Full text
PDF

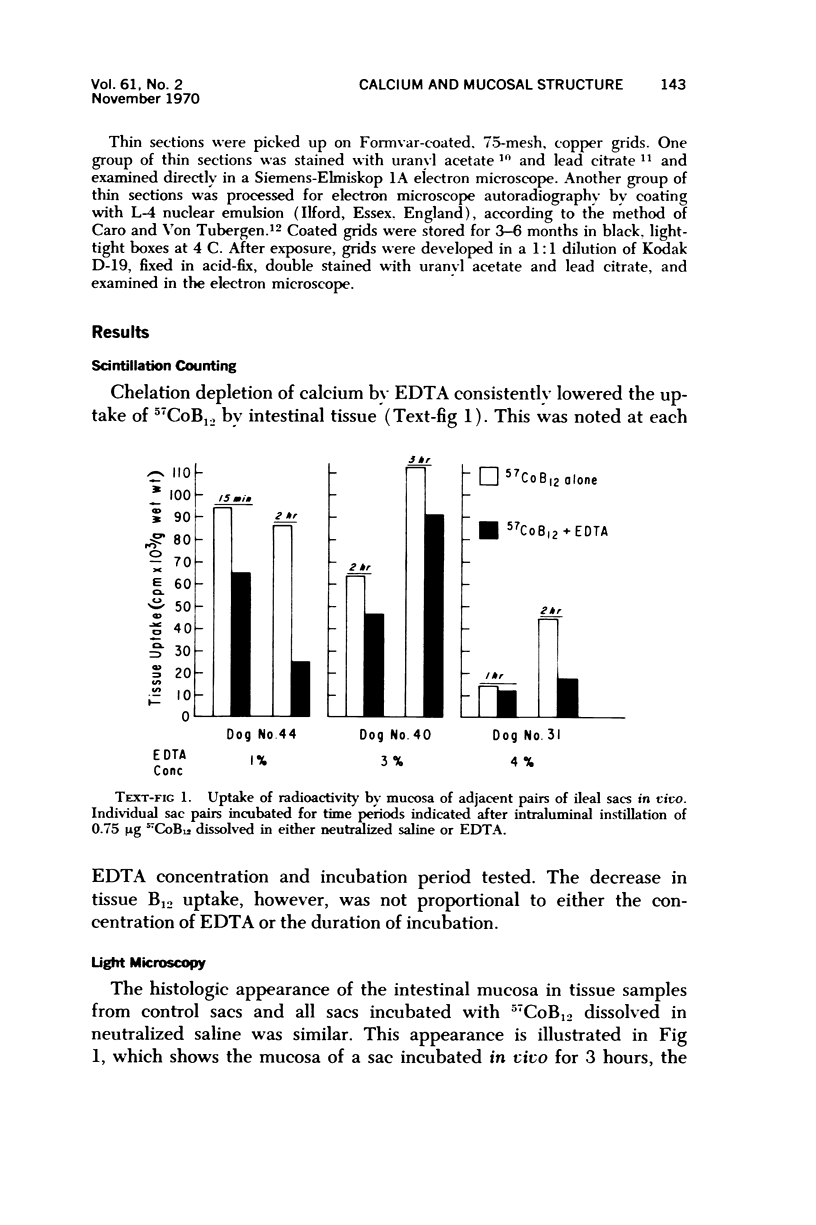







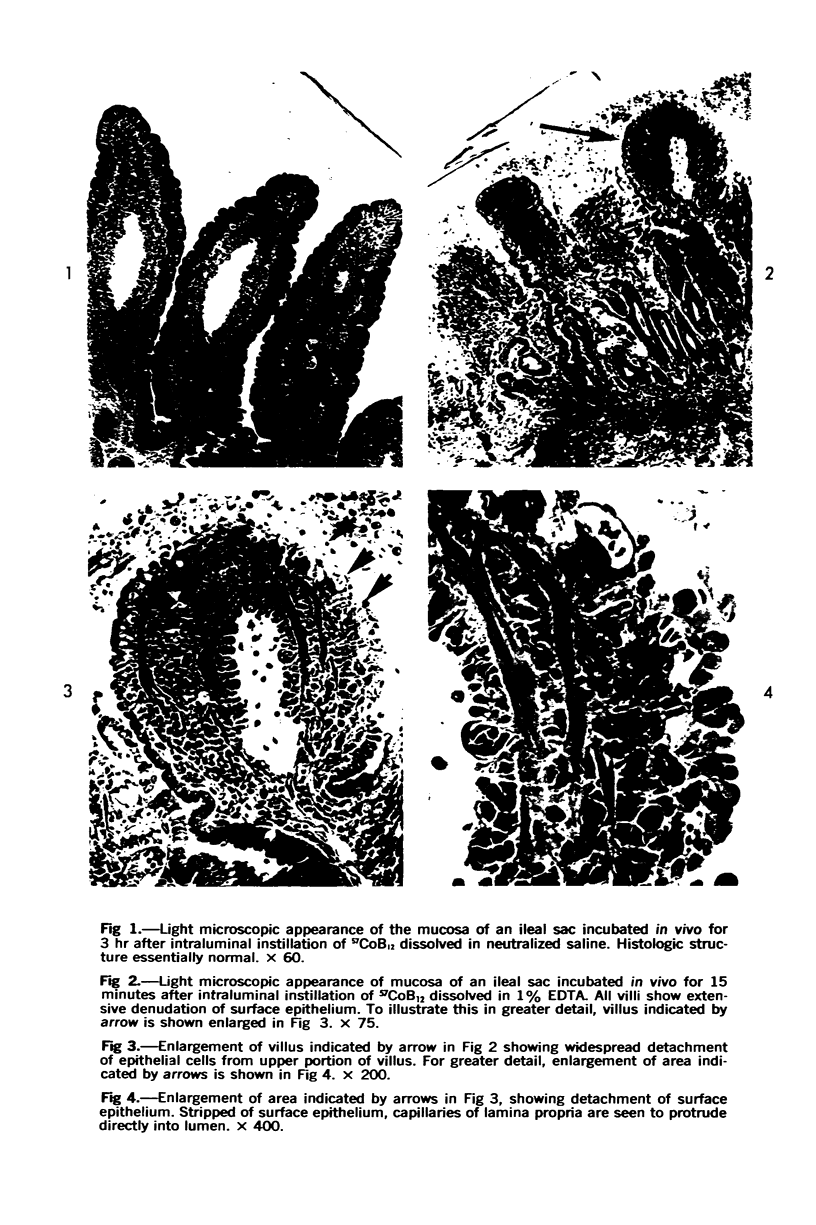
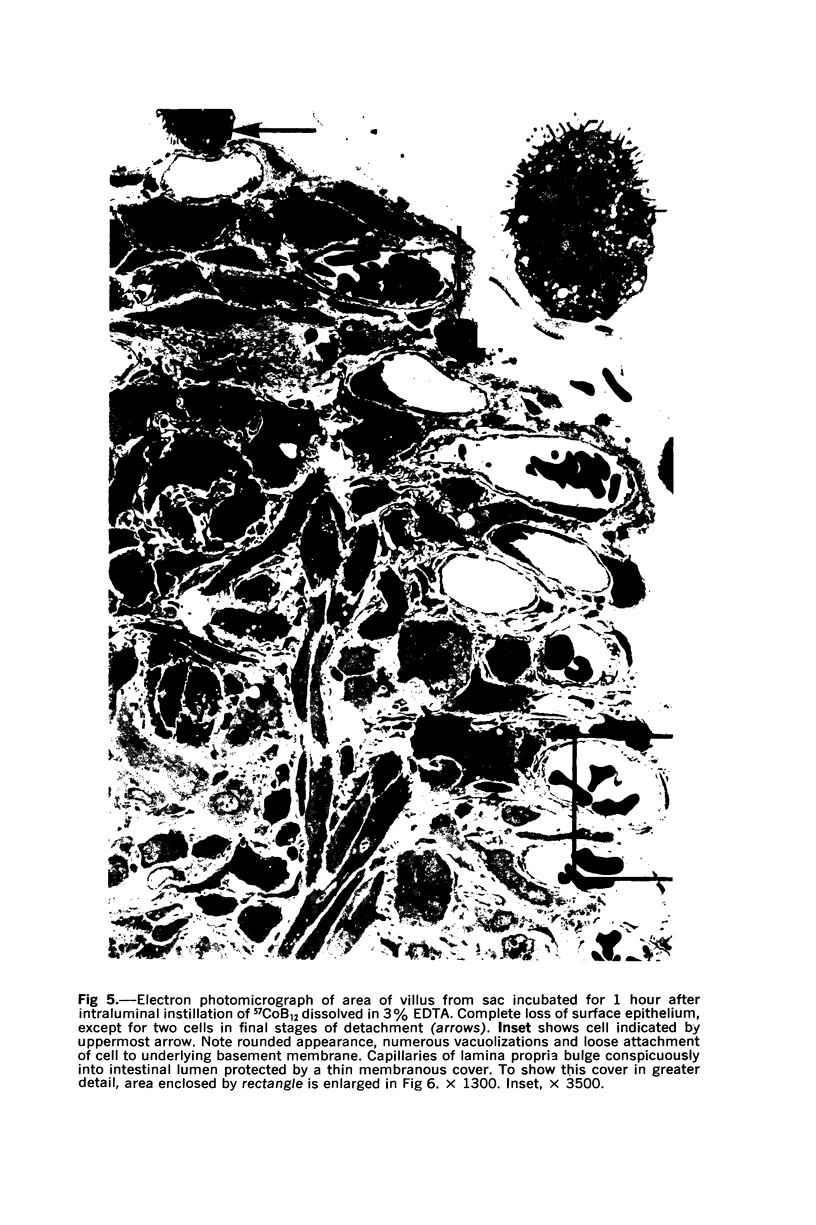

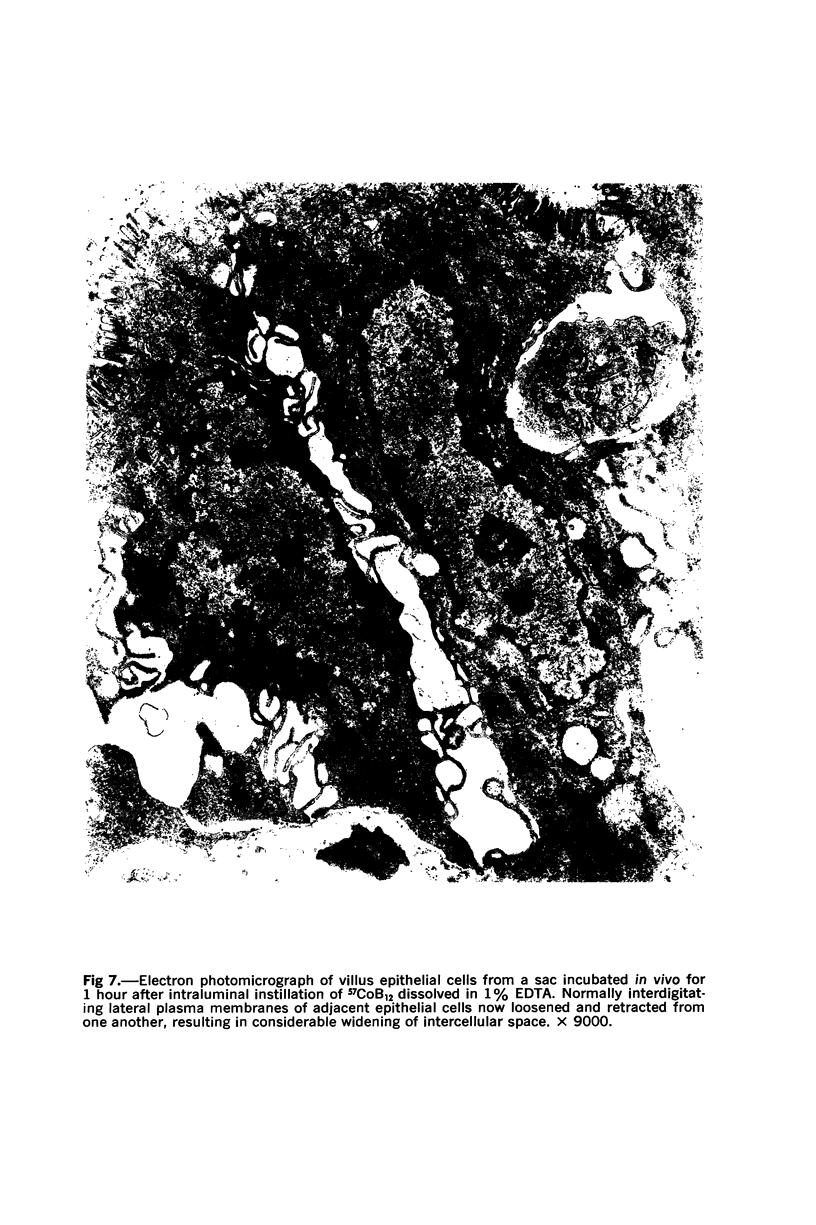
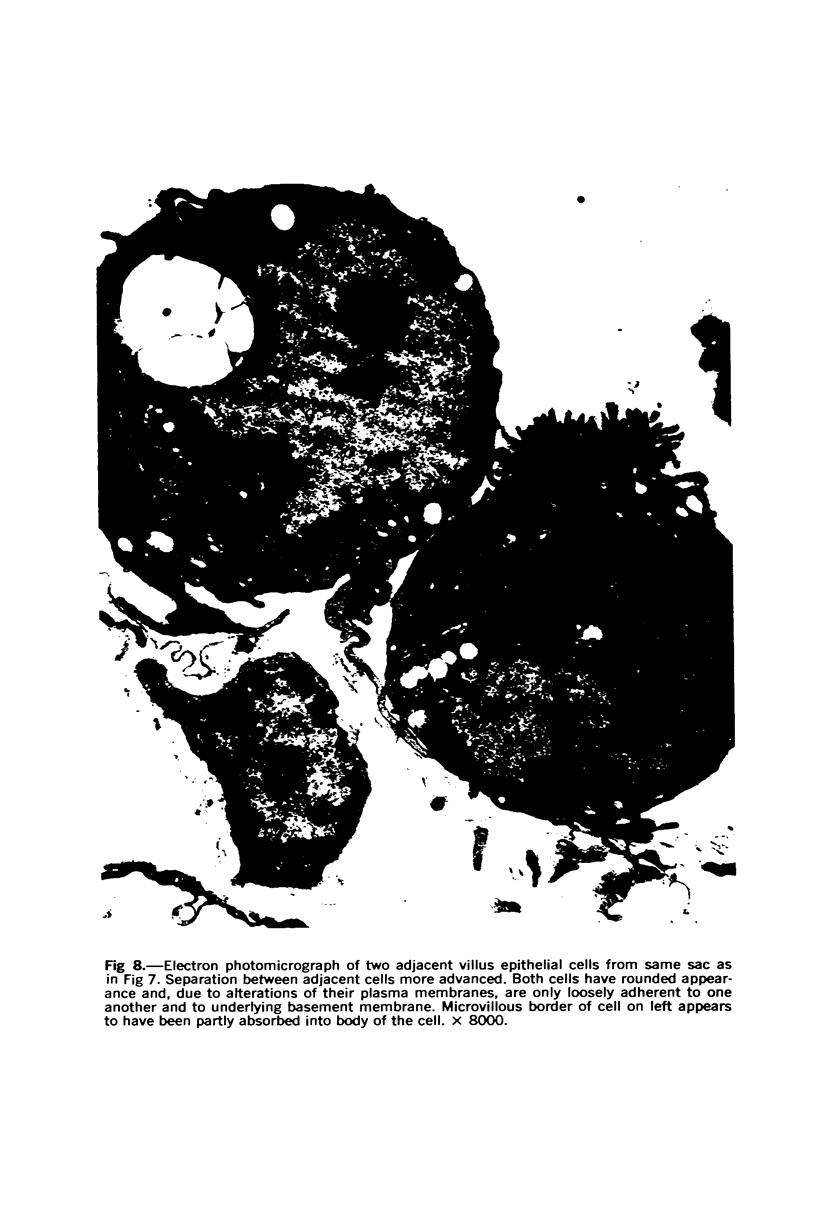
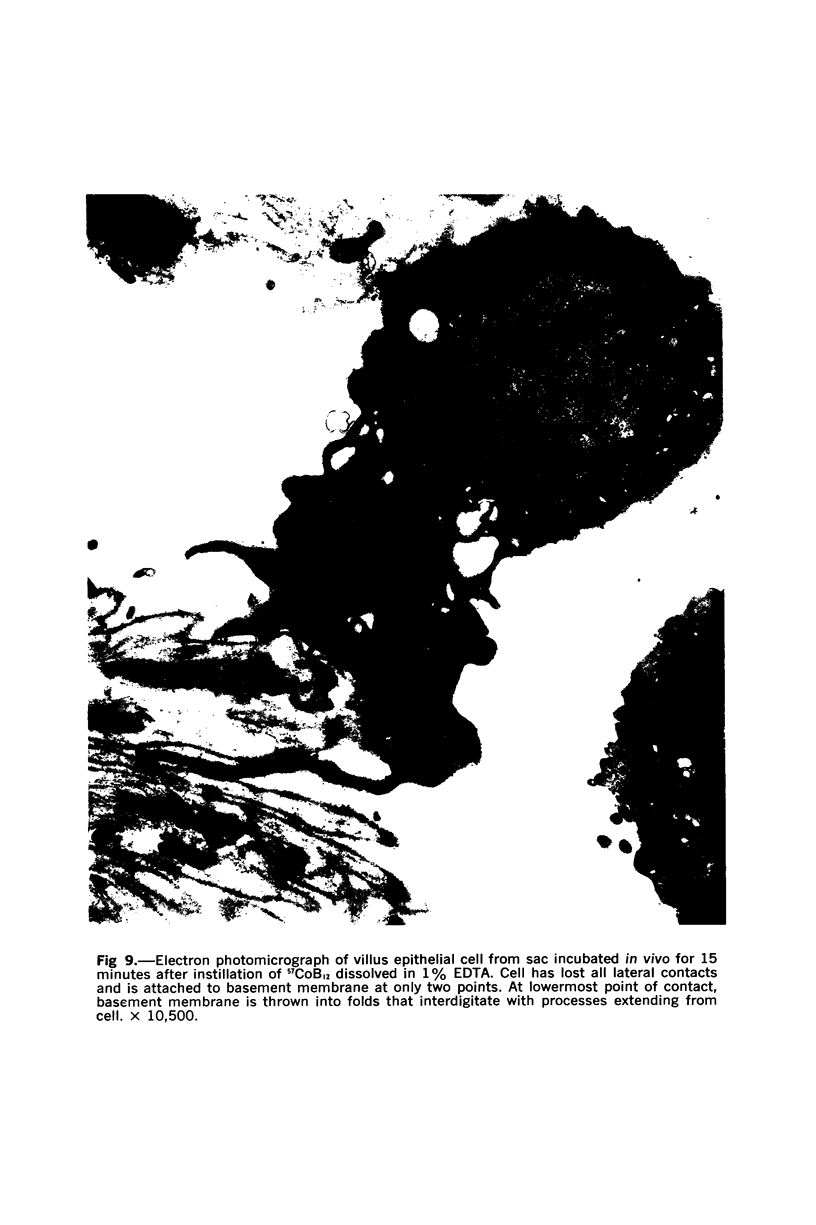
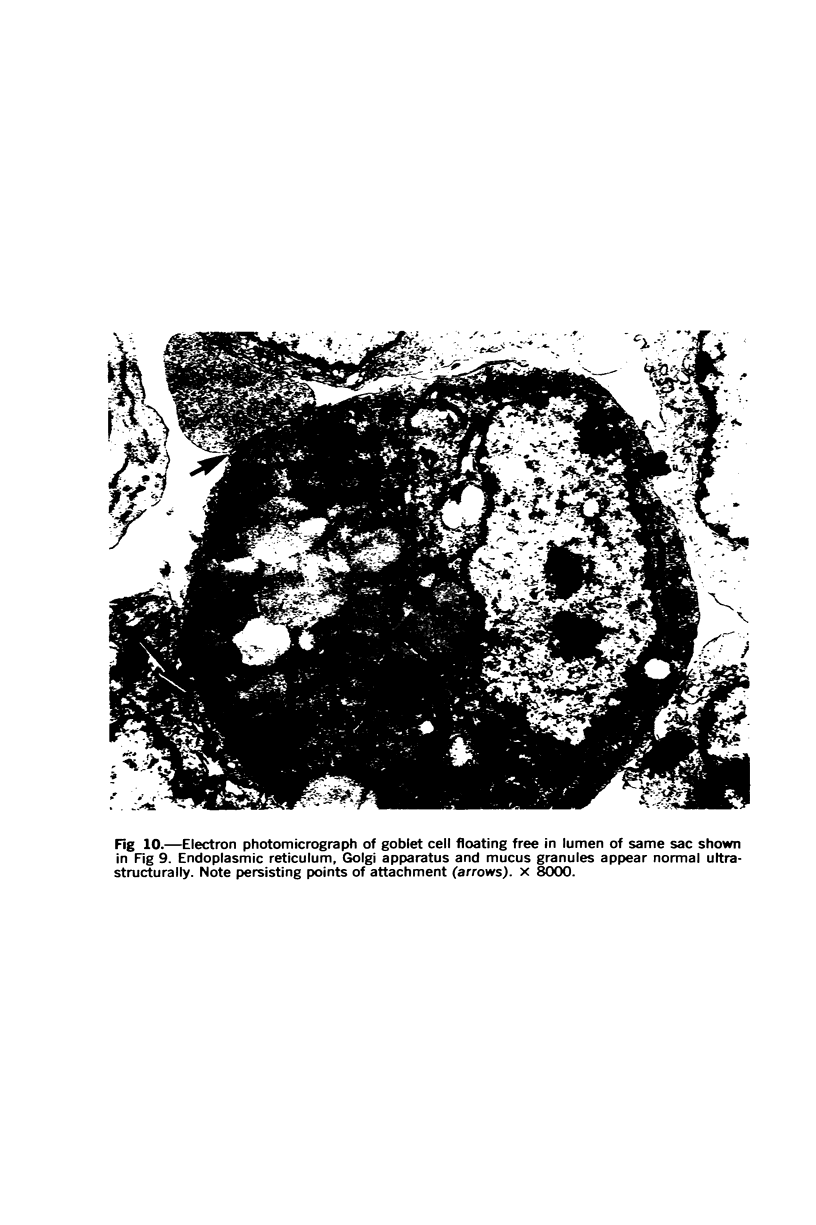
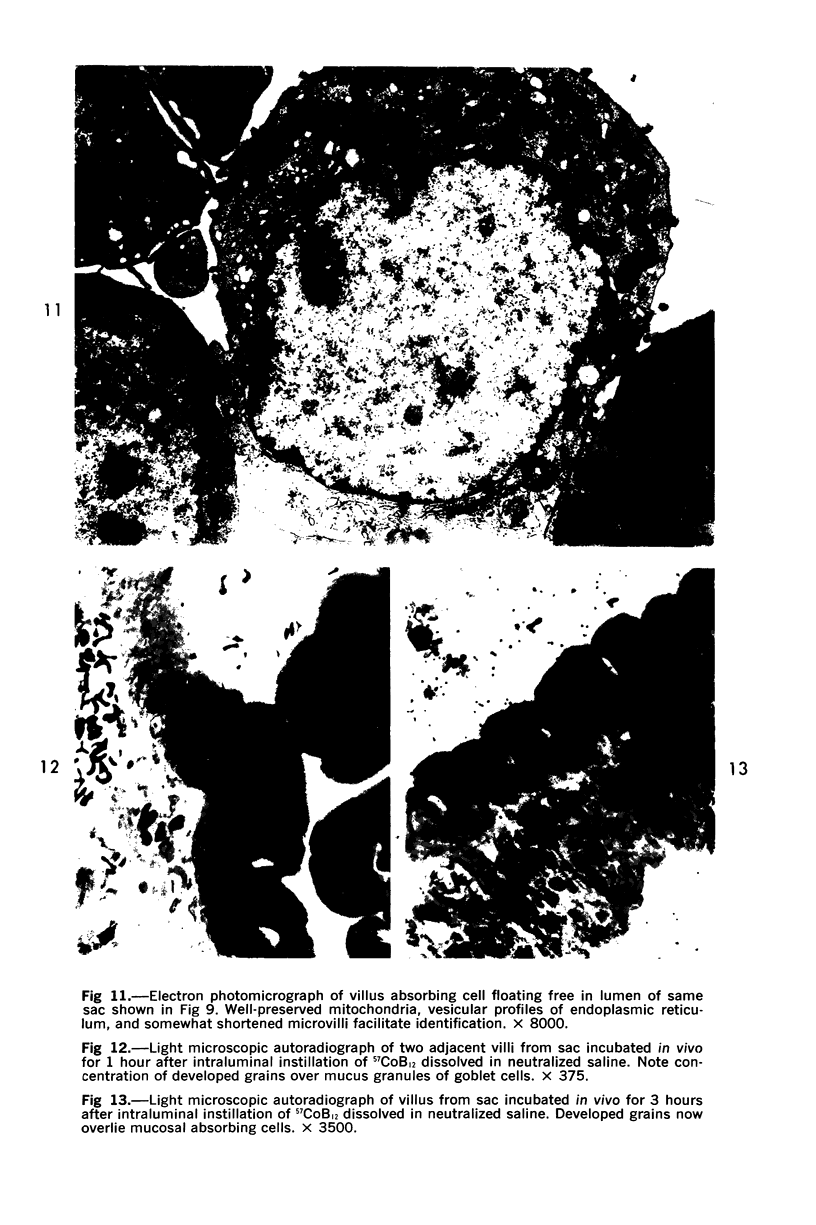
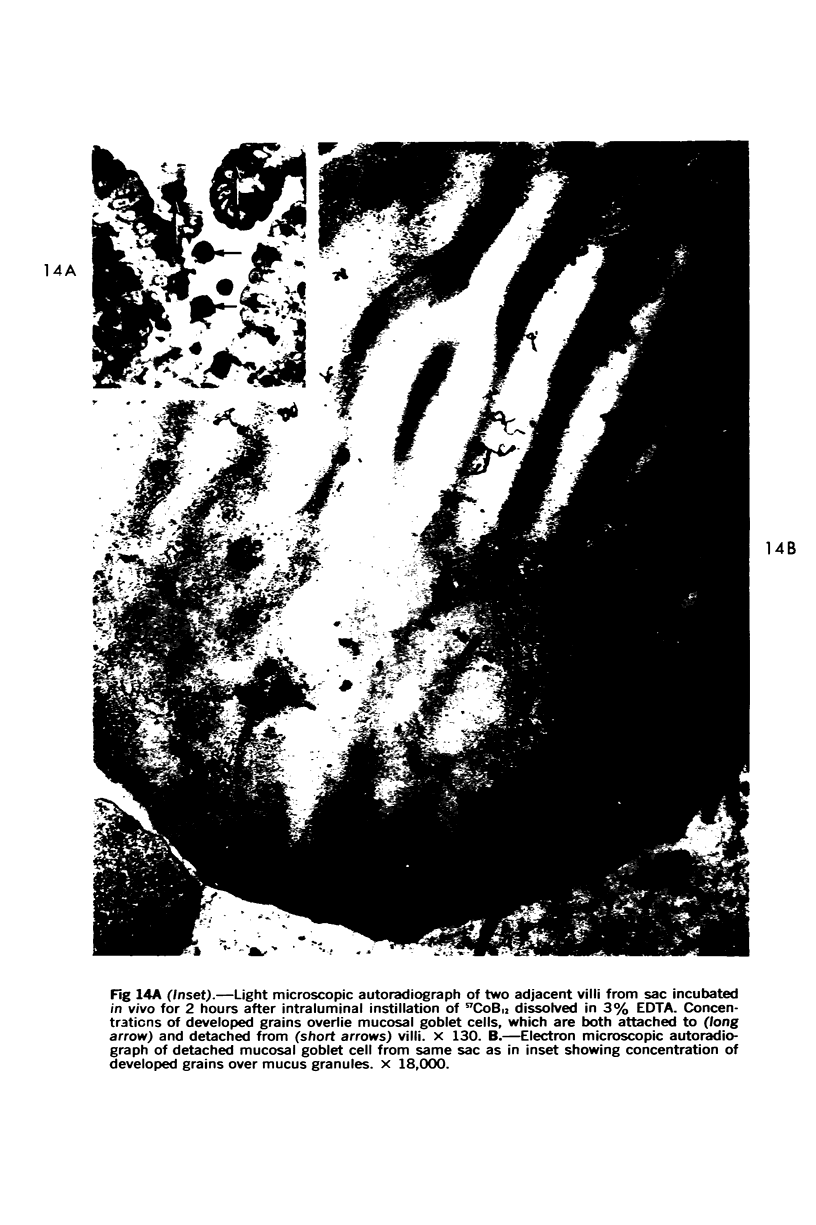
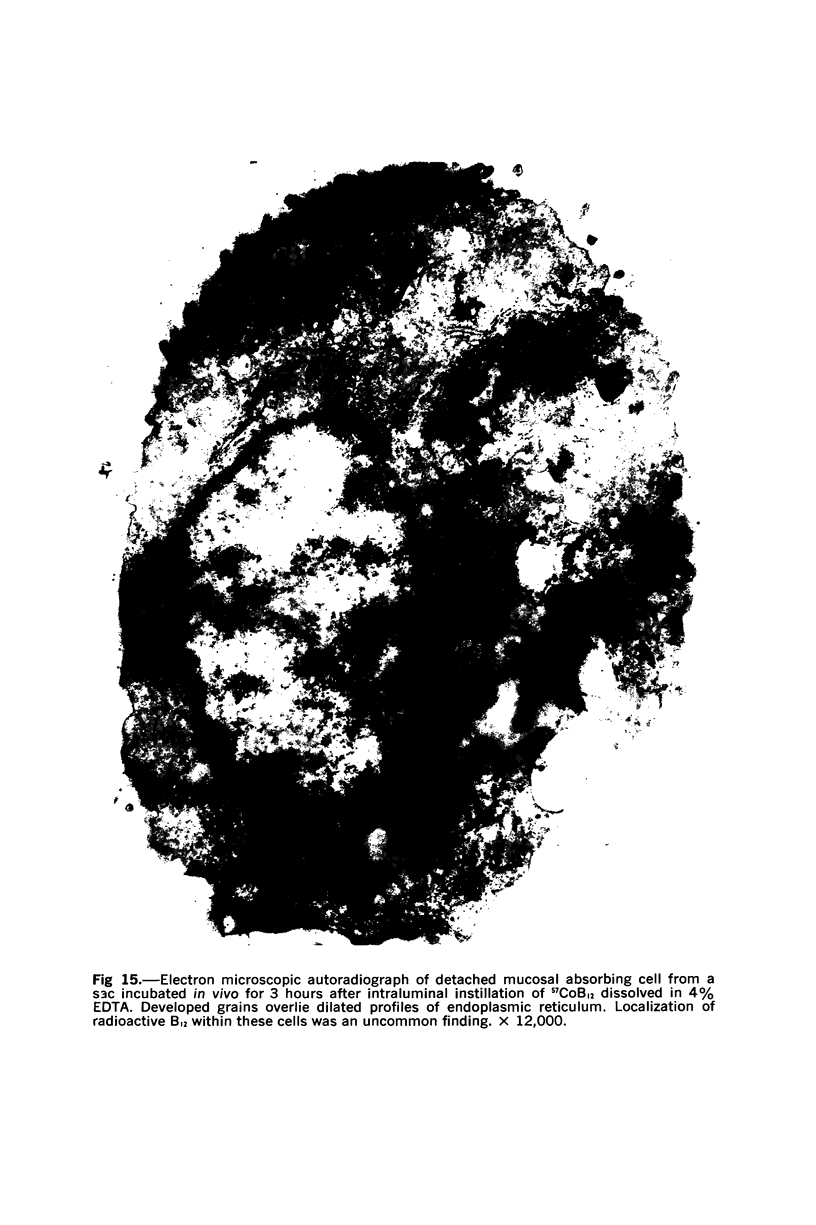
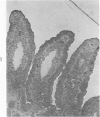
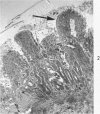
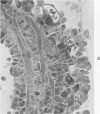
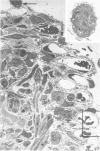
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CARO L. G., VAN TUBERGEN R. P., KOLB J. A. High-resolution autoradiography. I. Methods. J Cell Biol. 1962 Nov;15:173–188. doi: 10.1083/jcb.15.2.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHERNICK W. S., BARBERO G. J. Studies on human tracheobronchial and submaxillary secretions in normal and pathophysiological conditions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Mar 30;106:698–708. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb16678.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER B. A., CASTLE W. B. Sequential mechanisms in the enhanced absorption of vitamin B12 by intrinsic factor in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jan;39:199–214. doi: 10.1172/JCI104019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER B. A., PARANCHYCH W., LOWENSTEIN L. Studies on the absorption by guinea pig intestine of cyanocobalamin incubated with intrinsic factor. J Clin Invest. 1962 Feb;41:370–377. doi: 10.1172/JCI104491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmel R., Rosenberg A. H., Lau K. S., Streiff R. R., Herbert V. Vitamin B12 uptake by human small bowel homogenate and its enhancement by intrinsic factor. Gastroenterology. 1969 Mar;56(3):548–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy M. M., Tidball C. S. Cellular mechanism of intestinal permeability alterations produced by chelation depletion. J Cell Biol. 1967 Mar;32(3):685–698. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.3.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson R. M., Jr, Mackenzie I. L., Trier J. S. Intrinsic factor-mediated attachment of vitamin B12 to brush borders and microvillous membranes of hamster intestine. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jul;46(7):1215–1228. doi: 10.1172/JCI105615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dybing E., Nafstad P. H., Sognen E. The ultrastructure of free intestinal cells isolated with EDTA. Acta Vet Scand. 1969;10(3):219–224. doi: 10.1186/BF03548274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott R. L., Barnett W. O., Elliott M. C. An ultrastructural study of the small intestine after total vagotomy. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1967 May;124(5):1037–1042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLASS G. B. GASTRIC INTRINSIC FACTOR AND ITS FUNCTION IN THE METABOLISM OF VITAMIN B12. Physiol Rev. 1963 Oct;43:529–849. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1963.43.4.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRASBECK R., NYBERG W. Inhibition of radiovitamin B12 absorption by ethylenediaminetetraacetate (EDTA) and its reversal by calcium ions. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1958;10(4):448–448. doi: 10.3109/00365515809051257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERBERT V., CASTLE W. B. Divalent cation and pH dependence of rat intrinsic factor action in everted sacs and mucosal homogenates of rat small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1961 Nov;40:1978–1983. doi: 10.1172/JCI104423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERBERT V. Mechanism of intrinsic factor action in everted sacs of rat small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jan 1;38(1 Pt 1):102–109. doi: 10.1172/JCI103779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERBERT V. Studies on the role of intrinsic factor in vitamin B12 absorption, transport, and storage. Am J Clin Nutr. 1959 Jul-Aug;7:433–443. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/7.4.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hays R. M., Singer B., Malamed S. The effect of calcium withdrawal on the structure and function of the toad bladder. J Cell Biol. 1965 Jun;25(3 Suppl):195–208. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.3.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V. Absorption of vitamin B12 and folic acid. Gastroenterology. 1968 Jan;54(1):110–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLONIG G. A modified procedure for lead staining of thin sections. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Dec;11:736–739. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.3.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKUDA K. Vitamin B12 absorption in rats, studied by a 'loop' technique. Am J Physiol. 1960 Jul;199:84–90. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.199.1.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda K., Sasayama K. Effects of ethylenediaminetetraacetate and metal ions in intestinal absorption of vitamin B 12 in man and rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Oct;120(1):17–20. doi: 10.3181/00379727-120-30431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEACHEY L. D. Thin sections. I. A study of section thickness and physical distortion produced during microtomy. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 May 25;4(3):233–242. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.3.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABATINI D. D., BENSCH K., BARRNETT R. J. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:19–58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEMPAK J. G., WARD R. T. AN IMPROVED STAINING METHOD FOR ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1964 Sep;22:697–701. doi: 10.1083/jcb.22.3.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisberg H., Rhodin J., Glass G. B. Intestinal vitamin B12 absorption in the dog. 3. Demonstration of the intracellular pathway of absorption by light and electron microscope autoradiography. Lab Invest. 1968 Nov;19(5):516–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi N., Weisberg H., Glass G. B. Intestinal vitamin B 12 absorption in the dog. I. Evidence against an intrinsic factor mechanism for vitamin B 12 absorption. Gastroenterology. 1969 May;56(5):914–924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]