Abstract
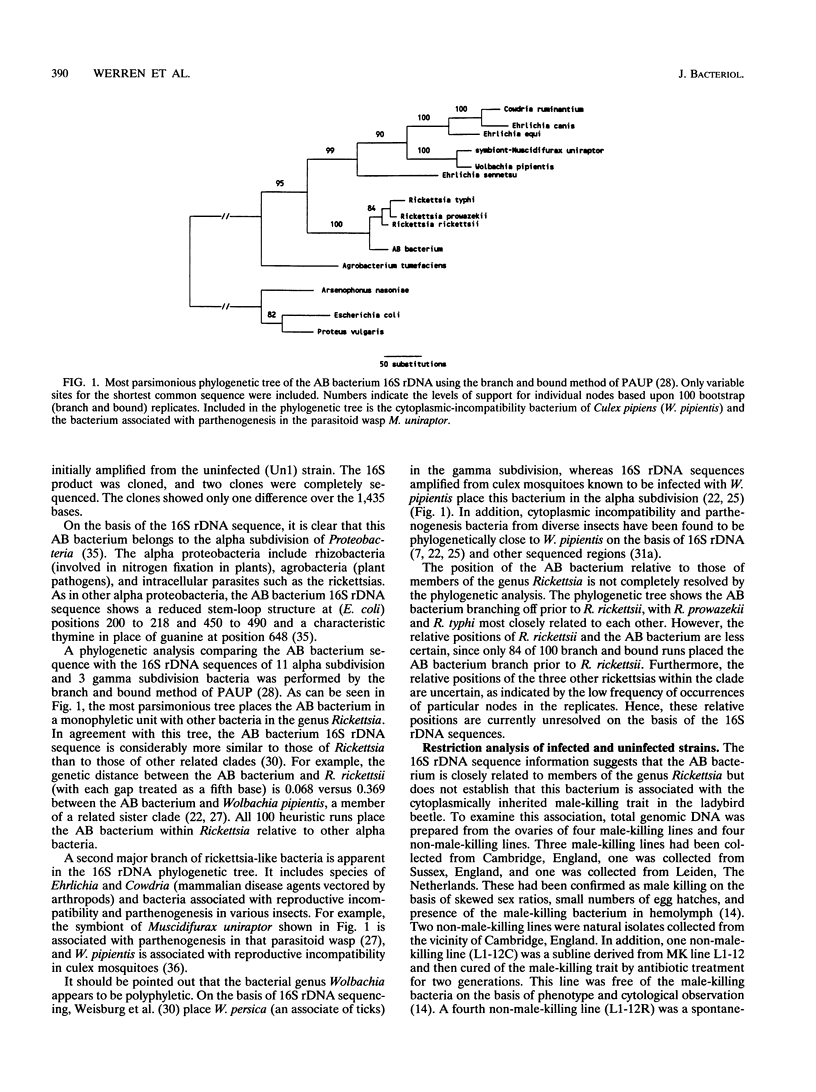
A cytoplasmically inherited microorganism associated with male killing in the two-spot ladybird beetle, Adalia bipunctata, is shown to be closely related to bacteria in the genus Rickettsia. Sequencing of a PCR-amplified product of the 16S genes coding for rRNA (16S rDNA) shows the organism associated with male killing in ladybirds to share a common ancestry with the Rickettsias relative to other genera (e.g., Anaplasma, Ehrlichia, and Cowdria). The rickettsial 16S rDNA product is found in four strains of ladybird beetle showing male embryo lethality and is absent from two uninfected strains and an antibiotic-cured strain. In addition, a revertant strain that had naturally lost the male-killing trait failed to amplify the rickettsial 16S rDNA product. Use of PCR primers for a 17-kDa protein antigen which is found only in rickettsias also resulted in an amplified product from infected strains. Uninfected, cured, and revertant strains and insect species infected with related bacteria (cytoplasmic-incompatibility bacteria from Nasonia wasps) failed to amplify the product. Discovery of a close relative of rickettsias associated with sex ratio distortion in insects has implications for the evolution and population dynamics of this bacterial genus.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. R., Schmidtmann E. T., Azad A. F. Infection of colonized cat fleas, Ctenocephalides felis (Bouché), with a rickettsia-like microorganism. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1990 Oct;43(4):400–409. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1990.43.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson B. E., Regnery R. L., Carlone G. M., Tzianabos T., McDade J. E., Fu Z. Y., Bellini W. J. Sequence analysis of the 17-kilodalton-antigen gene from Rickettsia rickettsii. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2385–2390. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2385-2390.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson B. E., Tzianabos T. Comparative sequence analysis of a genus-common rickettsial antigen gene. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5199–5201. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5199-5201.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreadis T. G., Hall D. W. Significance of transovarial infections of Amblyospora sp. (Microspora:Thelohaniidae) in relation to parasite maintenance in the mosquito Culex salinarius. J Invertebr Pathol. 1979 Sep;34(2):152–157. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(79)90095-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azad A. F., Sacci J. B., Jr, Nelson W. M., Dasch G. A., Schmidtmann E. T., Carl M. Genetic characterization and transovarial transmission of a typhus-like rickettsia found in cat fleas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):43–46. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azad A. F., Webb L., Carl M., Dasch G. A. Detection of rickettsiae in arthropod vectors by DNA amplification using the polymerase chain reaction. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;590:557–563. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breeuwer J. A., Stouthamer R., Barns S. M., Pelletier D. A., Weisburg W. G., Werren J. H. Phylogeny of cytoplasmic incompatibility micro-organisms in the parasitoid wasp genus Nasonia (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae) based on 16S ribosomal DNA sequences. Insect Mol Biol. 1992;1(1):25–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2583.1993.tb00074.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breeuwer J. A., Werren J. H. Microorganisms associated with chromosome destruction and reproductive isolation between two insect species. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):558–560. doi: 10.1038/346558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farhang-Azad A., Traub R., Baqar S. Transovarial transmission of murine typhus rickettsiae in Xenopsylla cheopis fleas. Science. 1985 Feb 1;227(4686):543–545. doi: 10.1126/science.3966162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine P. E. On the dynamics of symbiote-dependent cytoplasmic incompatibility in culicine mosquitoes. J Invertebr Pathol. 1978 Jan;31(1):10–18. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(78)90102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefs J. M., Van de Peer Y., Hendriks L., De Wachter R. Compilation of small ribosomal subunit RNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18 (Suppl):2237–2317. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.suppl.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill S. L., Giordano R., Colbert A. M., Karr T. L., Robertson H. M. 16S rRNA phylogenetic analysis of the bacterial endosymbionts associated with cytoplasmic incompatibility in insects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2699–2702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J., Overbeek R., Larsen N., Marsh T. L., McCaughey M. J., Maciukenas M. A., Kuan W. M., Macke T. J., Xing Y., Woese C. R. The Ribosomal Database Project. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 11;20 (Suppl):2199–2200. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.suppl.2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regnery R. L., Spruill C. L., Plikaytis B. D. Genotypic identification of rickettsiae and estimation of intraspecies sequence divergence for portions of two rickettsial genes. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1576–1589. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1576-1589.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts L. W., Rapmund G., Cadigan F. C., Jr Sex ratios in rickettsia tsutsugamushi-infected and noninfected colonies of Leptotrombidium (Acari: trombiculidae). J Med Entomol. 1977 Aug 20;14(1):89–92. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/14.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousset F., Bouchon D., Pintureau B., Juchault P., Solignac M. Wolbachia endosymbionts responsible for various alterations of sexuality in arthropods. Proc Biol Sci. 1992 Nov 23;250(1328):91–98. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1992.0135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou N., Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jul;4(4):406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg W. G., Barns S. M., Pelletier D. A., Lane D. J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):697–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.697-703.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg W. G., Dobson M. E., Samuel J. E., Dasch G. A., Mallavia L. P., Baca O., Mandelco L., Sechrest J. E., Weiss E., Woese C. R. Phylogenetic diversity of the Rickettsiae. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4202–4206. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4202-4206.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werren J. H., Skinner S. W., Huger A. M. Male-killing bacteria in a parasitic wasp. Science. 1986 Feb 28;231(4741):990–992. doi: 10.1126/science.3945814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. G., Sacci J. B., Jr, Schriefer M. E., Andersen E. M., Fujioka K. K., Sorvillo F. J., Barr A. R., Azad A. F. Typhus and typhuslike rickettsiae associated with opossums and their fleas in Los Angeles County, California. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jul;30(7):1758–1762. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.7.1758-1762.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen J. H., Barr A. R. The etiological agent of cytoplasmic incompatibility in Culex pipiens. J Invertebr Pathol. 1973 Sep;22(2):242–250. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(73)90141-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]