Abstract
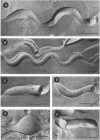
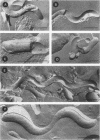
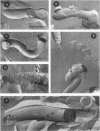
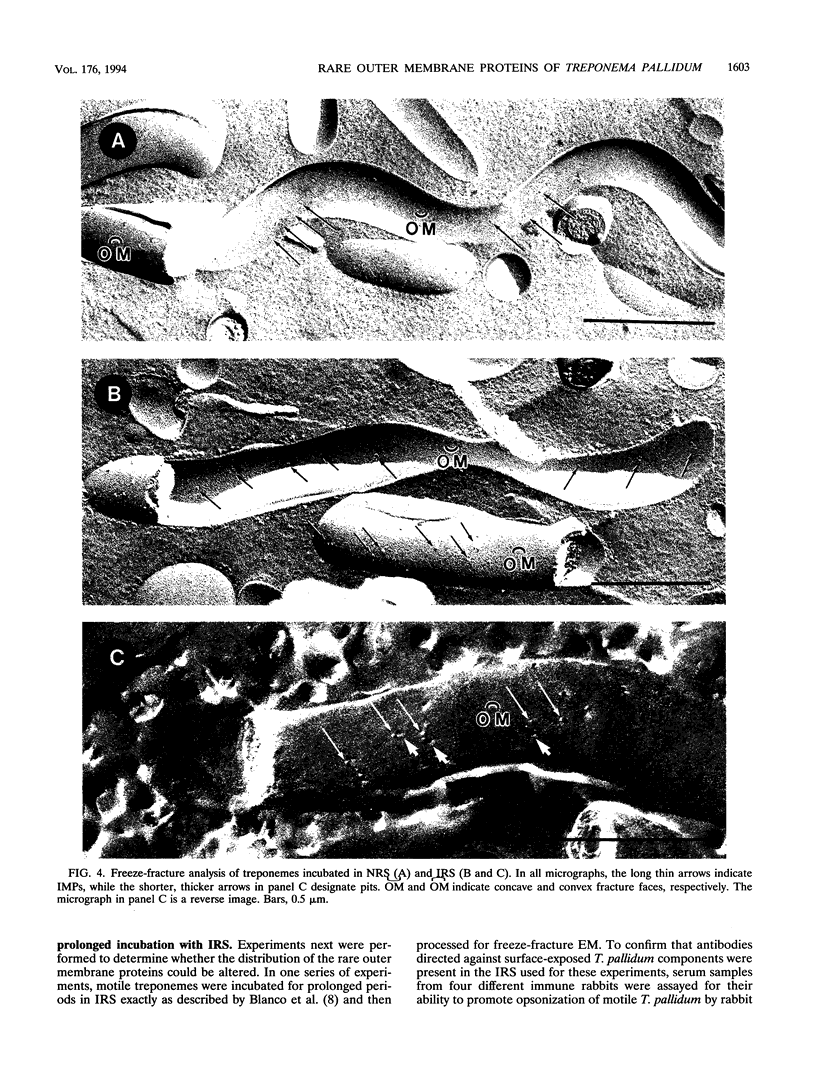
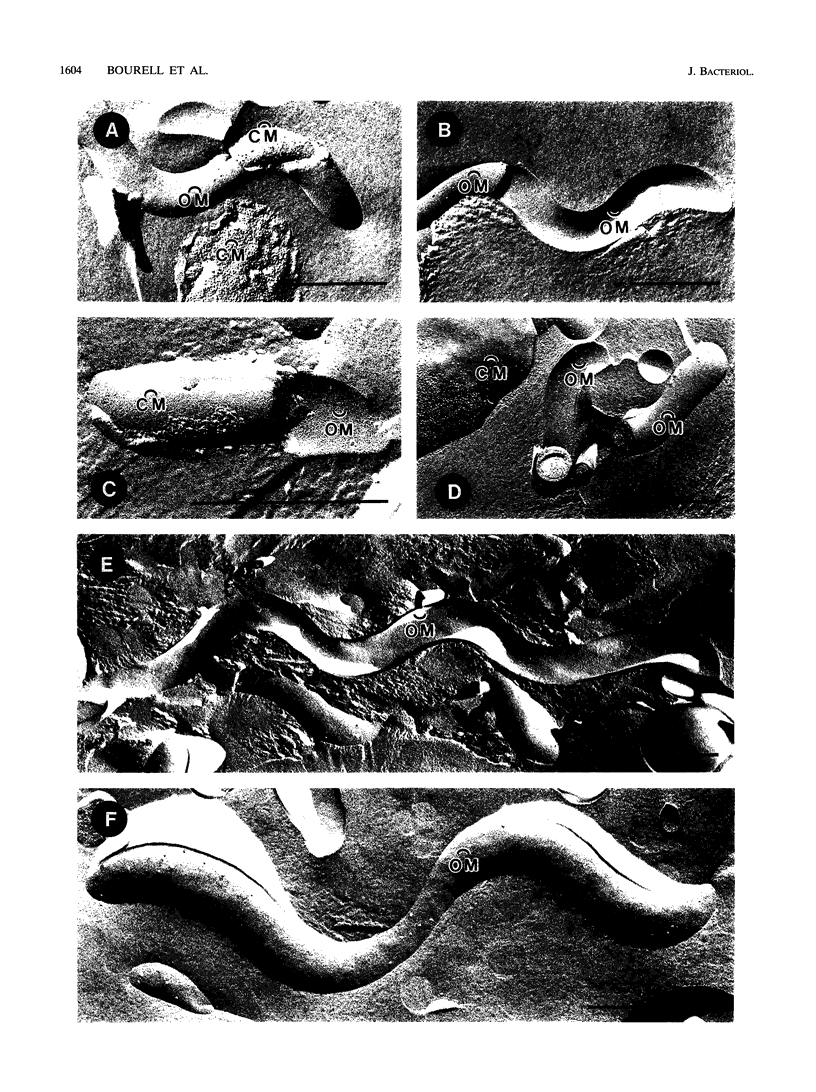
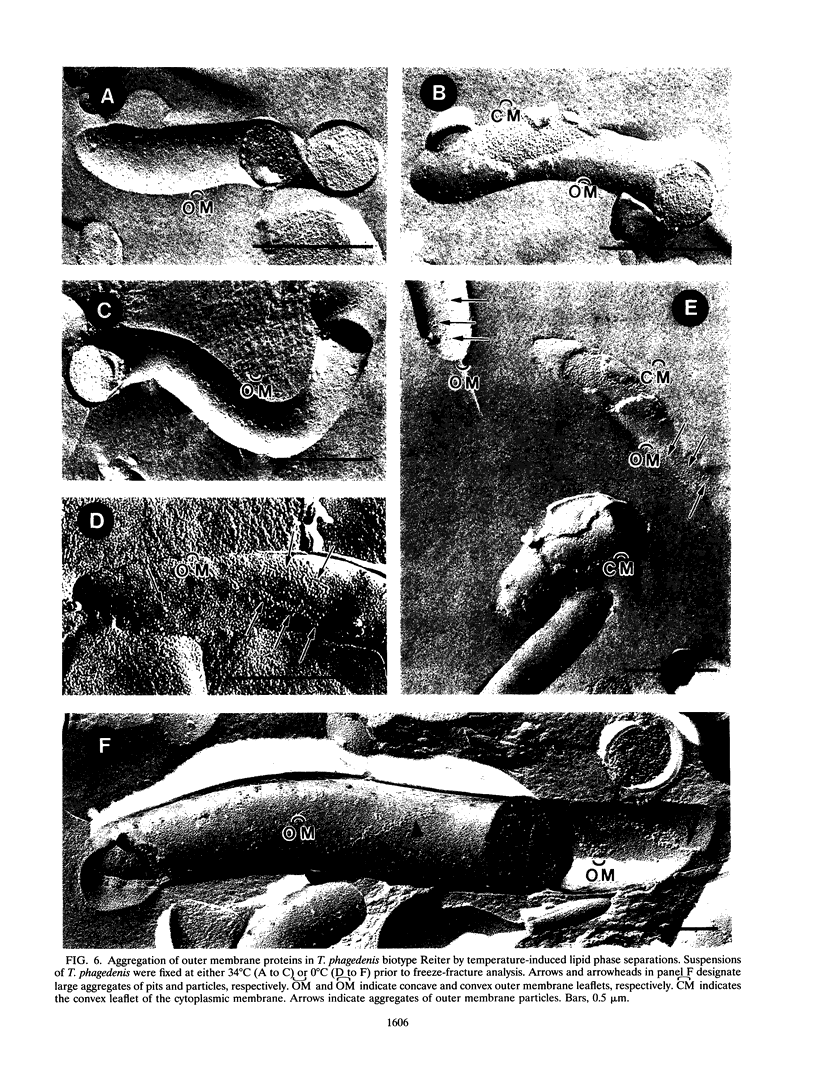
Freeze-fracture and deep-etch electron microscopy were used to investigate the molecular architecture of the Treponema pallidum outer membrane (OM). Freeze-fracture electron microscopy of treponemes freshly harvested from rabbit testes revealed that the intramembranous particles (IMPs) in both the concave and convex OM leaflets were distributed into alternating areas of relatively high and low particle density; in many OM fractures, IMPs formed rows that ran either parallel to or obliquely across the fracture faces. Statistical analysis (runs test) confirmed that the IMPs were nonrandomly distributed in both OM leaflets. Examination of deep-etched specimens revealed that the particles observed in freeze-fractured OMs also were surface exposed. Combined analysis of deep-etched and cross-fractured treponemes revealed that the OM particles were located in regions of the OM away from the endoflagella and closely apposed to the cytoplasmic membrane-peptidoglycan complex. When treponemes were incubated for extended periods with heat-inactivated immune rabbit syphilitic serum, no alteration in the distribution of OM IMPs was detected. In further experiments, approximately 1:1 mixtures of T. pallidum and Escherichia coli or separate suspensions of the nonpathogenic Treponema phagedenis biotype Reiter were fixed at 34 degrees C or after cooling to 0 degree C (to induce lateral phase separations that would aggregate IMPs). Only particles in the T. pallidum OM failed to aggregate in cells fixed at the lower temperature. The combined data suggest that the mobility of T. pallidum rare OM proteins is limited, perhaps as a result of interactions between their periplasmic domains and components of the peptidoglycan-cytoplasmic membrane complex.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akins D. R., Purcell B. K., Mitra M. M., Norgard M. V., Radolf J. D. Lipid modification of the 17-kilodalton membrane immunogen of Treponema pallidum determines macrophage activation as well as amphiphilicity. Infect Immun. 1993 Apr;61(4):1202–1210. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.4.1202-1210.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alder J. D., Friess L., Tengowski M., Schell R. F. Phagocytosis of opsonized Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum proceeds slowly. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1167–1173. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1167-1173.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker-Zander S. A., Hook E. W., 3rd, Bonin P., Handsfield H. H., Lukehart S. A. Antigens of Treponema pallidum recognized by IgG and IgM antibodies during syphilis in humans. J Infect Dis. 1985 Feb;151(2):264–272. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.2.264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker-Zander S. A., Lukehart S. A. Macrophage-mediated killing of opsonized Treponema pallidum. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;165(1):69–74. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E., Dolack M., Houser E. Effects of lipid phase transition of the freeze-cleaved envelope of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1563–1573. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1563-1573.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco D. R., Walker E. M., Haake D. A., Champion C. I., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Complement activation limits the rate of in vitro treponemicidal activity and correlates with antibody-mediated aggregation of Treponema pallidum rare outer membrane protein. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1914–1921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain N. R., Brandt M. E., Erwin A. L., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Major integral membrane protein immunogens of Treponema pallidum are proteolipids. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2872–2877. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2872-2877.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. L., Chang P., McDowall A. W., Radolf J. D. The outer membrane, not a coat of host proteins, limits antigenicity of virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):1076–1083. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.1076-1083.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Johnson R. C., Miller J. N., Sykes J. A. Characterization of the attachment of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) to cultured mammalian cells and the potential relationship of attachment to pathogenicity. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):467–478. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.467-478.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Miller J. N., Sykes J. A. Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) in tissue cultures: cellular attachment, entry, and survival. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):1133–1140. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.1133-1140.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanff P. A., Bishop N. H., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Humoral immune response in experimental syphilis to polypeptides of Treponema pallidum. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1973–1977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanff P. A., Fehniger T. E., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Humoral immune response in human syphilis to polypeptides of Treponema pallidum. J Immunol. 1982 Sep;129(3):1287–1291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindersson P., Cockayne A., Schouls L. M., van Emden J. D. Immunochemical characterization and purification of Treponema pallidum antigen TpD expressed by Escherichia coli K12. Sex Transm Dis. 1986 Oct-Dec;13(4):237–244. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198610000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. A., Marchitto K. S., Miller J. N., Norgard M. V. Monoclonal antibody with hemagglutination, immobilization, and neutralization activities defines an immunodominant, 47,000 mol wt, surface-exposed immunogen of Treponema pallidum (Nichols). J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1404–1420. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleemann W., Grant C. W., McConnell H. M. Lipid phase separations and protein distribution in membranes. J Supramol Struct. 1974;2(5-6):609–616. doi: 10.1002/jss.400020508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleemann W., McConnell H. M. Lateral phase separations in Escherichia coli membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 29;345(2):220–230. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90260-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livermore B. P., Johnson R. C. Lipids of the Spirochaetales: comparison of the lipids of several members of the genera Spirochaeta, Treponema, and Leptospira. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1268–1273. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1268-1273.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukehart S. A., Miller J. N. Demonstration of the in vitro phagocytosis of Treponema pallidum by rabbit peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):2014–2024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGNUSON H. J., THOMAS E. W., OLANSKY S., KAPLAN B. I., DE MELLO L., CUTLER J. C. Inoculation syphilis in human volunteers. Medicine (Baltimore) 1956 Feb;35(1):33–82. doi: 10.1097/00005792-195602000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGNUSON H. J., THOMPSON F. A., Jr, McLEOD C. P. Relationship between treponemal immobilizing antibodies and acquired immunity in experimental syphilis. J Immunol. 1951 Jul;67(1):41–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCLEOD C. P., MAGNUSON H. J. Production of immobilizing antibodies unaccompanied by active immunity to Treponema pallidum as shown by injecting rabbits and mice with the killed organisms. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1953 Jan;37(1):9–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. N. Immunity in experimental syphilis. VI. Successful vaccination of rabbits with Treponema pallidum, Nichols strain, attenuated by -irradiation. J Immunol. 1973 May;110(5):1206–1215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NELSON R. A., Jr, DIESENDRUCK J. A., ZHEUTLIN H. E. C., STACK P. S., BARNETT M. Studies on treponemal immobilizing antibodies in syphilis. I. Techniques of measurement and factors influencing immobilization. J Immunol. 1951 Jun;66(6):667–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overath P., Brenner M., Gulik-Krzywicki T., Shechter E., Letellier L. Lipid phase transitions in cytoplasmic and outer membranes of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 6;389(2):358–369. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90328-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto da Silva P., Branton D. Membrane splitting in freeze-ethching. Covalently bound ferritin as a membrane marker. J Cell Biol. 1970 Jun;45(3):598–605. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.3.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell B. K., Swancutt M. A., Radolf J. D. Lipid modification of the 15 kiloDalton major membrane immunogen of Treponema pallidum. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Aug;4(8):1371–1379. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Chamberlain N. R., Clausell A., Norgard M. V. Identification and localization of integral membrane proteins of virulent Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum by phase partitioning with the nonionic detergent triton X-114. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):490–498. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.490-498.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V., Schulz W. W. Outer membrane ultrastructure explains the limited antigenicity of virulent Treponema pallidum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):2051–2055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.2051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock P., Allietta M., Young W. W., Jr, Thompson T. E., Tillack T. W. Organization of glycosphingolipids in phosphatidylcholine bilayers: use of antibody molecules and Fab fragments as morphologic markers. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 11;29(36):8484–8490. doi: 10.1021/bi00488a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schouls L. M., Mout R., Dekker J., van Embden J. D. Characterization of lipid-modified immunogenic proteins of Treponema pallidum expressed in Escherichia coli. Microb Pathog. 1989 Sep;7(3):175–188. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm L. V., Hodinka R. L., Wyrick P. B., Bassford P. J., Jr Changes in the cell surface properties of Treponema pallidum that occur during in vitro incubation of freshly extracted organisms. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2255–2261. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2255-2261.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swancutt M. A., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. The 34-kilodalton membrane immunogen of Treponema pallidum is a lipoprotein. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):384–392. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.384-392.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swancutt M. A., Twehous D. A., Norgard M. V. Monoclonal antibody selection and analysis of a recombinant DNA-derived surface immunogen of Treponema pallidum expressed in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):110–119. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.110-119.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillack T. W., Scott R. E., Marchesi V. T. The structure of erythrocyte membranes studied by freeze-etching. II. Localization of receptors for phytohemagglutinin and influenza virus to the intramembranous particles. J Exp Med. 1972 Jun 1;135(6):1209–1227. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.6.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkleij A. J., Ververgaert P. H., van Deenen L. L., Elbers P. F. Phase transitions of phospholipid bilayers and membranes of Acholeplasma laidlawii B visualized by freeze fracturing electron microscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 2;288(2):326–332. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90253-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Váczi L., Király K., Réthy A. Lipid composition of treponemal strains. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1966;13(1):79–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker E. M., Zampighi G. A., Blanco D. R., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Demonstration of rare protein in the outer membrane of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum by freeze-fracture analysis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5005–5011. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5005-5011.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]