Abstract
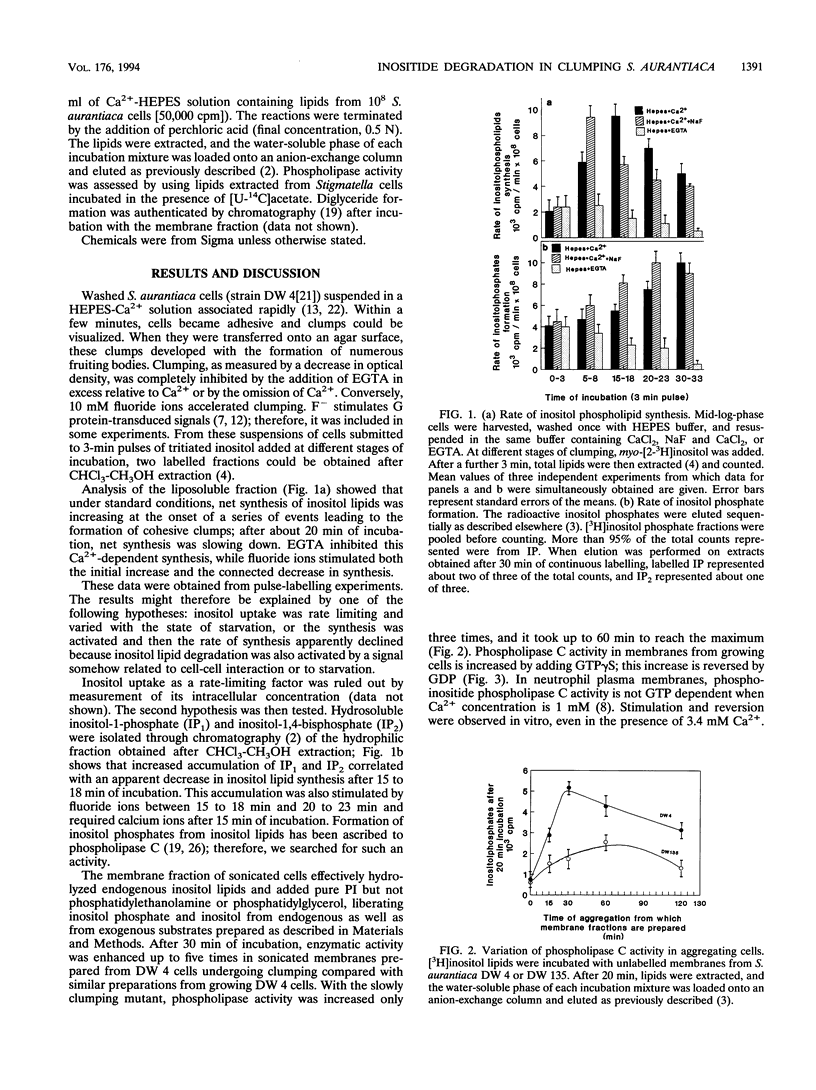
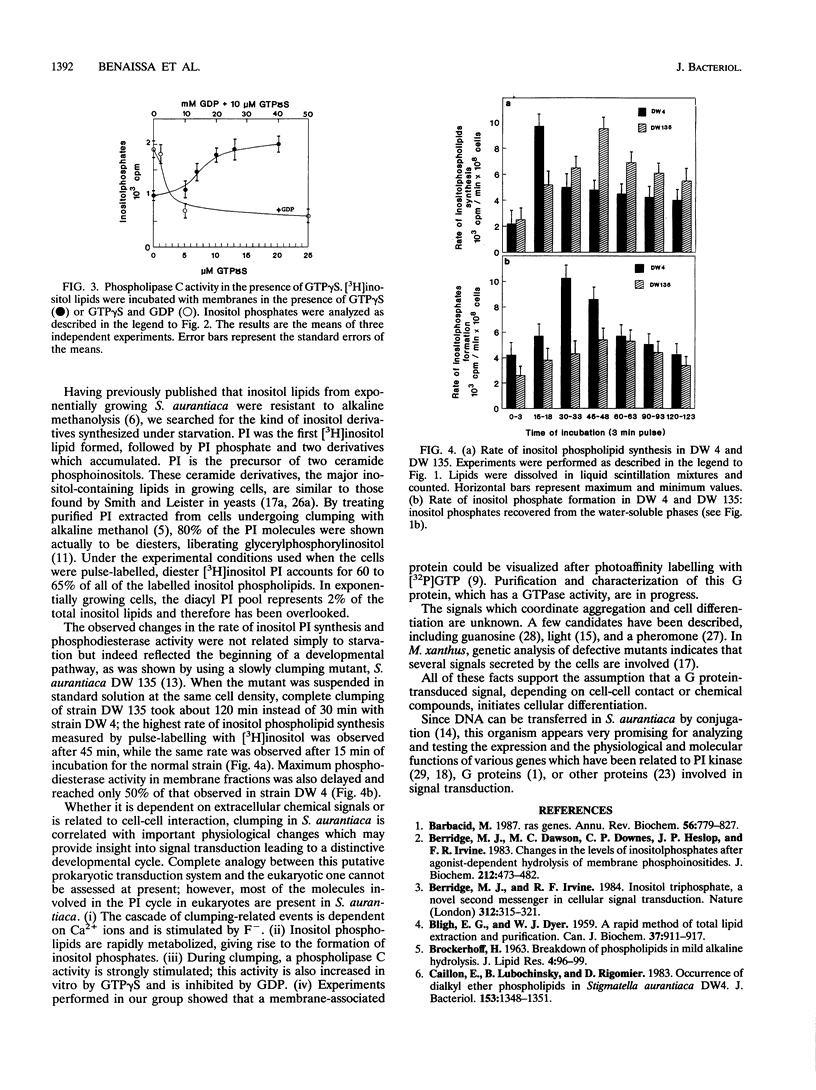
Numerous external signals which activate inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in eukaryotes are known; probably all of these signals are transduced by G proteins. So far, neither signal-transducing G protein nor receptor-regulated phospholipase C has been found in prokaryotes. However, a group of bacteria, the myxobacteria, displays cellular and tissue-like differentiation; therefore, it appeared that a search for the various activities involved in a signal-activated phosphatidylinositol cycle might be rewarding. Here, we report that in Stigmatella aurantiaca, under conditions which promote clumping, inositol phospholipid synthesis and degradation were stimulated with the resulting formation of inositol phosphate and inositol bisphosphate. The turnover was Ca2+ dependent and was increased by fluoride ions. Membrane preparations from these cells showed a phospholipase C activity which increased with the stage of incubation and which was stimulated by GTP gamma S, suggesting G protein dependency. To what extent this system in a prokaryotic cell shares properties of the phosphatidylinositol cycle in eukaryotes remains unexamined.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCKERHOFF H. BREAKDOWN OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS IN MILD ALKALINE HYDROLYSIS. J Lipid Res. 1963 Jan;4:96–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caillon E., Lubochinsky B., Rigomier D. Occurrence of dialkyl ether phospholipids in Stigmatella aurantiaca DW4. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1348–1351. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1348-1351.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claro E., Wallace M. A., Fain J. N. Dual effect of fluoride on phosphoinositide metabolism in rat brain cortex. Stimulation of phospholipase C and inhibition of polyphosphoinositide synthesis. Biochem J. 1990 Jun 15;268(3):733–737. doi: 10.1042/bj2680733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S. The dependence on Ca2+ of the guanine-nucleotide-activated polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase in neutrophil plasma membranes. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):503–507. doi: 10.1042/bj2400503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin M., Sadler W. Induction of cellular morphogenesis in Myxococcus xanthus. I. General description. J Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(4):1516–1519. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.4.1516-1519.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dérijard B., Ben Aïssa M., Lubochinsky B., Cenatiempo Y. Evidence for a membrane-associated GTP-binding protein in Stigmatella aurantiaca, a prokaryotic cell. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 31;158(2):562–568. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80086-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emilsson A., Sundler R. Differential activation of phosphatidylinositol deacylation and a pathway via diphosphoinositide in macrophages responding to zymosan and ionophore A23187. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3111–3116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore D. F., White D. Energy-dependent cell cohesion in myxobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):113–117. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.113-117.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomp I., Saulnier P., Guespin-Michel J., Schairer H. U. Transfer of IncP plasmids into Stigmatella aurantiaca leading to insertional mutants affected in spore development. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Oct;214(2):213–217. doi: 10.1007/BF00337713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., White D., Inouye M. Development of Stigmatella aurantiaca: effects of light and gene expression. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1360–1365. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1360-1365.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D., Manoil C., Dworkin M. Myxobacteria: cell interactions, genetics, and development. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:595–639. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.003115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. K., Kaiser D., Kuspa A. Control of cell density and pattern by intercellular signaling in Myxococcus development. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1992;46:117–139. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.46.100192.001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macara I. G., Marinetti G. V., Balduzzi P. C. Transforming protein of avian sarcoma virus UR2 is associated with phosphatidylinositol kinase activity: possible role in tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2728–2732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauco G., Chap H., Douste-Blazy L. Characterization and properties of a phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase (phospholipase C) from platelet cytosol. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 15;100(2):367–370. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80371-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell P. C., Telser A., Sussman M. Alternative developmental pathways determined by environmental conditions in the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):763–768. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.763-768.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qualls G. T., Stephens K., White D. Light-stimulated morphogenesis in the fruiting myxobacterium Stigmatella aurantiaca. Science. 1978 Aug 4;201(4354):444–445. doi: 10.1126/science.96528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Cohen D. R., Curran T., Bos T. J., Vogt P. K., Bohmann D., Tjian R., Franza B. R., Jr Fos-associated protein p39 is the product of the jun proto-oncogene. Science. 1988 May 20;240(4855):1010–1016. doi: 10.1126/science.3130660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse S. E. Human platelets contain phospholipase C that hydrolyzes polyphosphoinositides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5417–5420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. W., Lester R. L. Inositol phosphorylceramide, a novel substance and the chief member of a major group of yeast sphingolipids containing a single inositol phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3395–3405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens K., Hegeman G. D., White D. Pheromone produced by the myxobacterium Stigmatella aurantiaca. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):739–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.739-747.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens K., White D. Morphogenetic effects of light and guanine derivatives on the fruiting myxobacterium Stigmatella aurantiaca. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):322–326. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.322-326.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto Y., Whitman M., Cantley L. C., Erikson R. L. Evidence that the Rous sarcoma virus transforming gene product phosphorylates phosphatidylinositol and diacylglycerol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2117–2121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


