Abstract
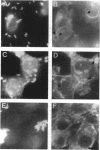
N1308, a chromosomal Tn5 mutant of Shigella flexneri 2a, was described previously as a lipopolysaccharide (LPS) mutant with a short O side chain. N1308 formed foci, but not plaques, in LLC-MK2 cell monolayers and was negative in the Serény test. In this study, the wild-type locus inactivated in N1308 was cloned and further defined by means of complementation analysis. A 4.3-kb BstEII-XhoI fragment of S. flexneri 2a YSH6200 DNA was sufficient to restore both normal LPS and virulence phenotype to the mutant. DNA sequencing of this region revealed four genes, rfbA, rfbB, rfbC, and rfbD, encoding the enzymes required for the biosynthesis of activated rhamnose. The four genes were expressed in Escherichia coli, and the expected protein products were visualized by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. N1308 was shown to have normal levels of surface IpaC and IpaD, while a Western blot (immunoblot) of whole-cell lysates or outer membrane fractions indicated an elevated level of appropriately localized VirG. An in vitro invasion assay revealed that N1308 had normal primary invasive capacity and was able to multiply and move normally within the initial infected cell. However, it exhibited a significant reduction in its ability to spread from cell to cell in the monolayer. A double immunofluorescence assay revealed differences between LLC-MK2 cells infected with the wild-type YSH6000 and those infected with N1308. The wild-type bacteria elicited the formation of the characteristic F-actin tails, whereas N1308 failed to do so. However, N1308 was capable of inducing deposition of F-actin, which accumulated in a peribacterial fashion with only slight, if any, unipolar accumulation of the cytoskeletal protein.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler B., Sasakawa C., Tobe T., Makino S., Komatsu K., Yoshikawa M. A dual transcriptional activation system for the 230 kb plasmid genes coding for virulence-associated antigens of Shigella flexneri. Mol Microbiol. 1989 May;3(5):627–635. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews G. P., Hromockyj A. E., Coker C., Maurelli A. T. Two novel virulence loci, mxiA and mxiB, in Shigella flexneri 2a facilitate excretion of invasion plasmid antigens. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):1997–2005. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.1997-2005.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastin D. A., Stevenson G., Brown P. K., Haase A., Reeves P. R. Repeat unit polysaccharides of bacteria: a model for polymerization resembling that of ribosomes and fatty acid synthetase, with a novel mechanism for determining chain length. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Mar;7(5):725–734. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batchelor R. A., Alifano P., Biffali E., Hull S. I., Hull R. A. Nucleotide sequences of the genes regulating O-polysaccharide antigen chain length (rol) from Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: protein homology and functional complementation. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(16):5228–5236. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.16.5228-5236.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardini M. L., Fontaine A., Sansonetti P. J. The two-component regulatory system ompR-envZ controls the virulence of Shigella flexneri. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6274–6281. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6274-6281.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardini M. L., Mounier J., d'Hauteville H., Coquis-Rondon M., Sansonetti P. J. Identification of icsA, a plasmid locus of Shigella flexneri that governs bacterial intra- and intercellular spread through interaction with F-actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3867–3871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. K., Romana L. K., Reeves P. R. Cloning of the rfb gene cluster of a group C2 Salmonella strain: comparison with the rfb regions of groups B and D. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Aug;5(8):1873–1881. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. K., Romana L. K., Reeves P. R. Molecular analysis of the rfb gene cluster of Salmonella serovar muenchen (strain M67): the genetic basis of the polymorphism between groups C2 and B. Mol Microbiol. 1992 May;6(10):1385–1394. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00859.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheah K. C., Beger D. W., Manning P. A. Molecular cloning and genetic analysis of the rfb region from Shigella flexneri type 6 in Escherichia coli K-12. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Oct 1;67(2):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90356-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc P., Sansonetti P. J. Entry of Shigella flexneri into HeLa cells: evidence for directed phagocytosis involving actin polymerization and myosin accumulation. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2681–2688. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2681-2688.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins L. V., Hackett J. Molecular cloning, characterization, and nucleotide sequence of the rfc gene, which encodes an O-antigen polymerase of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(8):2521–2529. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.8.2521-2529.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formal S. B., Gemski P., Baron L. S., Labrec E. H. Genetic Transfer of Shigella flexneri Antigens to Escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1970 Mar;1(3):279–287. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.3.279-287.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. B., Bârzu O., Parsot C., Sansonetti P. J. Unipolar localization and ATPase activity of IcsA, a Shigella flexneri protein involved in intracellular movement. J Bacteriol. 1993 Apr;175(8):2189–2196. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.8.2189-2196.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- High N., Mounier J., Prévost M. C., Sansonetti P. J. IpaB of Shigella flexneri causes entry into epithelial cells and escape from the phagocytic vacuole. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1991–1999. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05253.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hromockyj A. E., Tucker S. C., Maurelli A. T. Temperature regulation of Shigella virulence: identification of the repressor gene virR, an analogue of hns, and partial complementation by tyrosyl transfer RNA (tRNA1(Tyr)). Mol Microbiol. 1992 Aug;6(15):2113–2124. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang X. M., Neal B., Santiago F., Lee S. J., Romana L. K., Reeves P. R. Structure and sequence of the rfb (O antigen) gene cluster of Salmonella serovar typhimurium (strain LT2). Mol Microbiol. 1991 Mar;5(3):695–713. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00741.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klena J. D., Schnaitman C. A. Function of the rfb gene cluster and the rfe gene in the synthesis of O antigen by Shigella dysenteriae 1. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jul;9(2):393–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01700.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn M., Prévost M. C., Mounier J., Sansonetti P. J. A nonvirulent mutant of Listeria monocytogenes does not move intracellularly but still induces polymerization of actin. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3477–3486. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3477-3486.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawlor K. M., Daskaleros P. A., Robinson R. E., Payne S. M. Virulence of iron transport mutants of Shigella flexneri and utilization of host iron compounds. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):594–599. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.594-599.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. J., Romana L. K., Reeves P. R. Sequence and structural analysis of the rfb (O antigen) gene cluster from a group C1 Salmonella enterica strain. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Sep;138(9):1843–1855. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-9-1843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lett M. C., Sasakawa C., Okada N., Sakai T., Makino S., Yamada M., Komatsu K., Yoshikawa M. virG, a plasmid-coded virulence gene of Shigella flexneri: identification of the virG protein and determination of the complete coding sequence. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):353–359. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.353-359.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Kärnell A., Weintraub A. The lipopolysaccharide of Shigella bacteria as a virulence factor. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Mar-Apr;13 (Suppl 4):S279–S284. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.supplement_4.s279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macpherson D. F., Morona R., Beger D. W., Cheah K. C., Manning P. A. Genetic analysis of the rfb region of Shigella flexneri encoding the Y serotype O-antigen specificity. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jun;5(6):1491–1499. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00795.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Sasakawa C., Kamata K., Kurata T., Yoshikawa M. A genetic determinant required for continuous reinfection of adjacent cells on large plasmid in S. flexneri 2a. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):551–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90880-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata N., Sasakawa C., Okada N., Tobe T., Fukuda I., Suzuki T., Komatsu K., Yoshikawa M. Identification and characterization of virK, a virulence-associated large plasmid gene essential for intercellular spreading of Shigella flexneri. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Aug;6(16):2387–2395. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nassif X., Mazert M. C., Mounier J., Sansonetti P. J. Evaluation with an iuc::Tn10 mutant of the role of aerobactin production in the virulence of Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):1963–1969. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.1963-1969.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada N., Sasakawa C., Tobe T., Talukder K. A., Komatsu K., Yoshikawa M. Construction of a physical map of the chromosome of Shigella flexneri 2a and the direct assignment of nine virulence-associated loci identified by Tn5 insertions. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Sep;5(9):2171–2180. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02147.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada N., Sasakawa C., Tobe T., Yamada M., Nagai S., Talukder K. A., Komatsu K., Kanegasaki S., Yoshikawa M. Virulence-associated chromosomal loci of Shigella flexneri identified by random Tn5 insertion mutagenesis. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jan;5(1):187–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01839.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura N., Nagai T., Nakaya R., Kondo S., Murakami M., Hisatsune K. HeLa cell invasiveness and O antigen of Shigella flexneri as separate and prerequisite attributes of virulence to evoke keratoconjunctivitis in guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):505–513. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.505-513.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura N., Nakaya R. Rough mutant of Shigella flexneri 2a that penetrates tissue culture cells but does not evoke keratoconjunctivitis in guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):4–8. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.4-8.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. T., Kloser A. W., Schnaitman C. A., Stein M. A., Gottesman S., Gibson B. W. Role of the rfaG and rfaP genes in determining the lipopolysaccharide core structure and cell surface properties of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(8):2525–2538. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.8.2525-2538.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrovskaya V. G., Licheva T. A. A provisional chromosome map of Shigella and the regions related to pathogenicity. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1982;29(1):41–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves P. Evolution of Salmonella O antigen variation by interspecific gene transfer on a large scale. Trends Genet. 1993 Jan;9(1):17–22. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90067-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai T., Sasakawa C., Yoshikawa M. Expression of four virulence antigens of Shigella flexneri is positively regulated at the transcriptional level by the 30 kiloDalton virF protein. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Sep;2(5):589–597. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger J. M., Sanger J. W., Southwick F. S. Host cell actin assembly is necessary and likely to provide the propulsive force for intracellular movement of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1992 Sep;60(9):3609–3619. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.9.3609-3619.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa C., Adler B., Tobe T., Okada N., Nagai S., Komatsu K., Yoshikawa M. Functional organization and nucleotide sequence of virulence Region-2 on the large virulence plasmid in Shigella flexneri 2a. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Sep;3(9):1191–1201. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00269.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa C., Buysse J. M., Watanabe H. The large virulence plasmid of Shigella. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1992;180:21–44. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-77238-2_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa C., Kamata K., Sakai T., Makino S., Yamada M., Okada N., Yoshikawa M. Virulence-associated genetic regions comprising 31 kilobases of the 230-kilobase plasmid in Shigella flexneri 2a. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2480–2484. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2480-2484.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa C., Kamata K., Sakai T., Murayama S. Y., Makino S., Yoshikawa M. Molecular alteration of the 140-megadalton plasmid associated with loss of virulence and Congo red binding activity in Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):470–475. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.470-475.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa C., Komatsu K., Tobe T., Suzuki T., Yoshikawa M. Eight genes in region 5 that form an operon are essential for invasion of epithelial cells by Shigella flexneri 2a. J Bacteriol. 1993 Apr;175(8):2334–2346. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.8.2334-2346.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa C., Makino S., Kamata K., Yoshikawa M. Isolation, characterization, and mapping of Tn5 insertions into the 140-megadalton invasion plasmid defective in the mouse Sereny test in Shigella flexneri 2a. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):32–36. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.32-36.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen K., Nikaido H. Lipopolysaccharide structure required for in vitro trimerization of Escherichia coli OmpF porin. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):926–928. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.926-928.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. A., Romanowska E. Structure and biology of Shigella flexneri O antigens. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Jun;23(4):289–302. doi: 10.1099/00222615-23-4-289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobe T., Sasakawa C., Okada N., Honma Y., Yoshikawa M. vacB, a novel chromosomal gene required for expression of virulence genes on the large plasmid of Shigella flexneri. J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(20):6359–6367. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.20.6359-6367.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasselon T., Mounier J., Hellio R., Sansonetti P. J. Movement along actin filaments of the perijunctional area and de novo polymerization of cellular actin are required for Shigella flexneri colonization of epithelial Caco-2 cell monolayers. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):1031–1040. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.1031-1040.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasselon T., Mounier J., Prevost M. C., Hellio R., Sansonetti P. J. Stress fiber-based movement of Shigella flexneri within cells. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1723–1732. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1723-1732.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan M. M., Buysse J. M., Oaks E. V. Surface presentation of Shigella flexneri invasion plasmid antigens requires the products of the spa locus. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(6):1990–2001. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.6.1990-2001.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma N. K., Brandt J. M., Verma D. J., Lindberg A. A. Molecular characterization of the O-acetyl transferase gene of converting bacteriophage SF6 that adds group antigen 6 to Shigella flexneri. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jan;5(1):71–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao Z., Liu H., Valvano M. A. Acetylation of O-specific lipopolysaccharides from Shigella flexneri 3a and 2a occurs in Escherichia coli K-12 carrying cloned S. flexneri 3a and 2a rfb genes. J Bacteriol. 1992 Dec;174(23):7500–7508. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.23.7500-7508.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa M., Sasakawa C. Molecular pathogenesis of shigellosis: a review. Microbiol Immunol. 1991;35(10):809–824. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1991.tb02021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuasa R., Nakane K., Nikaido H. Structure of cell wall lipopolysaccharide from Salmonella typhimurium. Structure of lipopolysaccharide from a Semirough mutant. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jul;15(1):63–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00976.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- d'Hauteville H., Sansonetti P. J. Phosphorylation of IcsA by cAMP-dependent protein kinase and its effect on intracellular spread of Shigella flexneri. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Apr;6(7):833–841. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01534.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]