Abstract
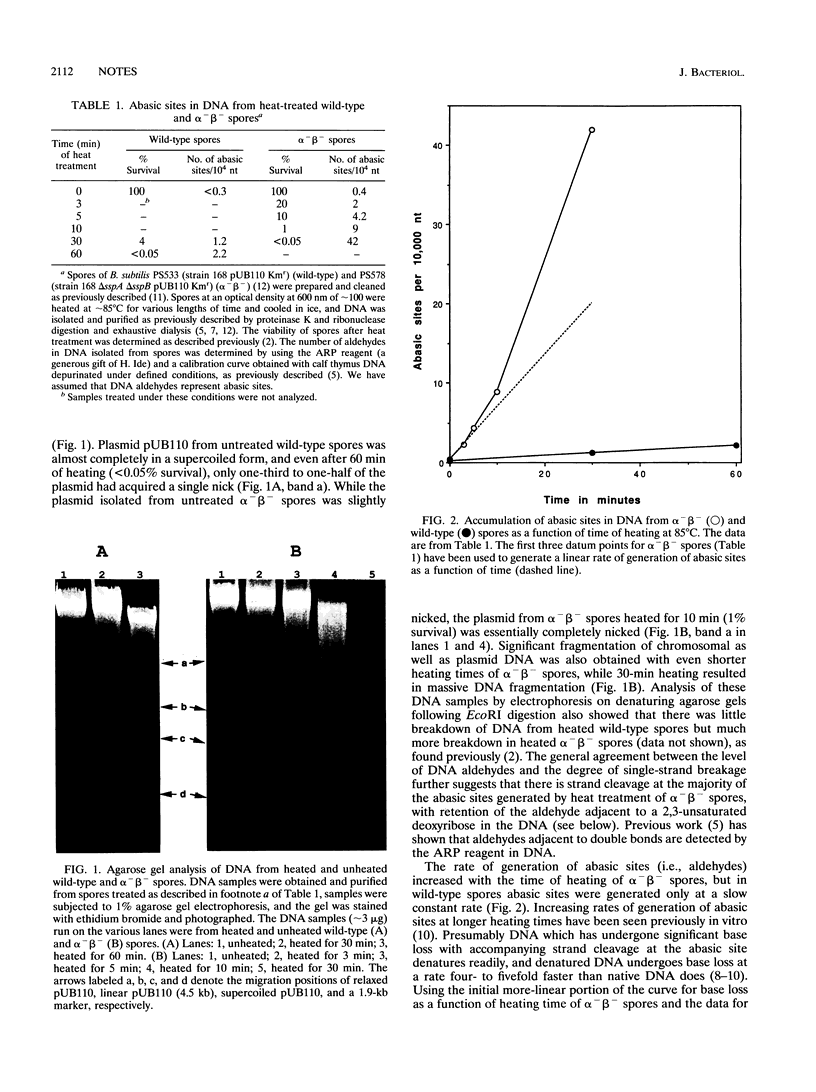
Previous work has shown that lethal heat treatment of Bacillus subtilis spores lacking the major DNA-binding proteins SASP-alpha and -beta (alpha-beta- spores) causes significant DNA damage, including many single-strand breaks. In this work we have used a reagent specific for aldehydes present in abasic sites in DNA to show that DNA from wild-type spores killed by heat treatment to levels of < 0.05% survival had at most two aldehydes (i.e., abasic sites) per 10(4) nucleotides, while DNA from alpha(-)beta- spores killed to similar levels had 7 to 20 times as many abasic sites per 10(4) nucleotides. These data were generally consistent with the level of single-strand breaks in DNA from these heated spores and strongly suggest that a major mechanism responsible for the heat killing of alpha(-)beta- (but not wild-type) spores is DNA depurination followed by strand breakage at the resultant abasic site. In contrast, hydrogen peroxide killing of alpha(-)beta - spores was not accompanied by generation of a high level of DNA aldehydes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Doetsch P. W., Cunningham R. P. The enzymology of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonucleases. Mutat Res. 1990 Sep-Nov;236(2-3):173–201. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(90)90004-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairhead H., Setlow B., Setlow P. Prevention of DNA damage in spores and in vitro by small, acid-soluble proteins from Bacillus species. J Bacteriol. 1993 Mar;175(5):1367–1374. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.5.1367-1374.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson F. Chemical changes induced in DNA by ionizing radiation. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1985;32:115–154. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60347-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ide H., Akamatsu K., Kimura Y., Michiue K., Makino K., Asaeda A., Takamori Y., Kubo K. Synthesis and damage specificity of a novel probe for the detection of abasic sites in DNA. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 17;32(32):8276–8283. doi: 10.1021/bi00083a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imlay J. A., Linn S. DNA damage and oxygen radical toxicity. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1302–1309. doi: 10.1126/science.3287616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo K., Ide H., Wallace S. S., Kow Y. W. A novel, sensitive, and specific assay for abasic sites, the most commonly produced DNA lesion. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 14;31(14):3703–3708. doi: 10.1021/bi00129a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Andersson A. Rate of chain breakage at apurinic sites in double-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1972 Sep 12;11(19):3618–3623. doi: 10.1021/bi00769a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Karlström O. Heat-induced depyrimidination of deoxyribonucleic acid in neutral solution. Biochemistry. 1973 Dec 4;12(25):5151–5154. doi: 10.1021/bi00749a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Nyberg B. Rate of depurination of native deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1972 Sep 12;11(19):3610–3618. doi: 10.1021/bi00769a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. M., Setlow P. Essential role of small, acid-soluble spore proteins in resistance of Bacillus subtilis spores to UV light. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):174–178. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.174-178.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson W. L., Setlow P. Dramatic increase in negative superhelicity of plasmid DNA in the forespore compartment of sporulating cells of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):7–14. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.7-14.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow B., Setlow P. Binding of small, acid-soluble spore proteins to DNA plays a significant role in the resistance of Bacillus subtilis spores to hydrogen peroxide. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Oct;59(10):3418–3423. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.10.3418-3423.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow B., Setlow P. Measurements of the pH within dormant and germinated bacterial spores. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2474–2476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow P. I will survive: protecting and repairing spore DNA. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(9):2737–2741. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.9.2737-2741.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow P. Small, acid-soluble spore proteins of Bacillus species: structure, synthesis, genetics, function, and degradation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:319–338. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace S. S. AP endonucleases and DNA glycosylases that recognize oxidative DNA damage. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1988;12(4):431–477. doi: 10.1002/em.2860120411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]