Abstract
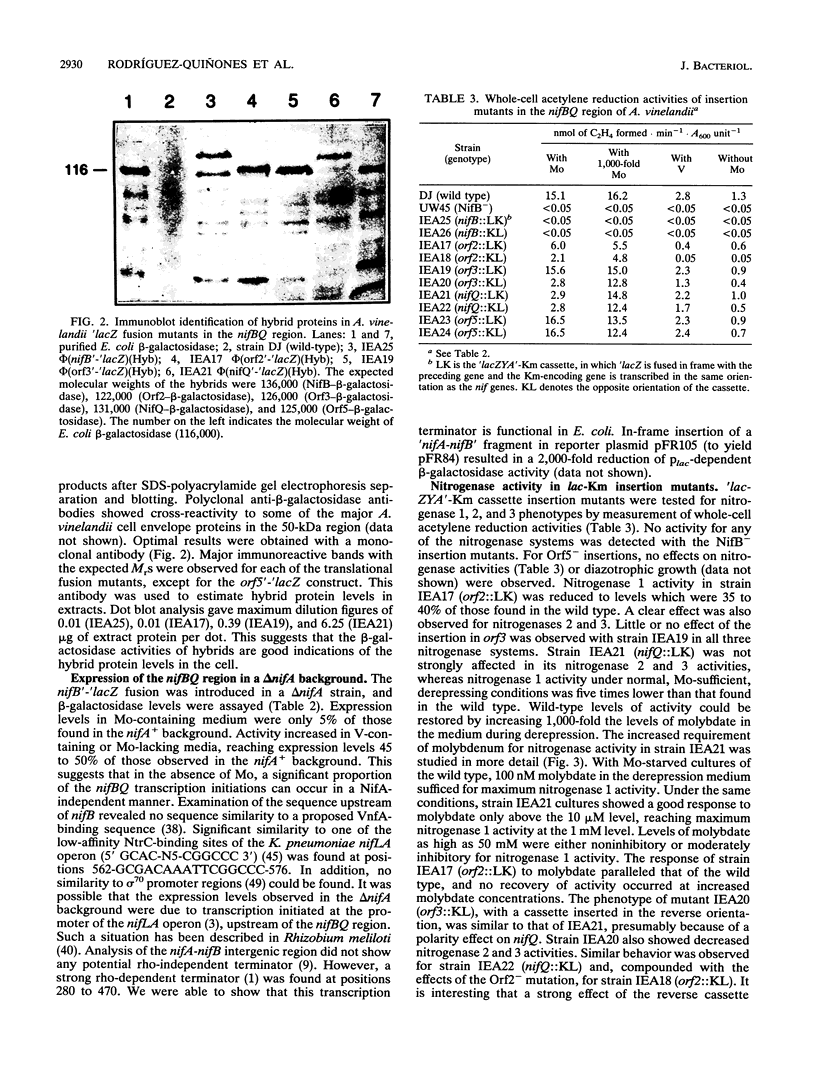
The nifBQ transcriptional unit of Azotobacter vinelandii has been previously shown to be required for activity of the three nitrogenase systems, Mo nitrogenase, V nitrogenase, and Fe nitrogenase, present in this organism. We studied regulation of expression and the role of the nifBQ region by means of translational beta-galactosidase fusions to each of the five open reading frames: nifB, orf2 (fdxN), orf3 (nifO), nifQ, and orf5. Expression of the first three open reading frames was observed under all three diazotrophic conditions; expression of orf5 was never observed. Genes nifB and fdxN were expressed at similar levels. With Mo, expression of nifO and nifQ was approximately 20- and approximately 400-fold lower than that of fdxN, respectively. Without Mo, expression of nifB dropped three- to fourfold and that of nifQ dropped to the detection limit. However, expression of nifO increased threefold. The products of nifB, fdxN, nifO, and nifQ have been visualized in A. vinelandii as beta-galactosidase fusion proteins with the expected molecular masses. The NifB- fusion lacked activity for any of the three nitrogenase systems and showed an iron-molybdenum cofactor-deficient phenotype in the presence of Mo. The FdxN- mutation resulted in reduced nitrogenase activities, especially when V was present. Dinitrogenase activity in extracts was similarly affected, suggesting a role of FdxN in iron-molybdenum cofactor synthesis. The NifO(-)-producing mutation did not affect any of the nitrogenases under standard diazotrophic conditions. The NifQ(-)-producing mutation resulted in an increased (approximately 1,000-fold) Mo requirement for Mo nitrogenase activity, a phenotype already observed with Klebsiella pneumoniae. No effect of the NifQ(-)-producing mutation on V or Fe nitrogenase was found; this is consistent with its very low expression under those conditions. Mutations in orf5 had no effect on nitrogenase activity.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alifano P., Rivellini F., Limauro D., Bruni C. B., Carlomagno M. S. A consensus motif common to all Rho-dependent prokaryotic transcription terminators. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):553–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90239-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold W., Rump A., Klipp W., Priefer U. B., Pühler A. Nucleotide sequence of a 24,206-base-pair DNA fragment carrying the entire nitrogen fixation gene cluster of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):715–738. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bali A., Blanco G., Hill S., Kennedy C. Excretion of ammonium by a nifL mutant of Azotobacter vinelandii fixing nitrogen. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 May;58(5):1711–1718. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.5.1711-1718.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett L. T., Cannon F., Dean D. R. Nucleotide sequence and mutagenesis of the nifA gene from Azotobacter vinelandii. Mol Microbiol. 1988 May;2(3):315–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. E., Jarlenski D. M., Hetherington D. R. Evidence for an alternative nitrogen fixation system in Azotobacter vinelandii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7342–7346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. E., Premakumar R., Dean D. R., Jacobson M. R., Chisnell J. R., Rizzo T. M., Kopczynski J. Nitrogen Fixation by Azotobacter vinelandii Strains Having Deletions in Structural Genes for Nitrogenase. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):92–94. doi: 10.1126/science.232.4746.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brendel V., Hamm G. H., Trifonov E. N. Terminators of transcription with RNA polymerase from Escherichia coli: what they look like and how to find them. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1986 Feb;3(4):705–723. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1986.10508457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brigle K. E., Newton W. E., Dean D. R. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Azotobacter vinelandii nitrogenase structural gene cluster. Gene. 1985;37(1-3):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90255-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill W. J., Steiner A. L., Shah V. K. Effect of molybdenum starvation and tungsten on the synthesis of nitrogenase components in Klebsiella pneumonia. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):986–989. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.986-989.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buikema W. J., Klingensmith J. A., Gibbons S. L., Ausubel F. M. Conservation of structure and location of Rhizobium meliloti and Klebsiella pneumoniae nifB genes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1120–1126. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1120-1126.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Martinez-Arias A., Shapira S. K., Chou J. Beta-galactosidase gene fusions for analyzing gene expression in escherichia coli and yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:293–308. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisnell J. R., Premakumar R., Bishop P. E. Purification of a second alternative nitrogenase from a nifHDK deletion strain of Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):27–33. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.27-33.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE WITT C. W., ROWE J. A. N,O-Diacetylneuraminic acid and N-acetylneuraminic acid in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1959 Aug 1;184(Suppl 6):381–382. doi: 10.1038/184381b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhaese P., De Greve H., Decraemer H., Schell J., Van Montagu M. Rapid mapping of transposon insertion and deletion mutations in the large Ti-plasmids of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):1837–1849. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.1837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebeling S., Noti J. D., Hennecke H. Identification of a new Bradyrhizobium japonicum gene (frxA) encoding a ferredoxinlike protein. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1999–2001. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1999-2001.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jones R., Woodley P. R., Wilborn J. R., Robson R. L. Nucleotide sequence and genetic analysis of the Azotobacter chroococcum nifUSVWZM gene cluster, including a new gene (nifP) which encodes a serine acetyltransferase. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(17):5457–5469. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.17.5457-5469.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filler W. A., Kemp R. M., Ng J. C., Hawkes T. R., Dixon R. A., Smith B. E. The nifH gene product is required for the synthesis or stability of the iron-molybdenum cofactor of nitrogenase from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 15;160(2):371–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09981.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales B. J., Case E. E., Morningstar J. E., Dzeda M. F., Mauterer L. A. Isolation of a new vanadium-containing nitrogenase from Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7251–7255. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes T. R., McLean P. A., Smith B. E. Nitrogenase from nifV mutants of Klebsiella pneumoniae contains an altered form of the iron-molybdenum cofactor. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 1;217(1):317–321. doi: 10.1042/bj2170317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover T. R., Imperial J., Liang J. H., Ludden P. W., Shah V. K. Dinitrogenase with altered substrate specificity results from the use of homocitrate analogues for in vitro synthesis of the iron-molybdenum cofactor. Biochemistry. 1988 May 17;27(10):3647–3652. doi: 10.1021/bi00410a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover T. R., Imperial J., Ludden P. W., Shah V. K. Biosynthesis of the iron-molybdenum cofactor of nitrogenase. Biofactors. 1988 Oct;1(3):199–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover T. R., Imperial J., Ludden P. W., Shah V. K. Homocitrate cures the NifV- phenotype in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1978–1979. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1978-1979.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover T. R., Imperial J., Ludden P. W., Shah V. K. Homocitrate is a component of the iron-molybdenum cofactor of nitrogenase. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 4;28(7):2768–2771. doi: 10.1021/bi00433a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperial J., Hoover T. R., Madden M. S., Ludden P. W., Shah V. K. Substrate reduction properties of dinitrogenase activated in vitro are dependent upon the presence of homocitrate or its analogues during iron-molybdenum cofactor synthesis. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 19;28(19):7796–7799. doi: 10.1021/bi00445a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperial J., Ugalde R. A., Shah V. K., Brill W. J. Role of the nifQ gene product in the incorporation of molybdenum into nitrogenase in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):187–194. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.187-194.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
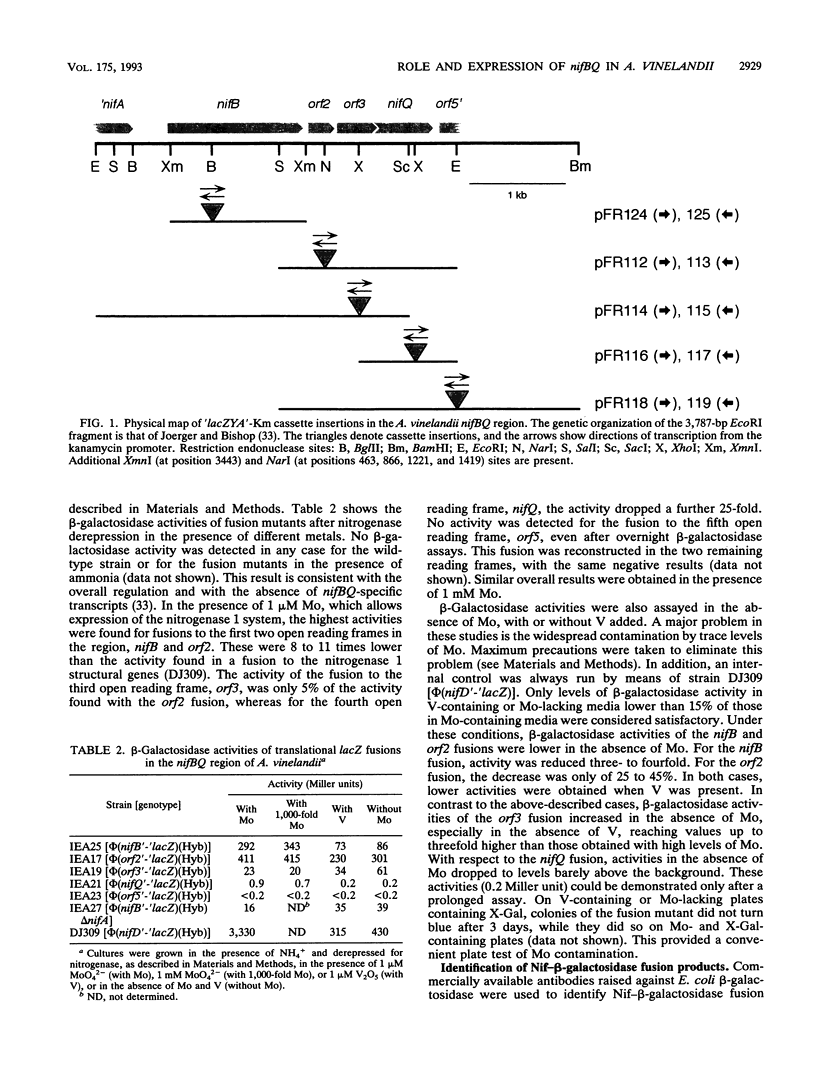
- Jacobson M. R., Brigle K. E., Bennett L. T., Setterquist R. A., Wilson M. S., Cash V. L., Beynon J., Newton W. E., Dean D. R. Physical and genetic map of the major nif gene cluster from Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):1017–1027. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.1017-1027.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joerger R. D., Bishop P. E. Nucleotide sequence and genetic analysis of the nifB-nifQ region from Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1475–1487. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1475-1487.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joerger R. D., Jacobson M. R., Premakumar R., Wolfinger E. D., Bishop P. E. Nucleotide sequence and mutational analysis of the structural genes (anfHDGK) for the second alternative nitrogenase from Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):1075–1086. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.1075-1086.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joerger R. D., Loveless T. M., Pau R. N., Mitchenall L. A., Simon B. H., Bishop P. E. Nucleotide sequences and mutational analysis of the structural genes for nitrogenase 2 of Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3400–3408. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3400-3408.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joerger R. D., Premakumar R., Bishop P. E. Tn5-induced mutants of Azotobacter vinelandii affected in nitrogen fixation under Mo-deficient and Mo-sufficient conditions. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):673–682. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.673-682.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy C., Dean D. The nifU, nifS and nifV gene products are required for activity of all three nitrogenases of Azotobacter vinelandii. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Feb;231(3):494–498. doi: 10.1007/BF00292722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipp W., Reiländer H., Schlüter A., Krey R., Pühler A. The Rhizobium meliloti fdxN gene encoding a ferredoxin-like protein is necessary for nitrogen fixation and is cotranscribed with nifA and nifB. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Apr;216(2-3):293–302. doi: 10.1007/BF00334368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreutzer R., Dayananda S., Klingmüller W. Cotranscription of the electron transport protein genes nifJ and nifF in Enterobacter agglomerans 333. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(10):3252–3256. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.10.3252-3256.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luque F., Pau R. N. Transcriptional regulation by metals of structural genes for Azotobacter vinelandii nitrogenases. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Jul;227(3):481–487. doi: 10.1007/BF00273941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNeil T., MacNeil D., Roberts G. P., Supiano M. A., Brill W. J. Fine-structure mapping and complementation analysis of nif (nitrogen fixation) genes in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):253–266. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.253-266.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden M. S., Kindon N. D., Ludden P. W., Shah V. K. Diastereomer-dependent substrate reduction properties of a dinitrogenase containing 1-fluorohomocitrate in the iron-molybdenum cofactor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6517–6521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minchin S. D., Austin S., Dixon R. A. The role of activator binding sites in transcriptional control of the divergently transcribed nifF and nifLA promoters from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Jul;2(4):433–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00049.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Vivian C., Hennecke S., Pühler A., Klipp W. Open reading frame 5 (ORF5), encoding a ferredoxinlike protein, and nifQ are cotranscribed with nifE, nifN, nifX, and ORF4 in Rhodobacter capsulatus. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2591–2598. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2591-2598.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan T. V., Lundell D. J., Burgess B. K. Azotobacter vinelandii ferredoxin I: cloning, sequencing, and mutant analysis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1370–1375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Buikema W. J., Haselkorn R. Bacterial-type ferredoxin genes in the nitrogen fixation regions of the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 and Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4406–4410. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4406-4410.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Hawley D. K., Entriken R., McClure W. R. Escherichia coli promoter sequences predict in vitro RNA polymerase selectivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):789–800. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page W. J., von Tigerstrom M. Induction of transformation competence in Azotobacter vinelandii iron-limited cultures. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Dec;24(12):1590–1594. doi: 10.1139/m78-254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page W. J., von Tigerstrom M. Optimal conditions for transformation of Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):1058–1061. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.1058-1061.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paustian T. D., Shah V. K., Roberts G. P. Apodinitrogenase: purification, association with a 20-kilodalton protein, and activation by the iron-molybdenum cofactor in the absence of dinitrogenase reductase. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 10;29(14):3515–3522. doi: 10.1021/bi00466a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. P., Brill W. J. Gene-product relationships of the nif regulon of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):210–216. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.210-216.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. P., MacNeil T., MacNeil D., Brill W. J. Regulation and characterization of protein products coded by the nif (nitrogen fixation) genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):267–279. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.267-279.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. C., Dean D. R., Burgess B. K. Iron-molybdenum cofactor biosynthesis in Azotobacter vinelandii requires the iron protein of nitrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14327–14332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen B. P., Weigel U., Monticello R. A., Edwards B. P. Molecular analysis of an anion pump: purification of the ArsC protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Feb 1;284(2):381–385. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90312-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider K., Müller A., Johannes K. U., Diemann E., Kottmann J. Selective removal of molybdenum traces from growth media of N2-fixing bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1991 Mar 2;193(2):292–298. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90024-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Brill W. J. Isolation of an iron-molybdenum cofactor from nitrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3249–3253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Davis I. C., Gordon J. K., Orme-Johnson W. H., Brill W. J. Nitrogenase. 3. Nitrogenaseless mutants of Azotobacter vinelandii: activities, cross-reactions and EPR spectra. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 18;292(1):246–255. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Imperial J., Ugalde R. A., Ludden P. W., Brill W. J. In vitro synthesis of the iron-molybdenum cofactor of nitrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1636–1640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silhavy T. J., Beckwith J. R. Uses of lac fusions for the study of biological problems. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Dec;49(4):398–418. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.4.398-418.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. E., Eady R. R., Lowe D. J., Gormal C. The vanadium-iron protein of vanadium nitrogenase from Azotobacter chroococcum contains an iron-vanadium cofactor. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 15;250(1):299–302. doi: 10.1042/bj2500299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandberg G. W., Wilson P. W. Formation of the nitrogen-fixing enzyme system in Azotobacter vinelandii. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Jan;14(1):25–31. doi: 10.1139/m68-005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiedeman A. A., Smith J. M. lacZY gene fusion cassettes with KanR resistance. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3587–3587. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfinger E. D., Bishop P. E. Nucleotide sequence and mutational analysis of the vnfENX region of Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7565–7572. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7565-7572.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




