Abstract
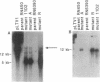
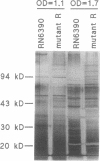
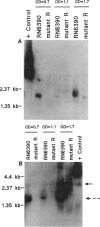
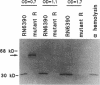
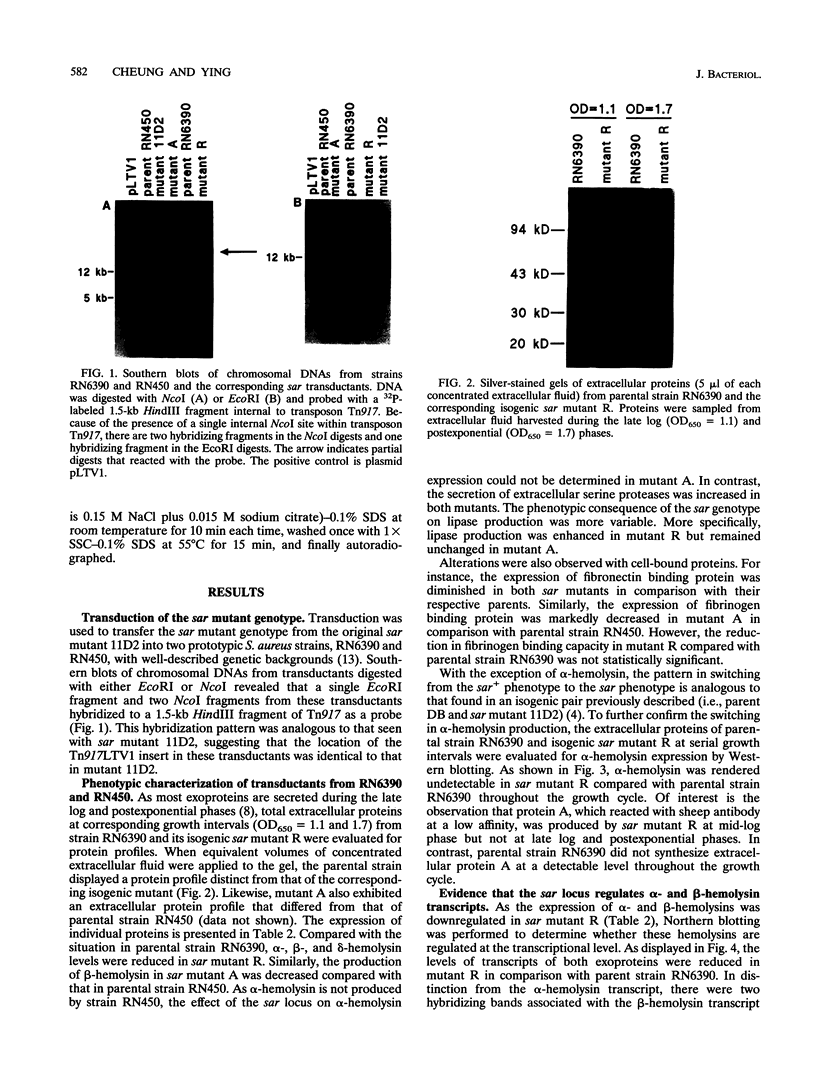
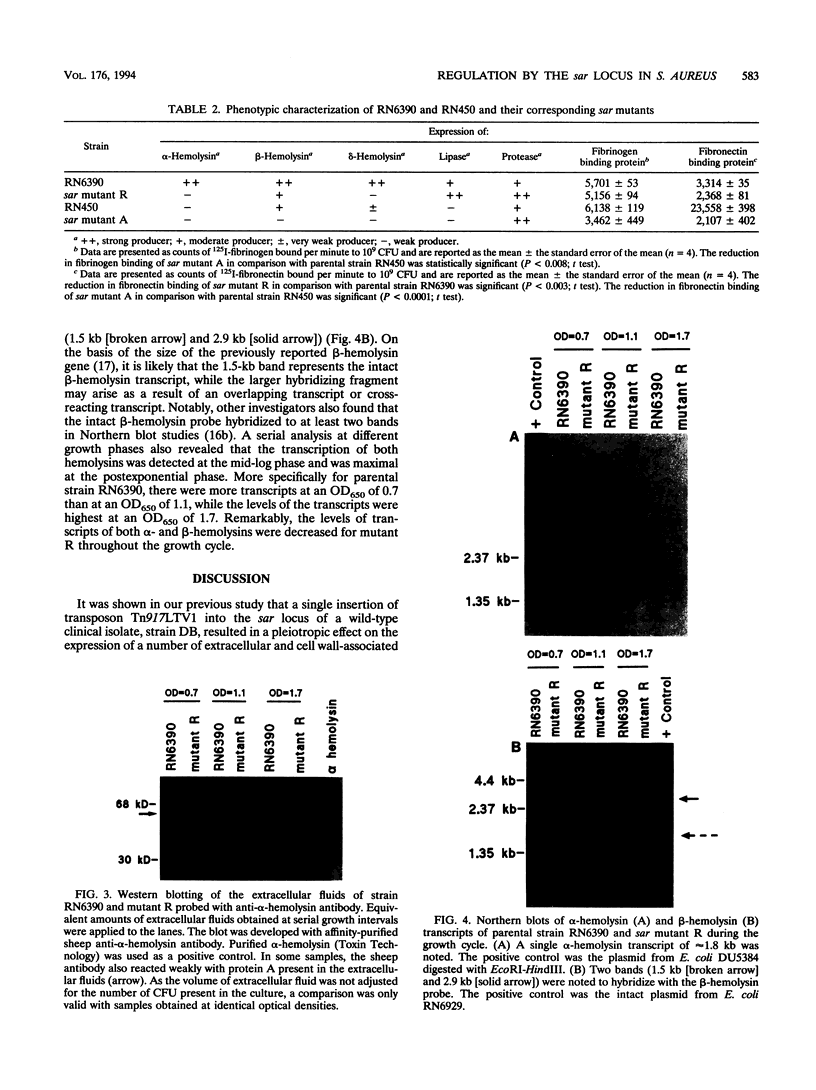
We recently identified a locus on the Staphylococcus aureus chromosome, designated sar, for staphylococcal accessory regulator, that is involved in the global regulation of extracellular and cell wall-associated proteins. Previous phenotypic and Southern blot analyses with Tn917 and agr probes indicated that this locus is distinct from agr, a previously described global regulator of exoproteins in S. aureus. To understand the mode of regulatory control of exoprotein synthesis by the sar locus, the sar genotype was transduced from the original sar mutant 11D2 into two prototypic S. aureus strains, RN6390 and RN450, with well-defined genetic backgrounds. An analysis of extracellular protein profiles by use of silver-stained sodium dodecyl sulfate gels revealed alterations in the pattern of exoprotein production in the late log-early stationary phase in the sar mutants in comparison with the corresponding parents. In addition, most of the phenotypic changes that occurred in the conversion from the sar+ genotype to the sar genotype in mutant 11D2 were also found in these mutants. Northern (RNA) blot analyses of two exoprotein transcripts (alpha- and beta-hemolysins) from strain RN6390 and its corresponding sar mutant revealed downregulation of these transcripts in the mutant. Serial studies of these hemolysin transcripts at various growth intervals demonstrated that the transcriptional regulation of the hemolysin genes by the sar locus began during the log phase and continued into the postexponential phase. These data suggested that the sar locus probably regulates exoprotein genes at the transcriptional level. This mode of regulation is similar to that of exoprotein target gene transcription by agr.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilli A., Portnoy A., Youngman P. Insertional mutagenesis of Listeria monocytogenes with a novel Tn917 derivative that allows direct cloning of DNA flanking transposon insertions. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3738–3744. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3738-3744.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A. L., Koomey J. M., Butler C. A., Projan S. J., Fischetti V. A. Regulation of exoprotein expression in Staphylococcus aureus by a locus (sar) distinct from agr. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6462–6466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compagnone-Post P., Malyankar U., Khan S. A. Role of host factors in the regulation of the enterotoxin B gene. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1827–1830. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1827-1830.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fröman G., Switalski L. M., Speziale P., Hök M. Isolation and characterization of a fibronectin receptor from Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6564–6571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janzon L., Arvidson S. The role of the delta-lysin gene (hld) in the regulation of virulence genes by the accessory gene regulator (agr) in Staphylococcus aureus. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1391–1399. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08254.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblum J. S., Projan S. J., Moghazeh S. L., Novick R. P. A rapid method to quantitate non-labeled RNA species in bacterial cells. Gene. 1988;63(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90547-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantz M. S., Allen R. D., Bounelis P., Switalski L. M., Hook M. Bacteroides gingivalis and Bacteroides intermedius recognize different sites on human fibrinogen. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):716–726. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.716-726.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Adler G. K., Projan S. J., Carleton S., Highlander S. K., Gruss A., Khan S. A., Iordanescu S. Control of pT181 replication I. The pT181 copy control function acts by inhibiting the synthesis of a replication protein. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2399–2405. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02146.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P. Genetic systems in staphylococci. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:587–636. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)04029-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly M., de Azavedo J. C., Kennedy S., Foster T. J. Inactivation of the alpha-haemolysin gene of Staphylococcus aureus 8325-4 by site-directed mutagenesis and studies on the expression of its haemolysins. Microb Pathog. 1986 Apr;1(2):125–138. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel A. H., Kornblum J., Kreiswirth B., Novick R., Foster T. J. Regulation of the protein A-encoding gene in Staphylococcus aureus. Gene. 1992 May 1;114(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90703-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Projan S. J., Kornblum J., Kreiswirth B., Moghazeh S. L., Eisner W., Novick R. P. Nucleotide sequence: the beta-hemolysin gene of Staphylococcus aureus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):3305–3305. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.3305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recsei P., Kreiswirth B., O'Reilly M., Schlievert P., Gruss A., Novick R. P. Regulation of exoprotein gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus by agar. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jan;202(1):58–61. doi: 10.1007/BF00330517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regassa L. B., Novick R. P., Betley M. J. Glucose and nonmaintained pH decrease expression of the accessory gene regulator (agr) in Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3381–3388. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3381-3388.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeltzer M. S., Hart M. E., Iandolo J. J. Phenotypic characterization of xpr, a global regulator of extracellular virulence factors in Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1993 Mar;61(3):919–925. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.3.919-925.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W. D., Jr, Archer G. L. Identification and cloning of the conjugative transfer region of Staphylococcus aureus plasmid pGO1. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):684–691. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.684-691.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenesch F., Kornblum J., Novick R. P. A temporal signal, independent of agr, is required for hla but not spa transcription in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(20):6313–6320. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.20.6313-6320.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]