Abstract
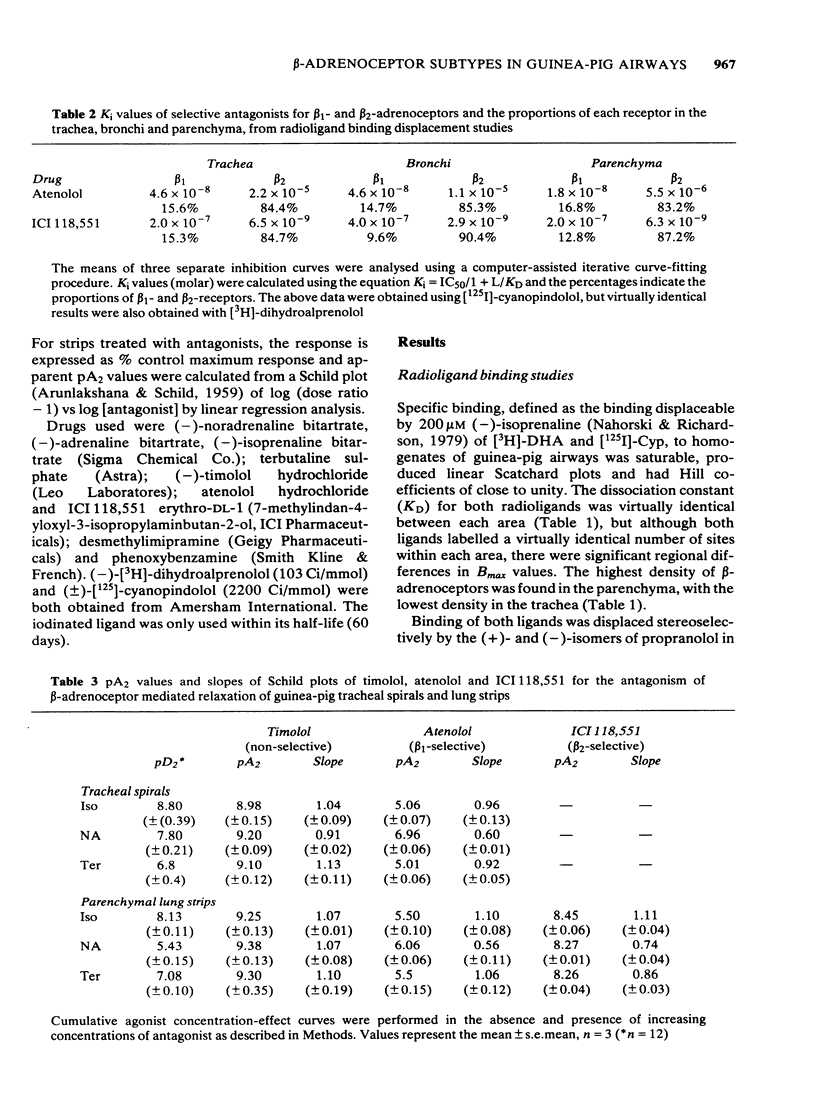
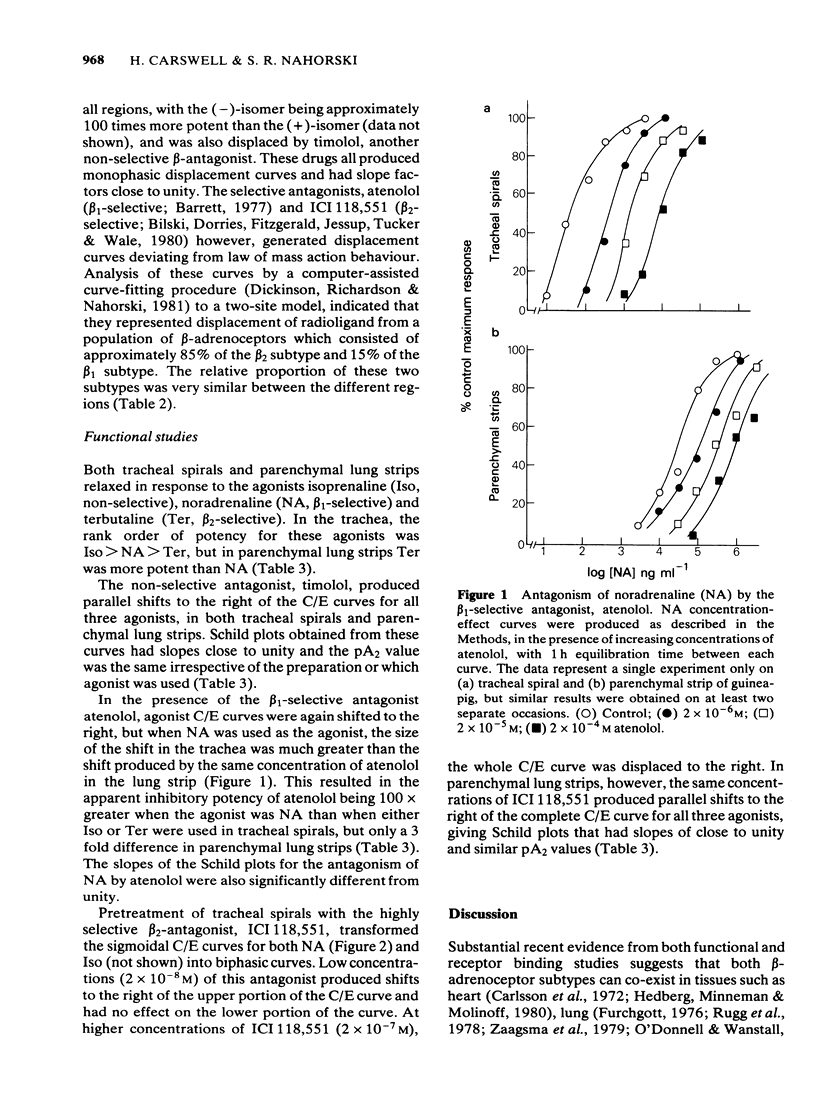
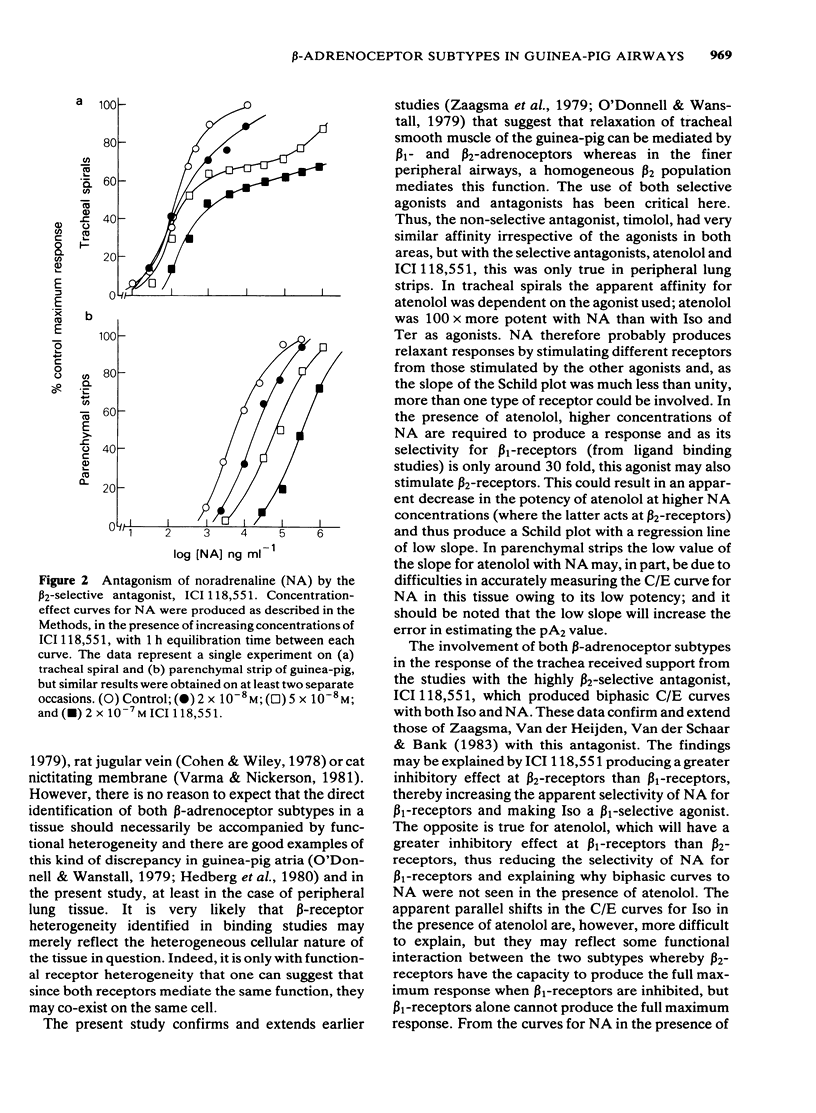
The distribution of beta-adrenoceptor subtypes in guinea-pig airways has been studied by radioligand binding assays and analysis of mechanical responses. Binding studies with the ligands [3H]-dihydroalprenolol and [125I]-cyanopindolol, revealed that beta-adrenoceptors were unevenly distributed throughout the airways with the highest density located in the parenchyma and the lowest density in the trachea. The relative proportion of beta 1:beta 2-adrenoceptor binding sites was assessed by computer-assisted analysis of the inhibition curves generated by selective agents. It was virtually identical in each region and in the order of 15:85%. beta-Adrenoceptor agonists caused concentration-dependent relaxations of both tracheal spirals and parenchymal lung strips. This response appeared to be mediated by both beta 1- and beta 2-adrenoceptors in tracheal spirals as the pA2 value for the beta 1-selective antagonist, atenolol, varied depending upon which agonist was used, and, in the presence of the beta 2-adrenoceptor antagonist ICI 118,551, noradrenaline and isoprenaline produced biphasic concentration-effect curves. In parenchymal lung strips only the one subtype was involved as antagonist pA2 values were not dependent on the agonist used and the properties were consistent with those expected for a beta 2-adrenoceptor.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ainsworth G. A., Garland L. G., Payne A. N. Modulation of bronchoconstrictor responses to histamine in pithed guinea-pigs by sympathetic nerve stimulation. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Oct;77(2):249–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09293.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. J., Basbaum C. B., Nadel J. A., Roberts J. M. Localization of beta-adrenoreceptors in mammalian lung by light microscopic autoradiography. Nature. 1982 Sep 30;299(5882):444–447. doi: 10.1038/299444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. M. The pharmacology of atenolol. Postgrad Med J. 1977;53 (Suppl 3):58–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell H., Nahorski S. R. Distribution and characteristics of histamine H1-receptors in guinea-pig airways identified by [3H]mepyramine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jul 9;81(2):301–307. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90448-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Wiley K. S. Beta1 and beta2 receptor mechanisms in rat jugular veins: differences between norepinephrine and isoproterenol-induced relaxation. Life Sci. 1978 Nov 13;23(20):1997–2006. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90231-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLean A., Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Simultaneous analysis of families of sigmoidal curves: application to bioassay, radioligand assay, and physiological dose-response curves. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E97–102. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson K., Richardson A., Nahorski S. R. Homogeneity of beta 2-adrenoceptors on rat erythrocytes and reticulocytes. A comparison with heterogeneous rat lung beta-adrenoceptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 Mar;19(2):194–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedberg A., Minneman K. P., Molinoff P. B. Differential distribution of beta-1 and beta-2 adrenergic receptors in cat and guinea-pig heart. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Mar;212(3):503–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapanci Y., Assimacopoulos A., Irle C., Zwahlen A., Gabbiani G. "Contractile interstitial cells" in pulmonary alveolar septa: a possible regulator of ventilation-perfusion ratio? Ultrastructural, immunofluorescence, and in vitro studies. J Cell Biol. 1974 Feb;60(2):375–392. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lands A. M., Arnold A., McAuliff J. P., Luduena F. P., Brown T. G., Jr Differentiation of receptor systems activated by sympathomimetic amines. Nature. 1967 May 6;214(5088):597–598. doi: 10.1038/214597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lulich K. M., Mitchell H. W., Sparrow M. P. The cat lung strip as an in vitro preparation of peripheral airways: a comparison of beta-adrenoceptor agonists, autacoids and anaphylactic challenge on the lung strip and trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Sep;58(1):71–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb07694.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahorski S. R., Richardson A. Pitfalls in the assessment of the specific binding of(-)[3H]-dihydroalprenolol to beta-adrenoceptors [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;66(3):469P–470P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell S. R., Saar N., Wood L. J. Tne density of adrenergic nerves at various levels in the guinea-pig lung. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1978 Jul-Aug;5(4):325–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1978.tb00681.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell S. R., Wanstall J. C. The importance of choice of agonist in studies designed to predict beta 2 : beta 1 adrenoceptor selectivity of antagonists from pA2 values on guinea-pig trachea and atria. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Sep;308(3):183–190. doi: 10.1007/BF00501381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rugg E. L., Barnett D. B., Nahorski S. R. Coexistence of beta1 and beta2 adrenoceptors in mammalian lung: evidence from direct binding studies. Mol Pharmacol. 1978 Nov;14(6):996–1005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN ROSSUM J. M. Cumulative dose-response curves. II. Technique for the making of dose-response curves in isolated organs and the evaluation of drug parameters. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1963;143:299–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varma D. R., Nickerson M. Beta-adrenoreceptors of the cat nictitating membrane. J Auton Pharmacol. 1981 Sep;1(4):291–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1981.tb00458.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


