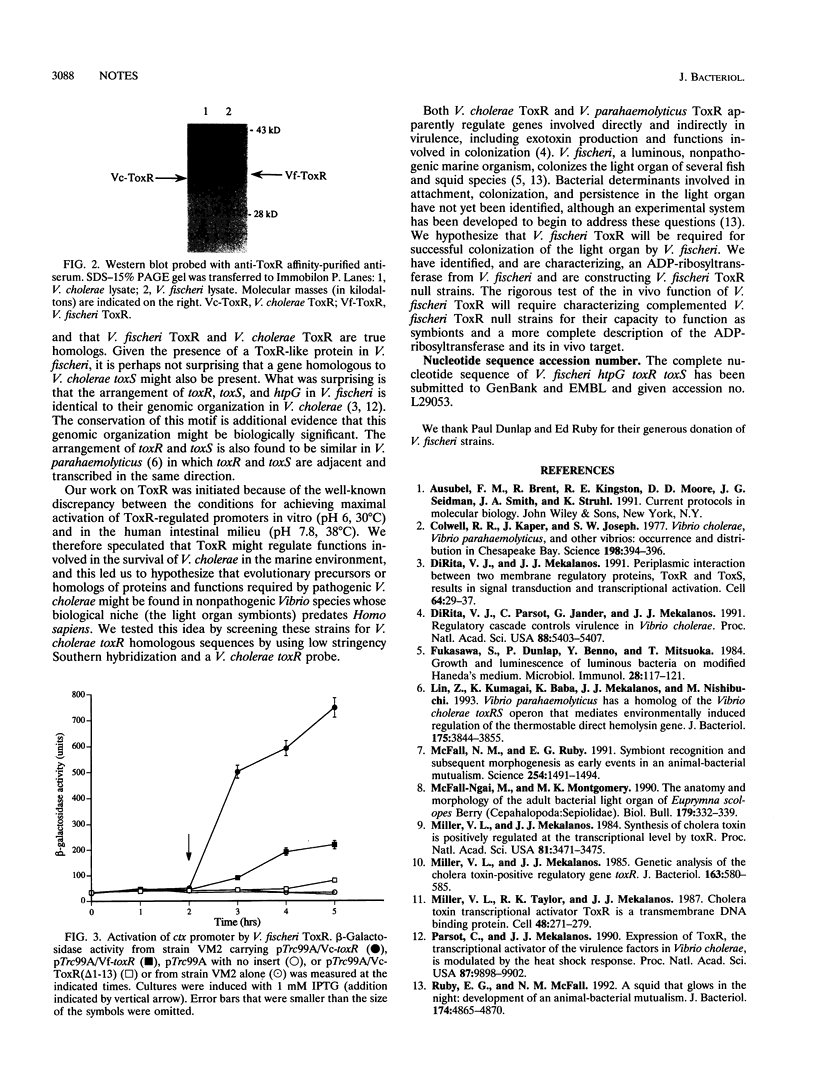
Abstract
A cross-hybridizing DNA fragment to Vibrio cholerae toxR was cloned from the nonpathogenic light organ symbiont Vibrio fischeri, and three proteins homologous to V. cholerae ToxR, ToxS, and HtpG were deduced from its DNA sequence. V. fischeri ToxR was found to activate a V. cholerae ToxR-regulated promoter, and an antiserum raised against the amino-terminal domain of V. cholerae ToxR cross-reacts V. fischeri ToxR.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Colwell R. R., Kaper J., Joseph S. W. Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and other vibrios: occurrence and distribution in Chesapeake Bay. Science. 1977 Oct 28;198(4315):394–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRita V. J., Mekalanos J. J. Periplasmic interaction between two membrane regulatory proteins, ToxR and ToxS, results in signal transduction and transcriptional activation. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):29–37. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90206-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRita V. J., Parsot C., Jander G., Mekalanos J. J. Regulatory cascade controls virulence in Vibrio cholerae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5403–5407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukasawa S., Dunlap P., Benno Y., Mitsuoka T. Growth and luminescence of luminous bacteria on modified Haneda's medium. Microbiol Immunol. 1984;28(1):117–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1984.tb02952.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Z., Kumagai K., Baba K., Mekalanos J. J., Nishibuchi M. Vibrio parahaemolyticus has a homolog of the Vibrio cholerae toxRS operon that mediates environmentally induced regulation of the thermostable direct hemolysin gene. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jun;175(12):3844–3855. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.12.3844-3855.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFall-Ngai M. J., Ruby E. G. Symbiont recognition and subsequent morphogenesis as early events in an animal-bacterial mutualism. Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1491–1494. doi: 10.1126/science.1962208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. Genetic analysis of the cholera toxin-positive regulatory gene toxR. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):580–585. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.580-585.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. Synthesis of cholera toxin is positively regulated at the transcriptional level by toxR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3471–3475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Taylor R. K., Mekalanos J. J. Cholera toxin transcriptional activator toxR is a transmembrane DNA binding protein. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):271–279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90430-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsot C., Mekalanos J. J. Expression of ToxR, the transcriptional activator of the virulence factors in Vibrio cholerae, is modulated by the heat shock response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9898–9902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby E. G., McFall-Ngai M. J. A squid that glows in the night: development of an animal-bacterial mutualism. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(15):4865–4870. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.15.4865-4870.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



