Abstract
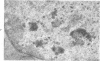
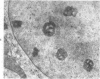
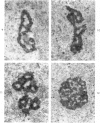
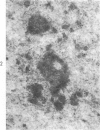
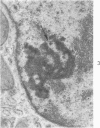
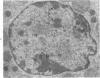
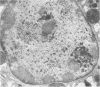
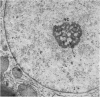
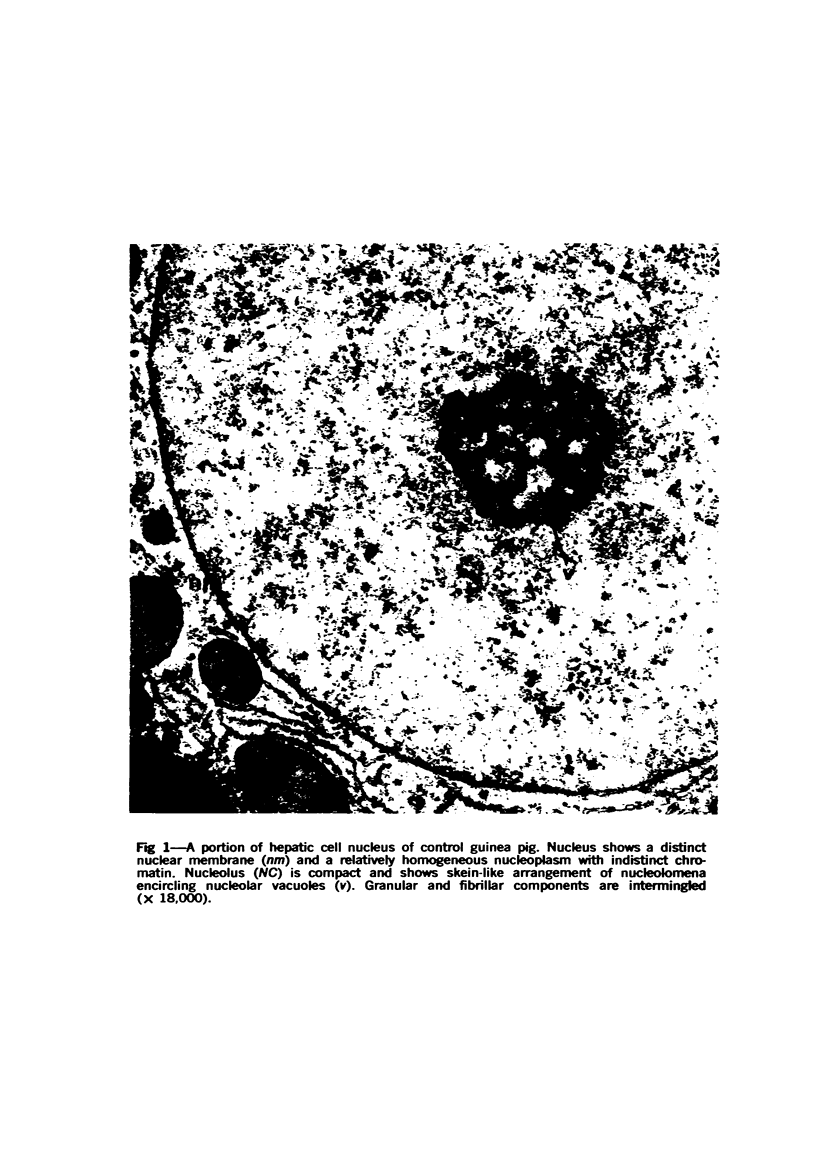
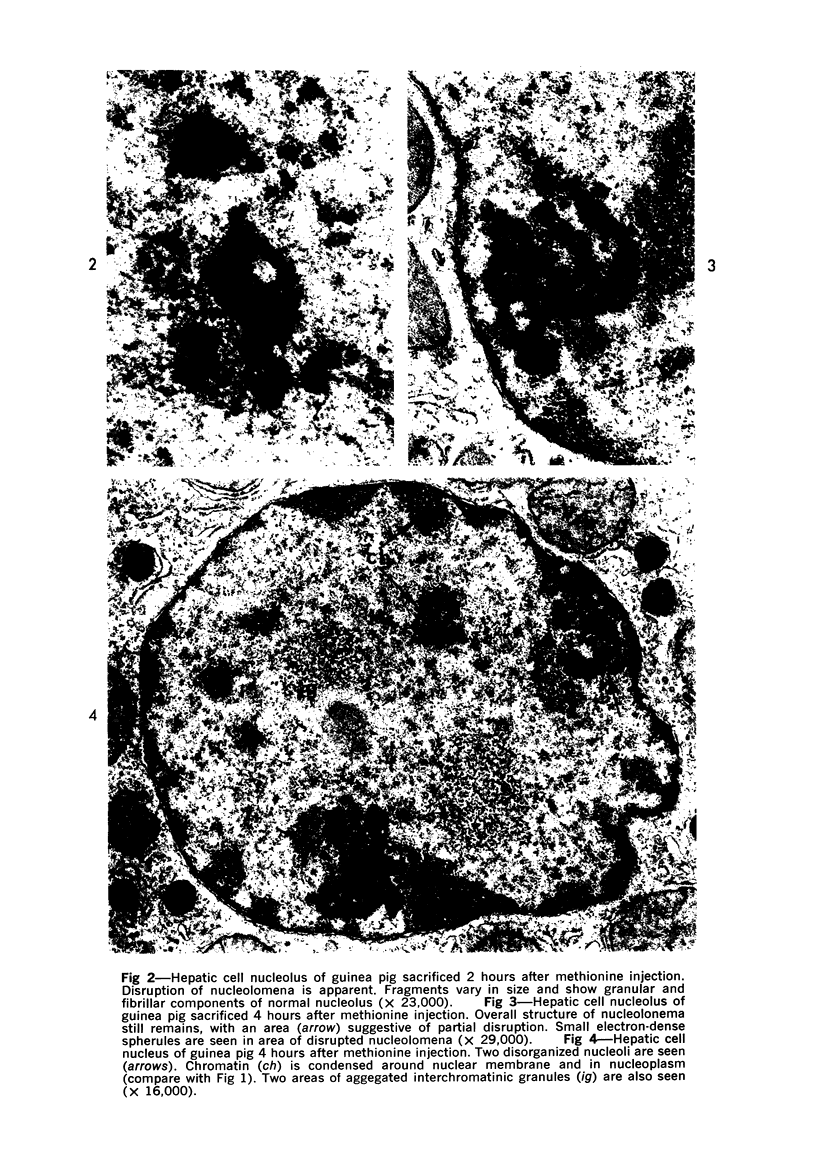
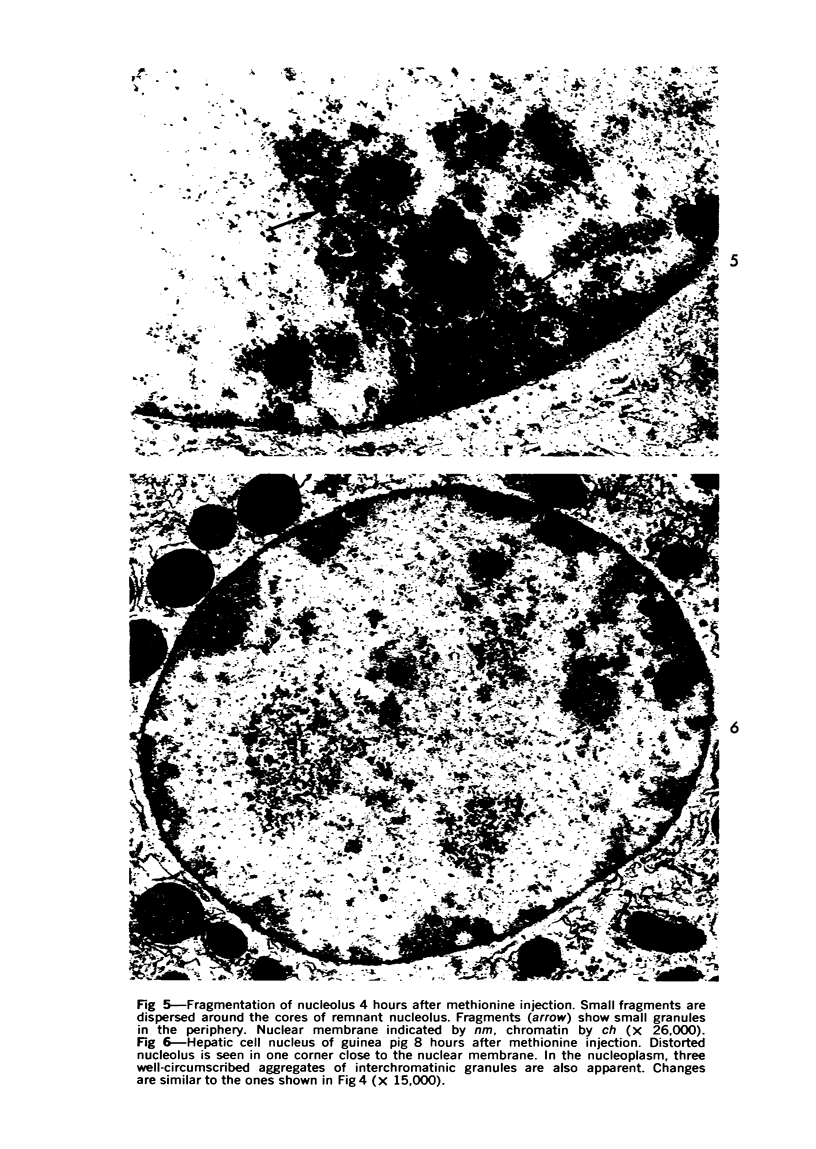
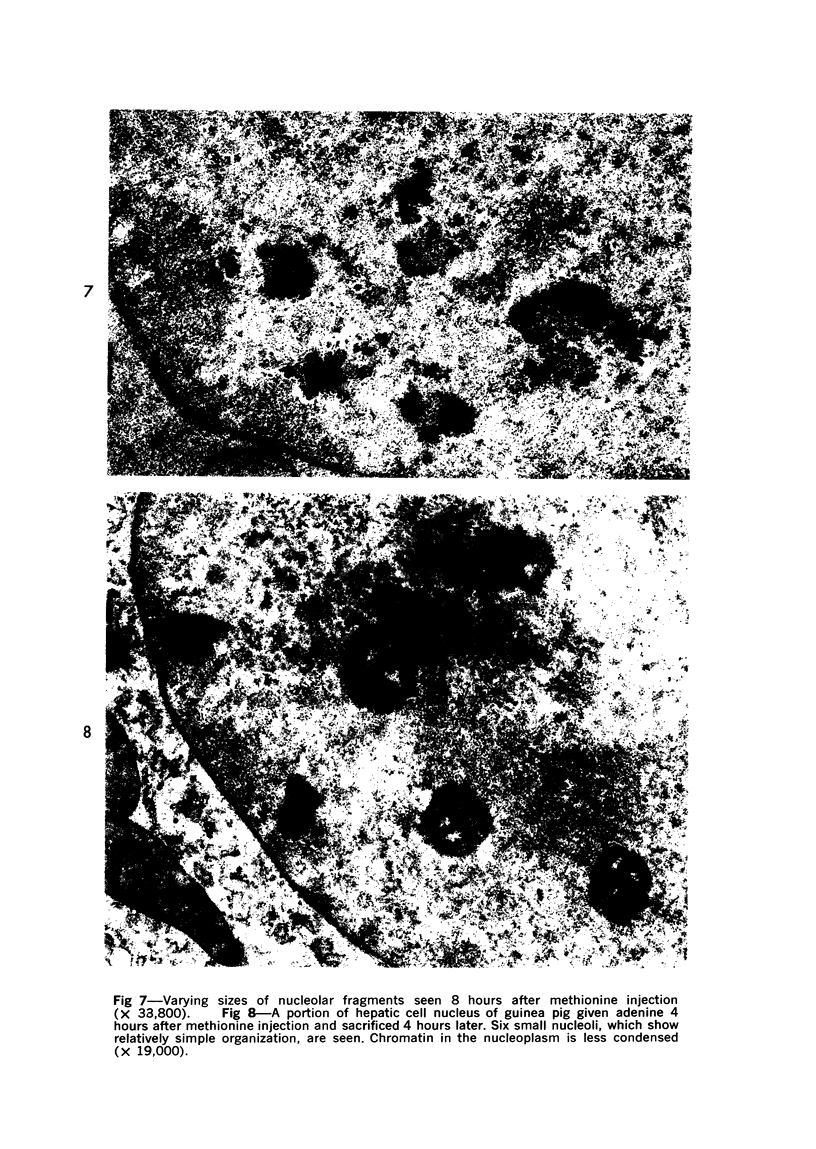
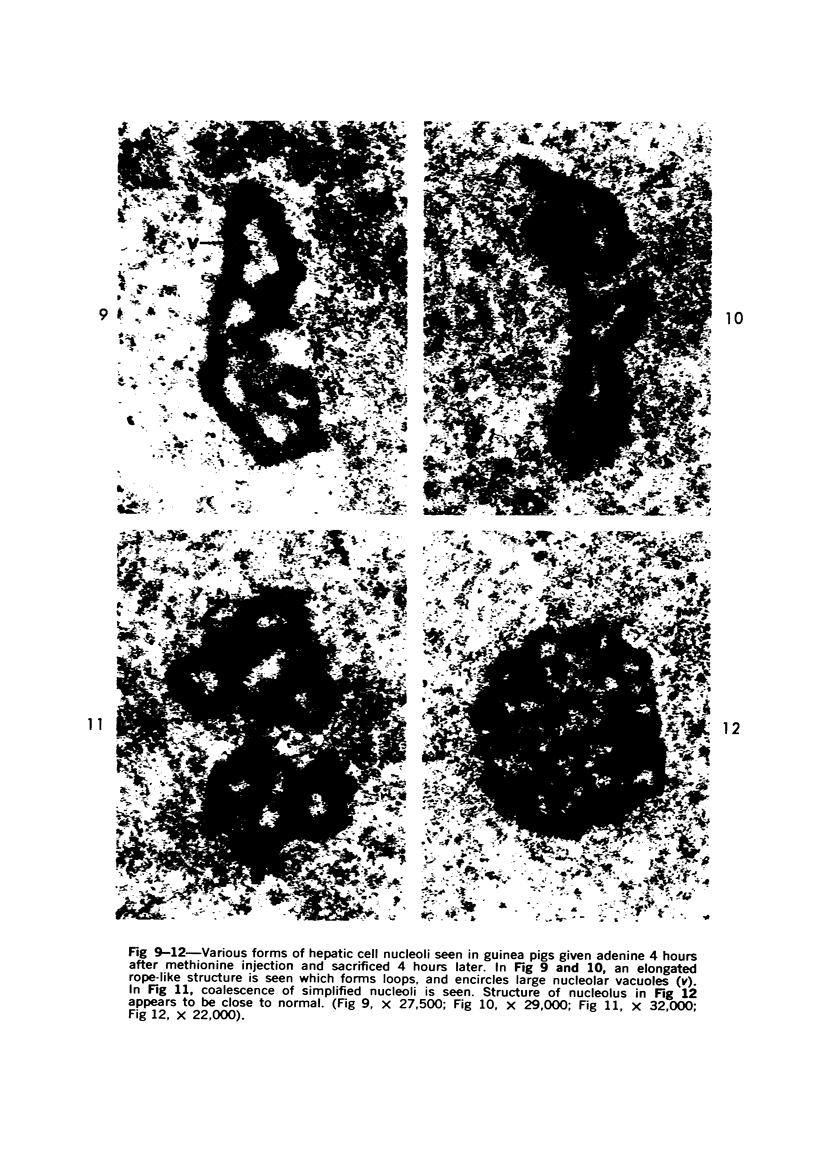
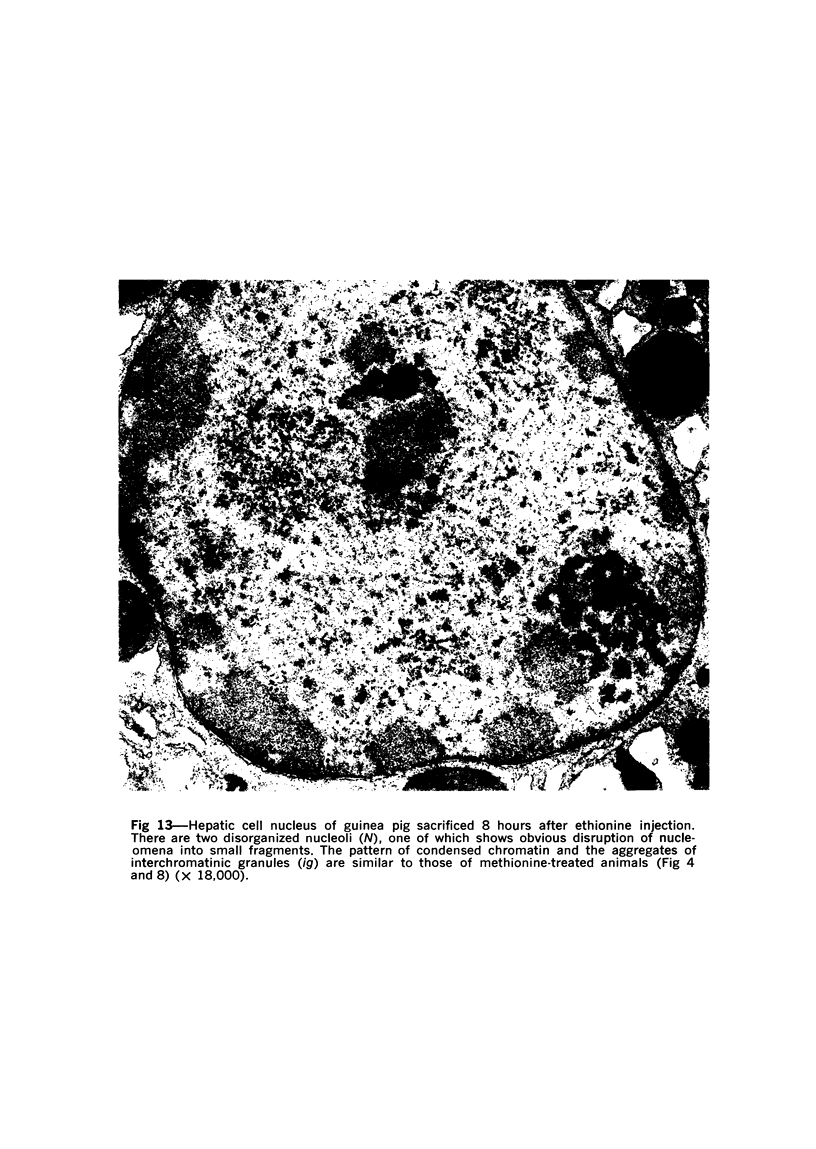
The effects of methionine and ethionine on the fine structure of hepatic cell nucleoli of guinea pigs and rats were investigated. A single intraperitoneal injection of methionine into guinea pigs results in the disruption of nucleolonema as early as 2 hours after the injection. By 4 hours, nucleoli show complete fragmentation consisting of many small fragments and small remnants of nucleoli. Large aggregates of interchromatinic granules and condensation of chromatin appear in the nucleoplasm. These changes are remarkably similar to the lesions induced by ethionine in the liver of the rat or the guinea pig. The methionine-induced nuclear and nucleolar lesions persist up to 10 hours after the injection. The administration of adenine 4 hours after the methionine injection reverses the nucleolar lesions by 8 hours. The appearance of incompletely reconstructed nucleoli with twisted ropelike structures suggests a pattern of recovery very similar to the adenine-induced nucleolar reformation in ethionine-treated rats. Injecting methionine into rats induced no nucleolar abnormalities. It is suggested that the mechanism of nucleolar fragmentation induced by methionine or ethionine is related to the accumulation of S-adenosyl compounds with concomitant ATP deficiency in the liver.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernhard W. Ultrastructural aspects of the normal and pathological nucleolus in mammalian cells. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1966 Dec;23:13–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boquist L. The effect of excess methionine on the pancreas. A light and electron microscopic study in the Chinese hamster with particular reference to degenerative changes. Lab Invest. 1969 Aug;21(2):96–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CANTONI G. L. Activation of methionine for transmethylation. J Biol Chem. 1951 Apr;189(2):745–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN H. P., CHOITZ H. C., BERG C. P. Response of rats to diets high in methionine and related compounds. J Nutr. 1958 Apr 10;64(4):555–569. doi: 10.1093/jn/64.4.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARBER E. ETHIONINE CARCINOGENESIS. Adv Cancer Res. 1963;7:383–474. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60986-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARBER E., SHULL K. H., VILLA-TREVINO S., LOMBARDI B., THOMAS M. BIOCHEMICAL PATHOLOGY OF ACUTE HEPATIC ADENOSINETRIPHOSPHATE DEFICIENCY. Nature. 1964 Jul 4;203:34–40. doi: 10.1038/203034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber E. Biochemical pathology. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1971;11:71–96. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.11.040171.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiume L., Marinozzi V., Nardi F. The effects of amanitin poisoning on mouse kidney. Br J Exp Pathol. 1969 Jun;50(3):270–276. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick D. F., Applegarth D. A., Cockcroft D. M., Ross P. M., Cder R. J. Pathogenesis of methionine-induced toxicity. Metabolism. 1970 May;19(5):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(70)90135-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOURNEY L. J., GOLDSTEIN M. N. Electron microscope studies on HeLa cell lines sensitive and resistant to actinomycin D. Cancer Res. 1961 Aug;21:929–932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. J. Simple methods for "staining with lead" at high pH in electron microscopy. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Dec;11:729–732. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.3.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLAVINS J. V., JOHANSEN P. V. PATHOLOGY OF AMINO ACID EXCESS. IV. EFFECTS AND INTERACTIONS OF EXCESSIVE AMOUNTS OF DIETARY METHIONINE, HOMOCYSTINE, AND SERINE. Arch Pathol. 1965 Jun;79:600–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLAVINS J. V., KINNEY T. D., KAUFMAN N. Histopathologic changes in methionine excess. Arch Pathol. 1963 Jun;75:661–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindell T. J., Weinberg F., Morris P. W., Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Specific inhibition of nuclear RNA polymerase II by alpha-amanitin. Science. 1970 Oct 23;170(3956):447–449. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3956.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLLENHAUER H. H. PLASTIC EMBEDDING MIXTURES FOR USE IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. Stain Technol. 1964 Mar;39:111–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyai K., Steiner J. W. Fine structure of interphase liver cell nuclei in acute ethionine intoxication. Lab Invest. 1967 May;16(5):677–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS R. C., MONTGOMERY P. O., HUGHES B. NUCLEOLAR "CAPS" PRODUCED BY ACTINOMYCIN D. Cancer Res. 1964 Aug;24:1269–1277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSSELL W. C., TAYLOR M. W., HOGAN J. M. Effect of excess essential amino acids on growth of the white rat. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Aug;39(2):249–253. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90331-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOEFL G. I. THE EFFECT OF ACTINOMYCIN D ON THE FINE STRUCTURE OF THE NUCLEOLUS. J Ultrastruct Res. 1964 Apr;10:224–243. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(64)80007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEKOL J. A. BIOCHEMICAL BASIS FOR ETHIONINE EFFECTS ON TISSUES. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1963;25:369–393. doi: 10.1002/9780470122709.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEKOL J. A., SZARAN J. Pathological effects of excessive methionine in the diet of growing rats. J Nutr. 1962 May;77:81–90. doi: 10.1093/jn/77.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozuka H., Farber E. Reformation of nucleoli after ethione-induced fragmentation in the absence of significant protein synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1969 Apr;41(1):280–286. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.1.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozuka H., Goldblatt P. J., Farber E. The disorganization of hepatic cell nucleoli induced by ethionine and its reversal by adenine. J Cell Biol. 1968 Feb;36(2):313–328. doi: 10.1083/jcb.36.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozuka H. Intranucleolar dense particles in rat hepatic cell nucleoli. J Ultrastruct Res. 1970 Sep;32(5):430–442. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(70)80020-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozuka H., Reid I. M., Shull K. H., Liang H., Farber E. Dynamics of liver cell injury and repair. I. Spontaneous reformation of the nucleolus and polyribosomes in the presence of extensive cytoplasmic damage induced by ethionine. Lab Invest. 1970 Sep;23(3):253–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull K. H., McConomy J., Vogt M., Castillo A., Farber E. On the mechanism of induction of hepatic adenosine triphosphate deficiency by ethionine. J Biol Chem. 1966 Nov 10;241(21):5060–5070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simard R., Bernhard W. Le phénomène de la ségrégation nucléolaire: spécificité d'action de certains antimétabolites. Int J Cancer. 1966 Sep 15;1(5):463–479. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910010506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simard R. The nucleus: action of chemical and physical agents. Int Rev Cytol. 1970;28:169–211. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62543-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. C., Salmon W. D. Formation of S-adenosylethionine by ethionine-treated rats. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Jul;111(1):191–196. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90339-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smuckler E. A., Koplitz M. The effects of carbon tetrachloride and ethionine on RNA synthesis in vivo and in isolated rat liver nuclei. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Jun;132(1):62–79. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90338-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Fiume L. Studies on the pathogenesis of liver necrosis by alpha-amanitin. Effect of alpha-amanitin on ribonucleic acid synthesis and on ribonucleic acid polymerase in mouse liver nuclei. Biochem J. 1967 Nov;105(2):779–782. doi: 10.1042/bj1050779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VILLA-TREVINO S., SHULL K. H., FARBER E. The role of adenosine triphosphate deficiency in ethionine-induced inhibition of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1963 May;238:1757–1763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]