Abstract
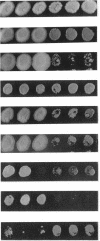
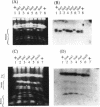
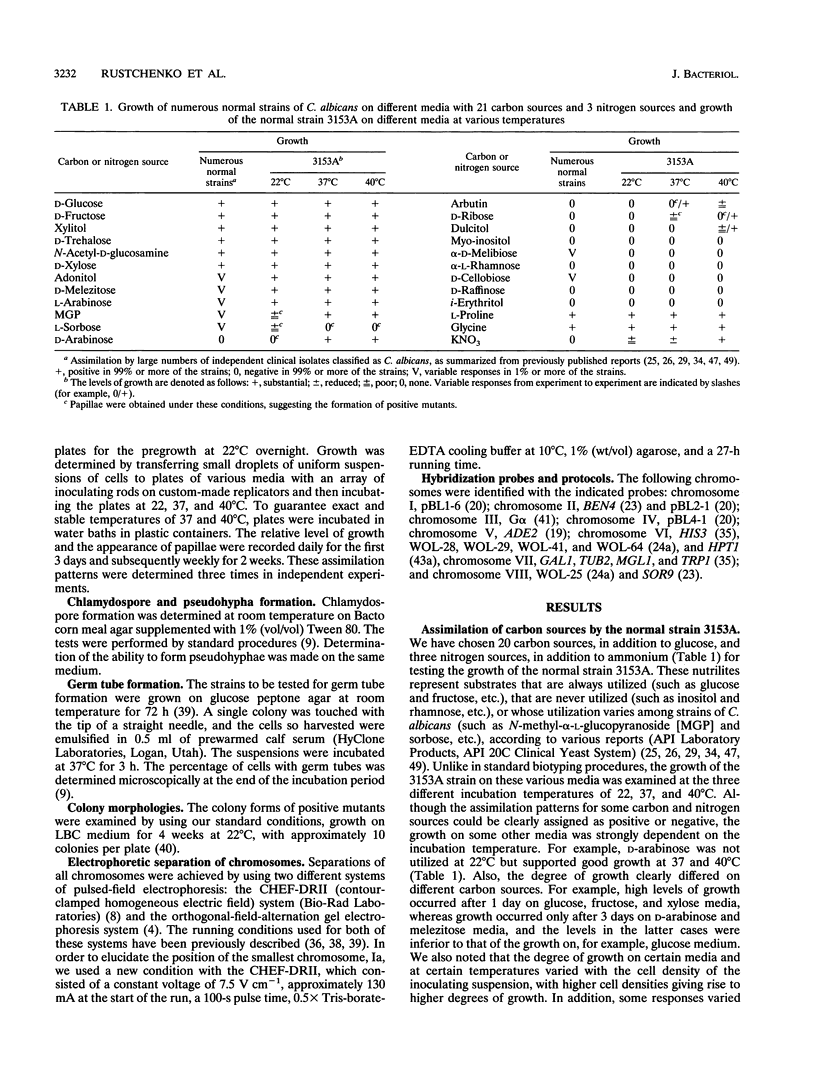
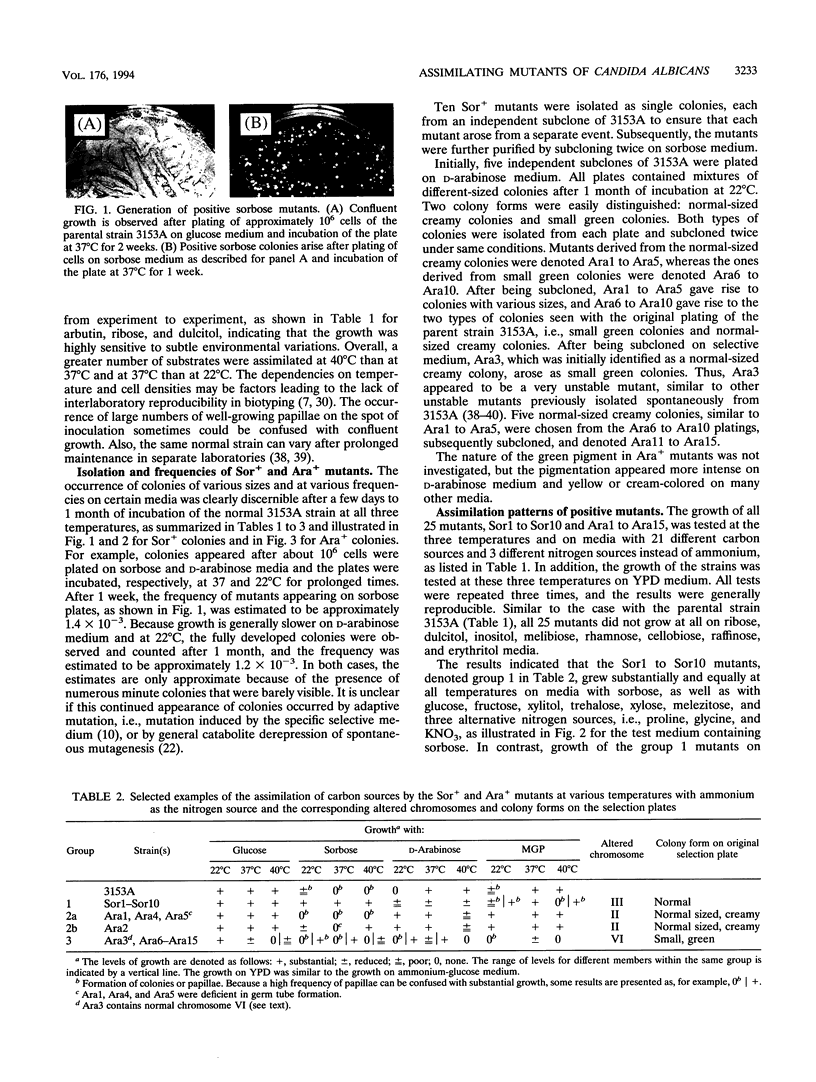
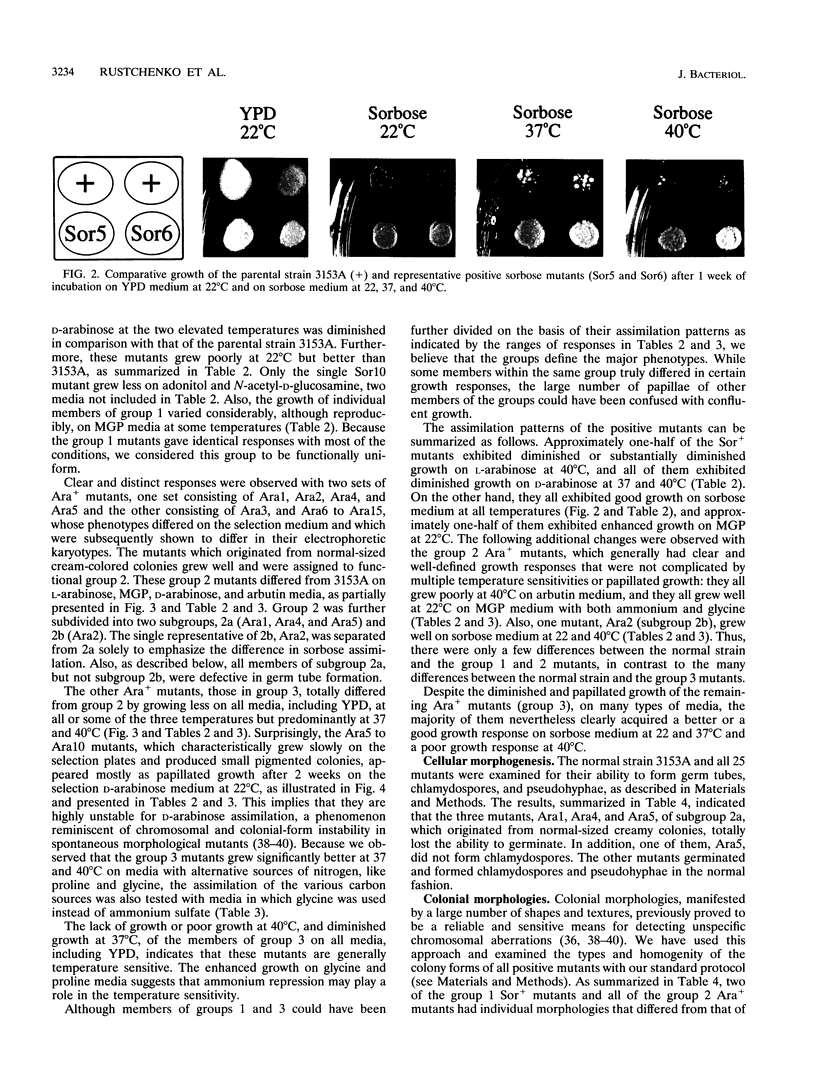
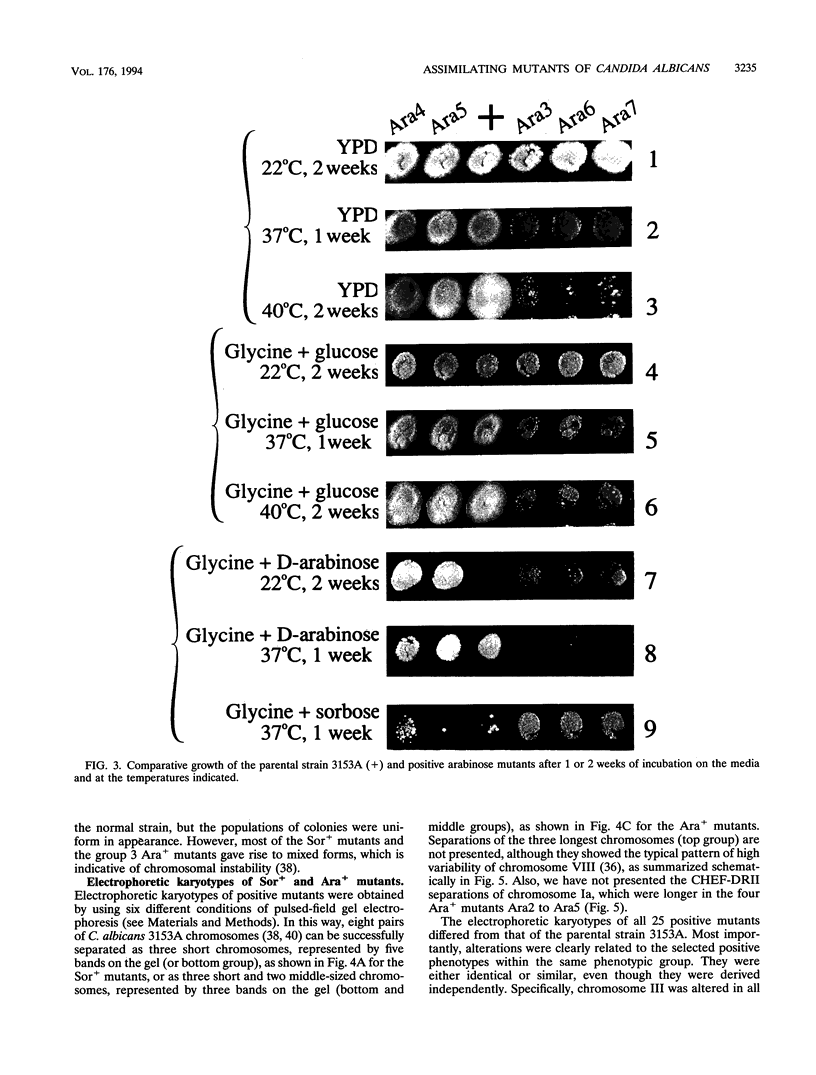
We have demonstrated that a normal laboratory strain of Candida albicans spontaneously produces mutants which acquire the ability to assimilate certain carbon sources that are not utilized by the parental strain. The examination of mutants acquiring the ability to utilize either sorbose or D-arabinose revealed a few additional phenotypic changes, including the gain and loss of the capacity to assimilate other carbon sources. The change of assimilation patterns resembled the polymorphic variation of assimilation patterns found among different wild-type strains of C. albicans. Most importantly, these sorbose- and D-arabinose-positive mutants were associated with chromosomal rearrangements, with each class of positive mutants having alterations of specific chromosomes. These findings demonstrated for the first time that chromosomal alterations in C. albicans are involved in genetic variation of fundamental functions of this asexual microorganism.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown-Thomsen J. Reverse variations between Candida albicans and Candida tropicalis? Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1966;66(1):143–144. doi: 10.1111/apm.1966.66.1.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. H., Lengyel J. A., Langridge J. Evolution of a second gene for beta-galactosidase in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1841–1845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Separation of chromosomal DNA molecules from yeast by orthogonal-field-alternation gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5647–5664. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Osmond B. C., Botstein D. Genetic evidence for a silent SUC gene in yeast. Genetics. 1981 May;98(1):41–54. doi: 10.1093/genetics/98.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron M. J., Michels C. A. The naturally occurring alleles of MAL1 in Saccharomyces species evolved by various mutagenic processes including chromosomal rearrangement. Genetics. 1988 Sep;120(1):83–93. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childress C. M., Holder I. A., Neely A. N. Modifications of a Candida albicans biotyping system. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1392–1394. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1392-1394.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster P. L. Adaptive mutation: the uses of adversity. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1993;47:467–504. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.47.100193.002343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. G. Selection, adaptation, and bacterial operons. Genome. 1989;31(1):265–271. doi: 10.1139/g89-044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. G. Selection-induced mutations occur in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4300–4303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. G., Xu L. Nucleotide sequence, function, activation, and evolution of the cryptic asc operon of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Biol Evol. 1992 Jul;9(4):688–706. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. G., Yokoyama S., Calhoun D. H. Role of cryptic genes in microbial evolution. Mol Biol Evol. 1983 Dec;1(1):109–124. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwaguchi S., Homma M., Tanaka K. Variation in the electrophoretic karyotype analysed by the assignment of DNA probes in Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Dec;136(12):2433–2442. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-12-2433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch S. A pseudogene for a novel ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase of S. cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1147–1147. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz M. B., Cortelyou M. W., Kirsch D. R. Integrative transformation of Candida albicans, using a cloned Candida ADE2 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):142–149. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasker B. A., Carle G. F., Kobayashi G. S., Medoff G. Comparison of the separation of Candida albicans chromosome-sized DNA by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis techniques. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3783–3793. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. L., Buckley H. R., Campbell C. C. An amino acid liquid synthetic medium for the development of mycelial and yeast forms of Candida Albicans. Sabouraudia. 1975 Jul;13(2):148–153. doi: 10.1080/00362177585190271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee B. B., Koltin Y., Gorman J. A., Magee P. T. Assignment of cloned genes to the seven electrophoretically separated Candida albicans chromosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4721–4726. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malavasic M. J., Cihlar R. L. Growth response of several Candida albicans strains to inhibitory concentrations of heavy metals. J Med Vet Mycol. 1992;30(6):421–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michels C. A., Read E., Nat K., Charron M. J. The telomere-associated MAL3 locus of Saccharomyces is a tandem array of repeated genes. Yeast. 1992 Aug;8(8):655–665. doi: 10.1002/yea.320080809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumov G. I., Naumova E. S., Michels C. A. Genetic variation of the repeated MAL loci in natural populations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Saccharomyces paradoxus. Genetics. 1994 Mar;136(3):803–812. doi: 10.1093/genetics/136.3.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C., Abbott A. B. Modification and extension of tests for differentiation of Candida species and strains. Sabouraudia. 1983 Mar;21(1):79–81. doi: 10.1080/00362178385380111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C., Auger P., Krogh P., Neely A. N., Segal E. Biotyping of Candida albicans: results of an international collaborative survey. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1506–1509. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1506-1509.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker L. L., Hall B. G. Mechanisms of activation of the cryptic cel operon of Escherichia coli K12. Genetics. 1990 Mar;124(3):473–482. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.3.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. E., Felton J., Wright A. Insertion of DNA activates the cryptic bgl operon in E. coli K12. Nature. 1981 Oct 22;293(5834):625–629. doi: 10.1038/293625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. E., Mahadevan S., LeGrice S. F., Wright A. Enhancement of bacterial gene expression by insertion elements or by mutation in a CAP-cAMP binding site. J Mol Biol. 1986 Sep 5;191(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90424-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbluh A., Mevarech M., Koltin Y., Gorman J. A. Isolation of genes from Candida albicans by complementation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;200(3):500–502. doi: 10.1007/BF00425739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
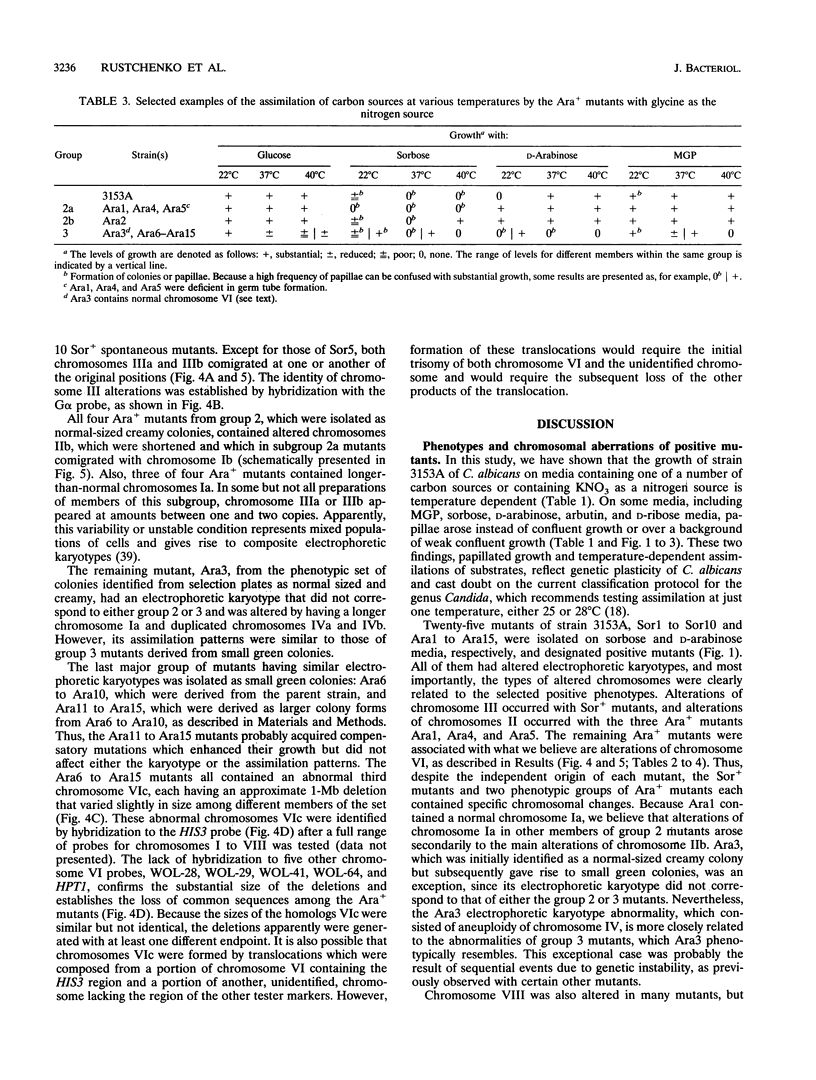
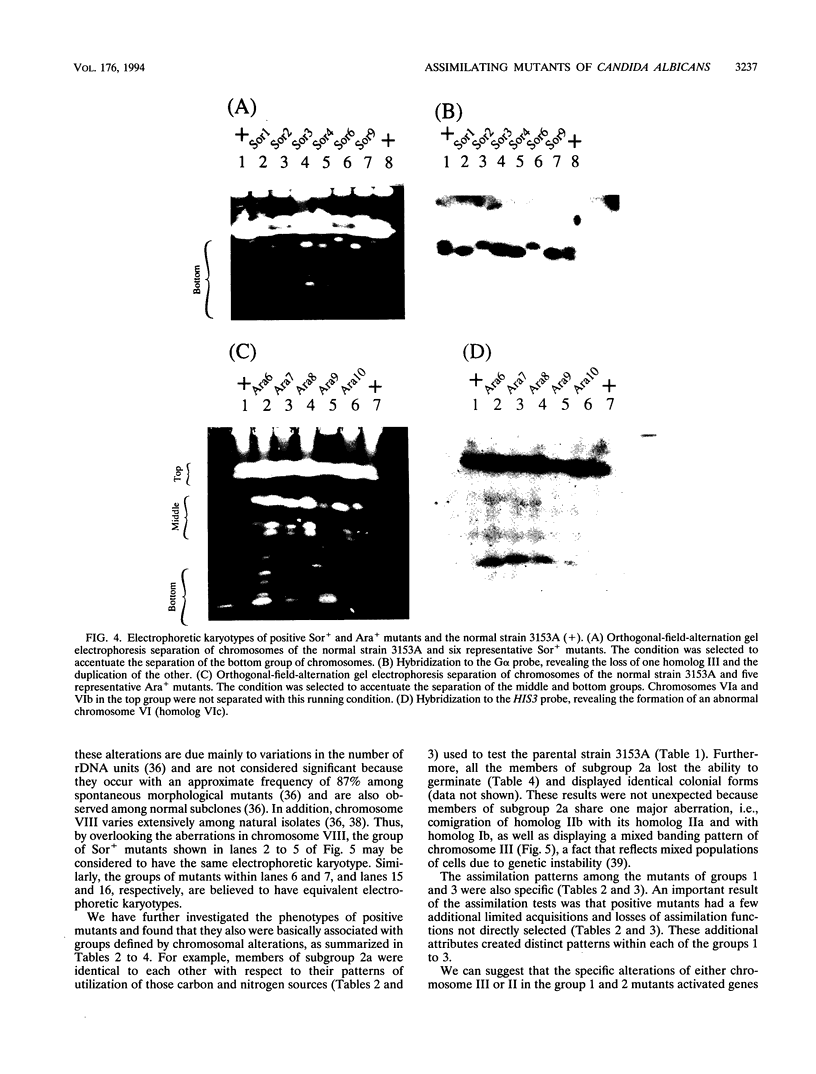
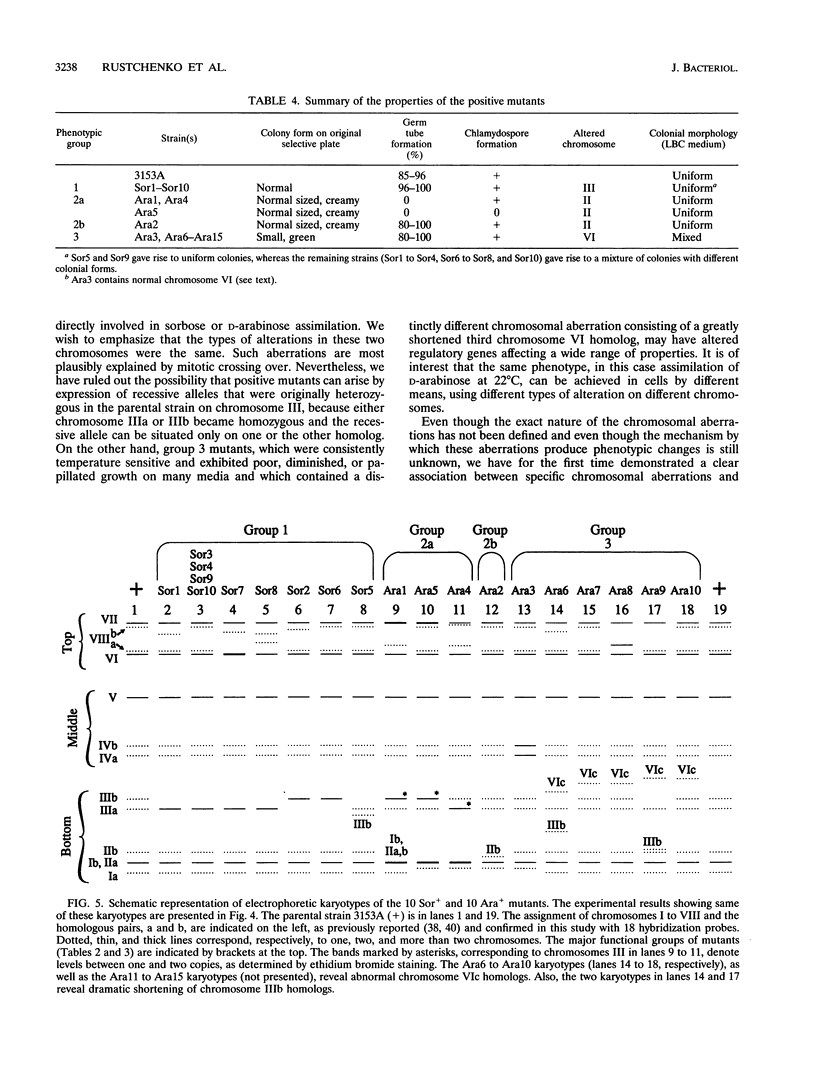
- Rustchenko-Bulgac E. P., Howard D. H. Multiple chromosomal and phenotypic changes in spontaneous mutants of Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1993 Jun;139(Pt 6):1195–1207. doi: 10.1099/00221287-139-6-1195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rustchenko-Bulgac E. P., Sherman F., Hicks J. B. Chromosomal rearrangements associated with morphological mutants provide a means for genetic variation of Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1276–1283. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1276-1283.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rustchenko-Bulgac E. P. Variations of Candida albicans electrophoretic karyotypes. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(20):6586–6596. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.20.6586-6596.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rustchenko E. P., Curran T. M., Sherman F. Variations in the number of ribosomal DNA units in morphological mutants and normal strains of Candida albicans and in normal strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1993 Nov;175(22):7189–7199. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.22.7189-7199.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadhu C., Hoekstra D., McEachern M. J., Reed S. I., Hicks J. B. A G-protein alpha subunit from asexual Candida albicans functions in the mating signal transduction pathway of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and is regulated by the a1-alpha 2 repressor. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):1977–1985. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarachek A., Brecher C. A., Rhoads D. D. Differentiation of Candida stellatoidea from C. albicans and C. tropicalis by temperature-dependent growth responses on defined media. Mycopathologia. 1981 Sep 11;75(3):179–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00482814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele D. F., Jinks-Robertson S. An examination of adaptive reversion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1992 Sep;132(1):9–21. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele D. F., Jinks-Robertson S. Time-dependent mitotic recombination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet. 1993 May-Jun;23(5-6):423–429. doi: 10.1007/BF00312629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickes B. L., Golin J. E., Kwon-Chung K. J. Chromosomal rearrangement in Candida stellatoidea results in a positive effect on phenotype. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1762–1771. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1762-1771.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson M. I., Samaranayake L. P., MacFarlane T. W. Biotypes of oral Candida albicans and Candida tropicalis isolates. J Med Vet Mycol. 1986 Feb;24(1):81–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson V. M., Paquin C. E. Homology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ADH4 to an iron-activated alcohol dehydrogenase from Zymomonas mobilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Sep;209(2):374–381. doi: 10.1007/BF00329668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]