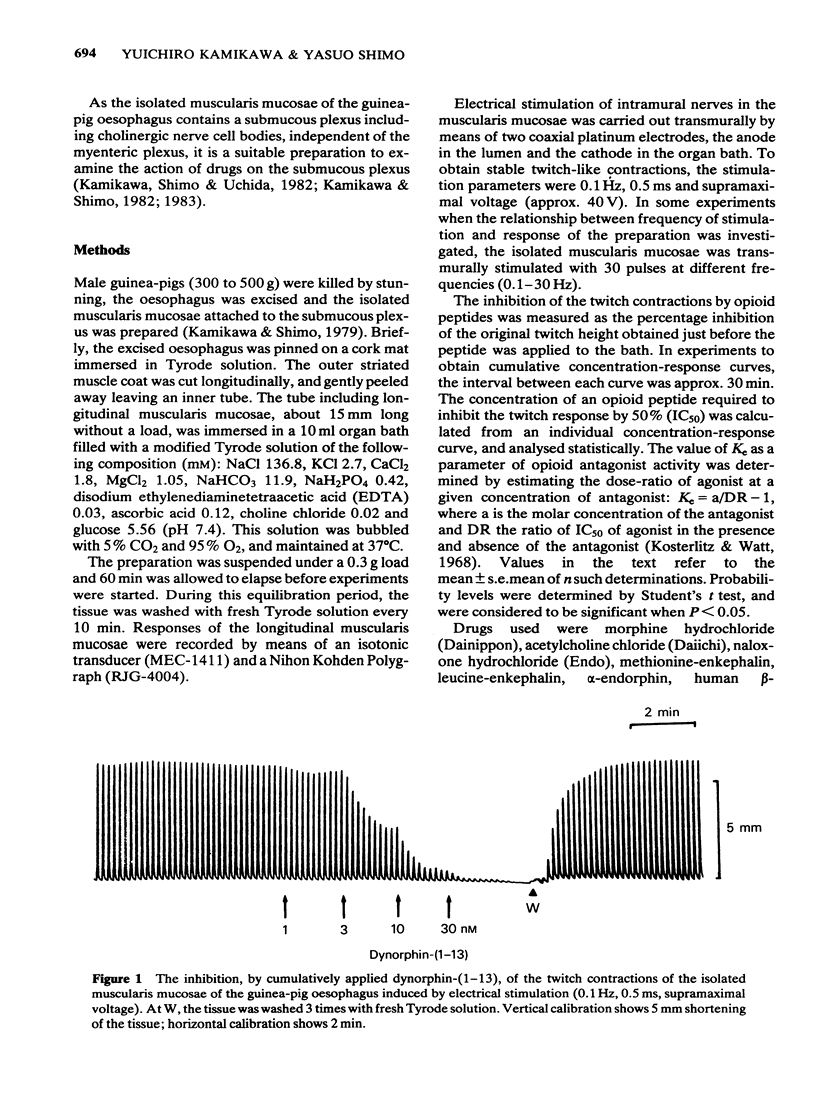
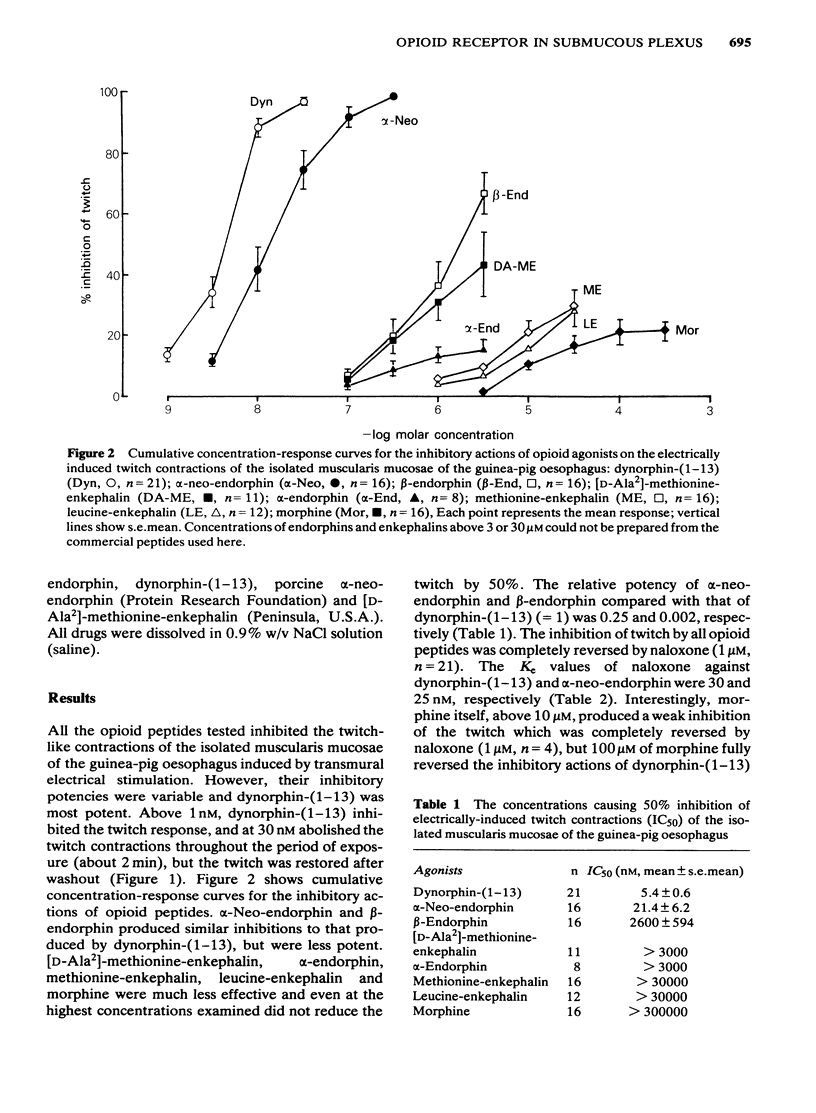
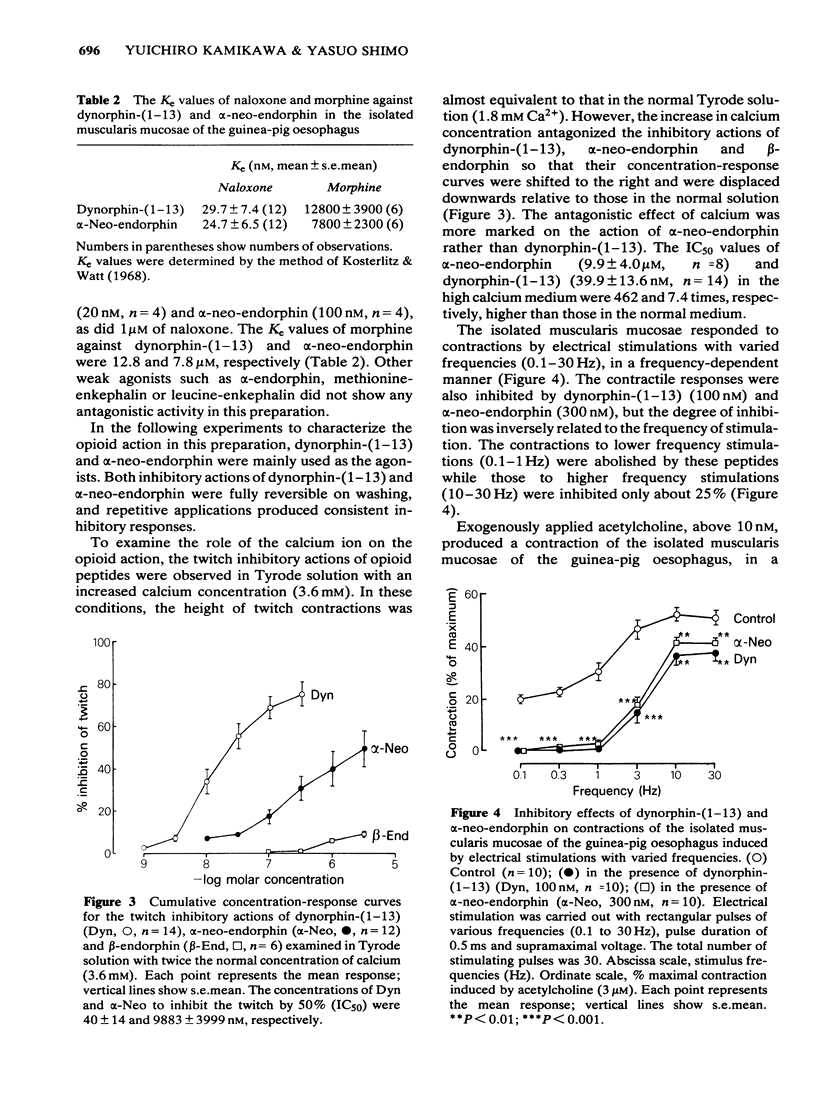
1 The cholinergically mediated electrically-induced contractions of the submucous plexus-longitudinal muscularis mucosae preparation of the guinea-pig oesophagus were used to study the actions of opioid peptides and morphine. 2 The twitch contractions of the tissue (0.1 Hz, 0.5 ms, supramaximal voltage) were inhibited by all the opioid peptides and morphine in a concentration-dependent manner. The order of potency was dynorphin-(1-13) greater than alpha-neo-endorphin greater than beta-endorphin greater than [D-Ala2]-methionine-enkephalin much greater than alpha-endorphin, methionine-enkephalin, leucine-enkephalin and morphine. 3 The inhibitory actions of dynorphin-(1-13) (20 nM), alpha-neo-endorphin (100 nM) and beta-endorphin (3 microM) were completely reversed either by naloxone (1 microM) or by morphine (100 microM). The Ke values of naloxone against dynorphin-(1-13) and alpha-neo-endorphin were 30 and 25 nM, respectively. 4 Increasing the concentration of calcium from 1.8 to 3.6 mM in Tyrode solution decreased the sensitivity of the tissue to dynorphin-(1-13) 7.4 times and to alpha-neo-endorphin 462 times. 5 The inhibitory actions of dynorphin-(1-13) (100 nM) and alpha-neo-endorphin (300 nM) were inversely related to stimulus frequency, being most active at low frequencies (0.1-1 Hz), and least active at high (30 Hz). 6 Exogenously applied acetylcholine produced concentration-dependent contractions of the isolated muscularis mucosae, with an EC50 of 72.6 +/- 4.5 nM. The contractile response of the oesophagus to acetylcholine was not affected by the pretreatment of the tissue with dynorphin-(1-13) (100 nM), alpha-neo-endorphin (300 nM) or beta-endorphin (3 microM). 7 It is concluded that the submucous plexus-longitudinal muscularis mucosae of the guinea-pig oesophagus is inhibited by opioid peptides acting at prejunctional opioid receptors, probably of the kappa-subtype.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alumets J., Håkanson R., Sundler F., Chang K. J. Leu-enkephalin-like material in nerves and enterochromaffin cells in the gut. An immunohistochemical study. Histochemistry. 1978 Jul 12;56(3-4):187–196. doi: 10.1007/BF00495979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavkin C., James I. F., Goldstein A. Dynorphin is a specific endogenous ligand of the kappa opioid receptor. Science. 1982 Jan 22;215(4531):413–415. doi: 10.1126/science.6120570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox B. M., Weinstock M. The effect of analgesic drugs on the release of acetylcholine from electrically stimulated guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1966 May;27(1):81–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1966.tb01643.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennessy M. R., Heimans R. L., Rand M. J. Comparison of effect of morphine-like analgesics on transmurally stimulated guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Oct;37(2):436–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb10580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Tachibana S., Lowney L. I., Hunkapiller M., Hood L. Dynorphin-(1-13), an extraordinarily potent opioid peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6666–6670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyand E. A., Kosterlitz H. W. Agonist and antagonist actions of morphine-like drugs on the guinea-pig isolated ileum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1966 Sep;27(3):514–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1966.tb01864.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Smith T. W., Kosterlitz H. W., Fothergill L. A., Morgan B. A., Morris H. R. Identification of two related pentapeptides from the brain with potent opiate agonist activity. Nature. 1975 Dec 18;258(5536):577–580. doi: 10.1038/258577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huidobro-Toro J. P., Yoshimura K., Lee N. M., Loh H. H., Way E. L. Dynorphin interaction at the kappa-opiate site. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jun 19;72(2-3):265–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90284-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huidobro F., Huidobro-Toro J. P., Miranda H. Interactions between morphine and the opioid-like peptides in the rat vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Dec;70(4):519–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb09770.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii K., Yamamoto S., Muraki T., Kato R. Partial agonistic action of morphine in the rat vas deferens. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1981 Dec;31(6):905–909. doi: 10.1254/jjp.31.905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto E. T., Martin W. R. Multiple opioid receptors. Med Res Rev. 1981 Winter;1(4):411–440. doi: 10.1002/med.2610010406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessen K. R., Saffrey M. J., Van Noorden S., Bloom S. R., Polak J. M., Burnstock G. Immunohistochemical studies of the enteric nervous system in tissue culture and in situ: localization of vascoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP), substance-P and enkephalin immunoreactive nerves in the guinea-pig gut. Neuroscience. 1980;5(10):1717–1735. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90091-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamikawa Y., Shimo Y. Antagonistic effect of compound 48/80 on the inhibitory actions of morphine and methionine-enkephalin on electrically-induced contractions of the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Dec;64(4):511–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb17312.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamikawa Y., Shimo Y. Cholinergic and adrenergic innervations of the muscularis mucosae in guinea-pig esophagus. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1979 Apr;238(2):220–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamikawa Y., Shimo Y. Indirect action of 5-hydroxytryptamine on the isolated muscularis mucosae of the guinea-pig oesophagus. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan;78(1):103–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb09368.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamikawa Y., Shimo Y., Uchida K. Inhibitory actions of catecholamines on electrically induced contractions of the submucous plexus-longitudinal muscularis mucosae preparation of the guinea-pig oesophagus. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Jun;76(2):271–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09217.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kangawa K., Matsuo H. alpha-Neo-endorphin : a "big" Leu-enkephalin with potent opiate activity from porcine hypothalami. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jan 15;86(1):153–160. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90394-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kangawa K., Minamino N., Chino N., Sakakibara S., Matsuo H. The complete amino acid sequence of alpha-neo-endorphin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Apr 15;99(3):871–878. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91244-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Watt A. J. Kinetic parameters of narcotic agonists and antagonists, with particular reference to N-allylnoroxymorphone (naloxone). Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Jun;33(2):266–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka T., Negishi K., Kajiwara M., Watanabe Y., Ishizuka Y., Matsumiya T. The choice of opiate receptor subtype by neo-endorphins. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Apr 23;79(3-4):301–305. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90636-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka T., Negishi K., Suda M., Matsumiya T., Inazu T., Ueki M. Rabbit vas deferens: a specific bioassay for opioid kappa-receptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 17;73(2-3):235–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90098-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka T., Negishi K., Suda M., Sawa A., Fujino M., Wakimasu M. Evidence that dynorphin-(1-13) acts as an agonist on opioid kappa-receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jan 22;77(2-3):137–141. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opmeer F. A., Van Ree J. M. Competitive antagonism of morphine action in vitro by calcium. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Feb 1;53(4):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90467-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opmeer F. A., Van Ree J. M. Differential involvement of calcium in acute and chronic opioid action in the guinea-pig ileum in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Apr;213(1):188–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. The action of morphine and related substances on contraction and on acetylcholine output of coaxially stimulated guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Mar;12(1):119–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb01373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz R., Wüster M., Herz A. Pharmacological characterization of the epsilon-opiate receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Mar;216(3):604–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uddman R., Alumets J., Håkanson R., Sundler F., Walles B. Peptidergic (enkephalin) innervation of the mammalian esophagus. Gastroenterology. 1980 Apr;78(4):732–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaught J. L. A characterization of dynorphin-(1-13) on the guinea pig ileal longitudinal muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Dec 17;76(4):453–456. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90121-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüster M., Schulz R., Herz A. Highly specific opiate receptors for dynorphin-(1-13) in the mouse vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Mar 21;62(2-3):235–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90283-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüster M., Schulz R., Herz A. Multiple opiate receptors in peripheral tissue preparations. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 15;30(14):1883–1887. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90194-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura K., Huidobro-Toro J. P., Lee N. M., Löh H. H., Way E. L. Kappa opioid properties of dynorphin and its peptide fragments on the guinea-pig Ileum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Jul;222(1):71–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


