Abstract
A hydroperoxidase purified from the halophilic archaeon Halobacterium halobium exhibited both catalase and peroxidase activities, which were greatly diminished in a low-salt environment. Therefore, the purification was carried out in 2 M NaCl. Purified protein exhibited catalase activity over the narrow pH range of 6.0 to 7.5 and exhibited peroxidase activity between pH 6.5 and 8.0. Peroxidase activity was maximal at NaCl concentrations above 1 M, although catalase activity required 2 M NaCl for optimal function. Catalase activity was greatest at 50 degrees C; at 90 degrees C, the enzymatic activity was 20% greater than at 25 degrees C. Peroxidase activity decreased rapidly above its maximum at 40 degrees C. An activation energy of 2.5 kcal (ca. 10 kJ)/mol was calculated for catalase, and an activation energy of 4.0 kcal (ca. 17 kJ)/mol was calculated for peroxidase. Catalase activity was not inhibited by 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole but was inhibited by KCN and NaN3 (apparent Ki [KiApp] of 50 and 67.5 microM, respectively). Peroxidative activity was inhibited equally by KCN and NaN3 (KiApp for both, approximately 30 microM). The absorption spectrum showed a Soret peak at 404 nm, and there was no apparent reduction by dithionite. A heme content of 1.43 per tetramer was determined. The protein has a pI of 3.8 and an M(r) of 240,000 and consists of four subunits of 60,300 each.
Full text
PDF

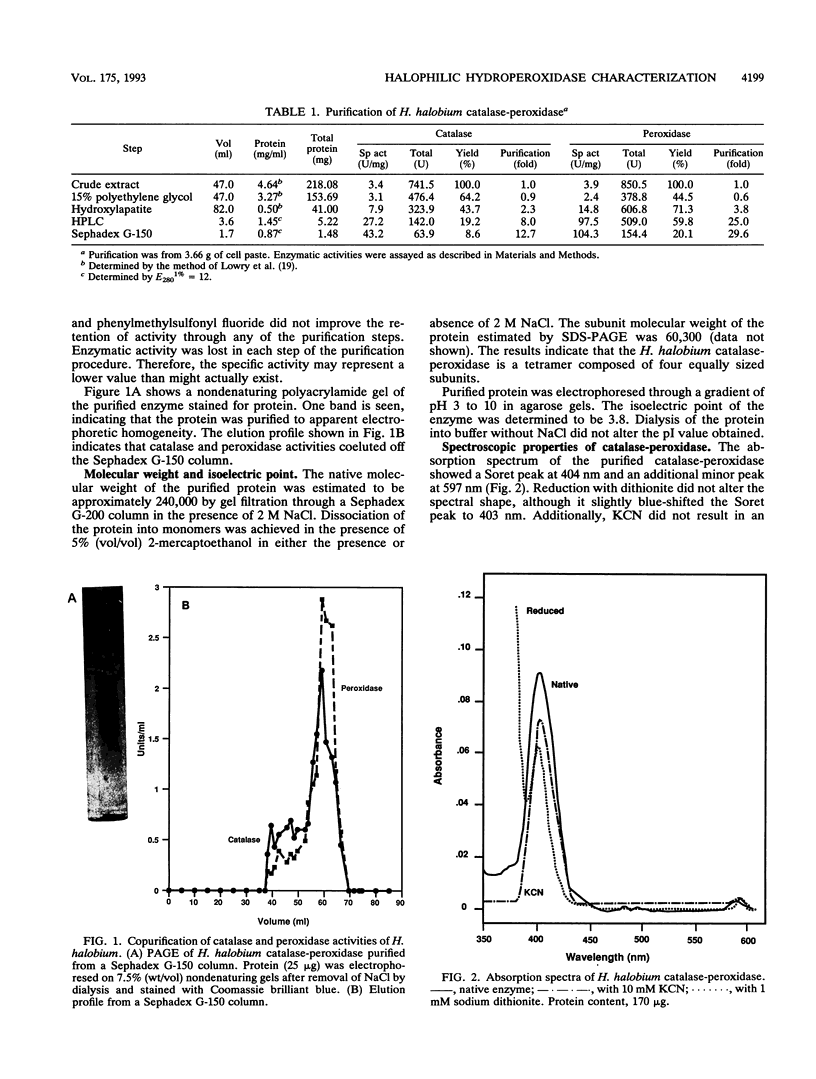
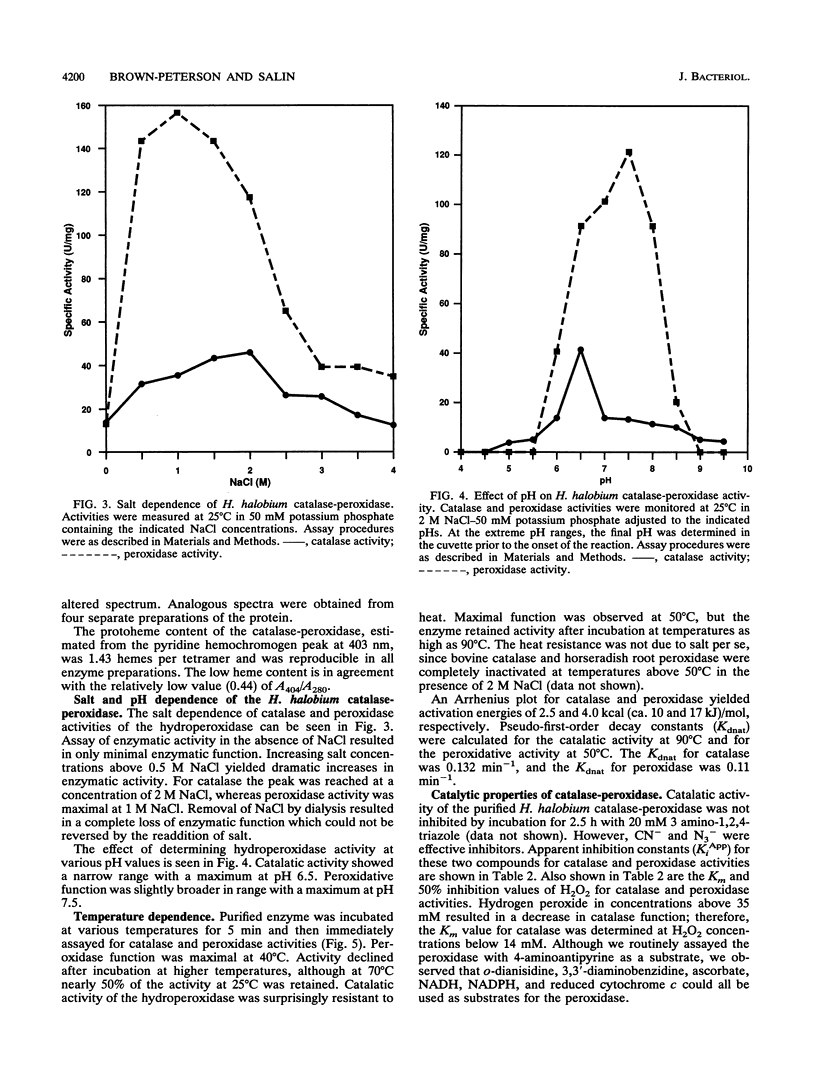
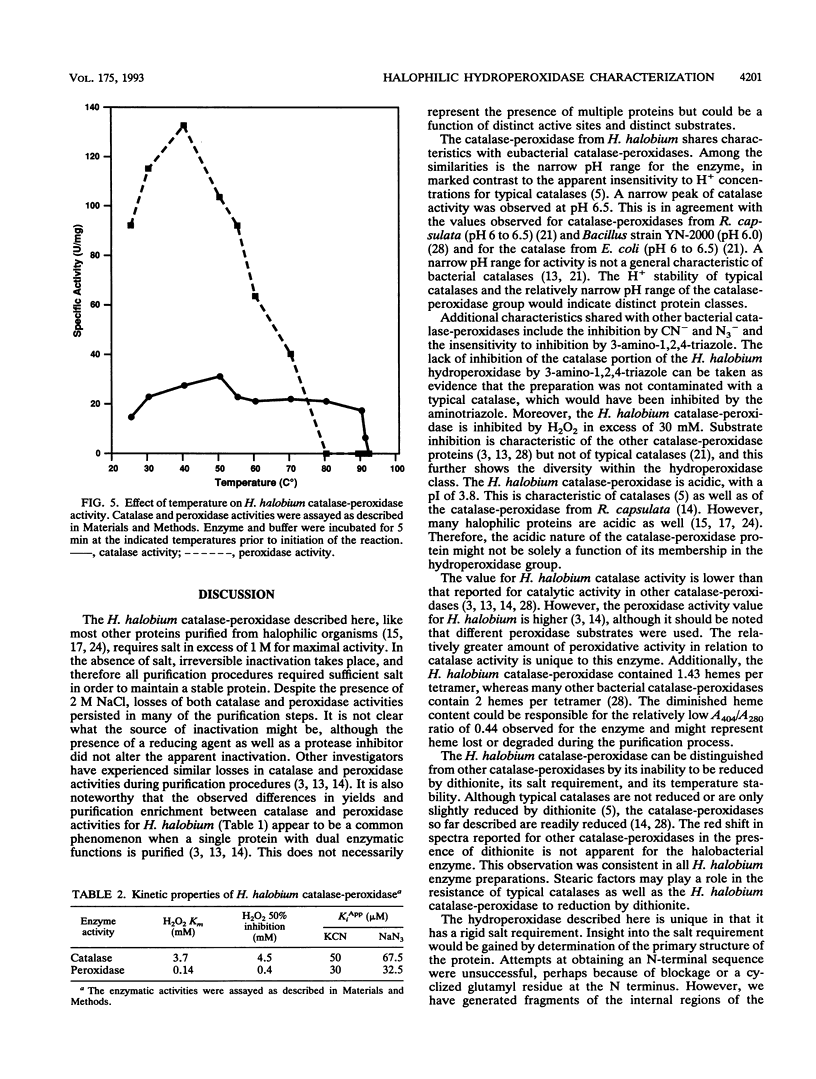

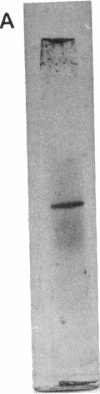
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEERS R. F., Jr, SIZER I. W. A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):133–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claiborne A., Fridovich I. Purification of the o-dianisidine peroxidase from Escherichia coli B. Physicochemical characterization and analysis of its dual catalatic and peroxidatic activities. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4245–4252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisseroth A., Dounce A. L. Catalase: Physical and chemical properties, mechanism of catalysis, and physiological role. Physiol Rev. 1970 Jul;50(3):319–375. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1970.50.3.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridovich I. Biological effects of the superoxide radical. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 May 15;247(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90526-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumori Y., Fujiwara T., Okada-Takahashi Y., Mukohata Y., Yamanaka T. Purification and properties of a peroxidase from Halobacterium halobium L-33. J Biochem. 1985 Oct;98(4):1055–1061. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I., Hochman A. Purification and characterization of a novel type of catalase from the bacterium Klebsiella pneumoniae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 May 31;991(2):330–336. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(89)90124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann R., Sickinger H. D., Oesterhelt D. Quantitative aspects of energy conversion in halobacteria. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 1;82(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80873-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochman A., Figueredo A., Wall J. D. Physiological functions of hydroperoxidases in Rhodobacter capsulatus. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(10):3386–3391. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.10.3386-3391.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochman A., Goldberg I. Purification and characterization of a catalase-peroxidase and a typical catalase from the bacterium Klebsiella pneumoniae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 29;1077(3):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(91)90544-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochman A., Shemesh A. Purification and characterization of a catalase-peroxidase from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6871–6876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K. Salt-dependent properties of proteins from extremely halophilic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Sep;38(3):272–290. doi: 10.1128/br.38.3.272-290.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewen P. C., Stauffer G. V. Nucleotide sequence of katG of Salmonella typhimurium LT2 and characterization of its product, hydroperoxidase I. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Oct;224(1):147–151. doi: 10.1007/BF00259461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May B. P., Dennis P. P. Superoxide dismutase from the extremely halophilic archaebacterium Halobacterium cutirubrum. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1417–1422. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1417-1422.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salin M. L. Chloroplast and mitochondrial mechanisms for protection against oxygen toxicity. Free Radic Res Commun. 1991;12-13 Pt 2:851–858. doi: 10.3109/10715769109145867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salin M. L., Duke M. V., Oesterhelt D., Ma D. P. Cloning and determination of the nucleotide sequence of the Mn-containing superoxide dismutase gene from Halobacterium halobium. Gene. 1988 Oct 15;70(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salin M. L., Oesterhelt D. Purification of a manganese-containing superoxide dismutase from Halobacterium halobium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Feb 1;260(2):806–810. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90511-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takao M., Kobayashi T., Oikawa A., Yasui A. Tandem arrangement of photolyase and superoxide dismutase genes in Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6323–6329. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6323-6329.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yumoto I., Fukumori Y., Yamanaka T. Purification and characterization of catalase from a facultative alkalophilic Bacillus. J Biochem. 1990 Oct;108(4):583–587. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]