Abstract
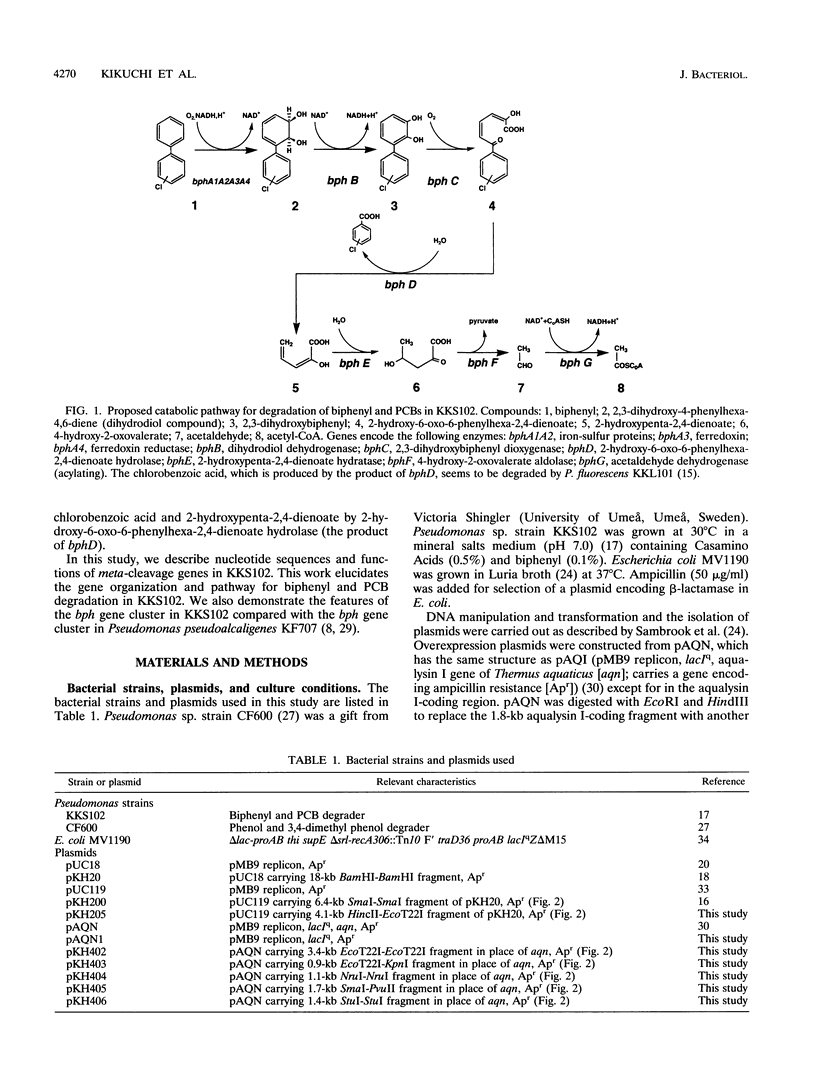
Pseudomonas sp. strain KKS102 is able to degrade biphenyl and polychlorinated biphenyls via the meta-cleavage pathway. We sequenced the upstream region of the bphA1A2A3BCD (open reading frame 1 [ORF1]) A4 and found four ORFs in this region. As the deduced amino acid sequences of the first, second, and third ORFs are homologous to the meta-cleavage enzymes from Pseudomonas sp. strain CF600 (V. Shingler, J. Powlowski, and U. Marklund, J. Bacteriol. 174:711-724, 1992), these ORFs have been named bphE, bphG, and bphF, respectively. The fourth ORF (ORF4) showed homology with ORF3 from Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes KF707 (K. Taira, J. Hirose, S. Hayashida, and K. Furukawa, J. Biol. Chem. 267:4844-4853, 1992), whose function is unknown. The functions of meta-cleavage enzymes (BphE, BphG, and BphF) were analyzed by using crude extracts of Escherichia coli which expressed the encoding genes. The results showed that bphE, bphG, and bphF encode 2-hydroxypenta-2,4-dienoate hydratase, acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (acylating), and 4-hydroxy-2-oxovalerate aldolase, respectively. The biphenyl and polychlorinated biphenyl degradation pathway of KKS102 is encoded by 12 genes in the order bphEGF (ORF4)A1A2A3BCD (ORF1)A4. The functions of ORF1 and ORF4 are unknown. The features of this bph gene cluster are discussed.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assinder S. J., Williams P. A. Comparison of the meta pathway operons on NAH plasmid pWW60-22 and TOL plasmid pWW53-4 and its evolutionary significance. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Oct;134(10):2769–2778. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-10-2769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assinder S. J., Williams P. A. The TOL plasmids: determinants of the catabolism of toluene and the xylenes. Adv Microb Physiol. 1990;31:1–69. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlage R. S., Hooper S. W., Sayler G. S. The TOL (pWW0) catabolic plasmid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1323–1328. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1323-1328.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collinsworth W. L., Chapman P. J., Dagley S. Stereospecific enzymes in the degradation of aromatic compounds by pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):922–931. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.922-931.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., GIBSON D. T. THE BACTERIAL DEGRADATION OF CATECHOL. Biochem J. 1965 May;95:466–474. doi: 10.1042/bj0950466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. The xylABC promoter from the Pseudomonas putida TOL plasmid is activated by nitrogen regulatory genes in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Apr;203(1):129–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00330393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Hirose J., Suyama A., Zaiki T., Hayashida S. Gene components responsible for discrete substrate specificity in the metabolism of biphenyl (bph operon) and toluene (tod operon). J Bacteriol. 1993 Aug;175(16):5224–5232. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.16.5224-5232.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harayama S., Rekik M. Bacterial aromatic ring-cleavage enzymes are classified into two different gene families. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15328–15333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harayama S., Rekik M. The meta cleavage operon of TOL degradative plasmid pWW0 comprises 13 genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Mar;221(1):113–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00280375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harayama S., Rekik M., Wasserfallen A., Bairoch A. Evolutionary relationships between catabolic pathways for aromatics: conservation of gene order and nucleotide sequences of catechol oxidation genes of pWW0 and NAH7 plasmids. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Dec;210(2):241–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00325689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn J. M., Harayama S., Timmis K. N. DNA sequence determination of the TOL plasmid (pWWO) xylGFJ genes of Pseudomonas putida: implications for the evolution of aromatic catabolism. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Oct;5(10):2459–2474. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., Nagata Y., Hinata M., Kimbara K., Fukuda M., Yano K., Takagi M. Identification of the bphA4 gene encoding ferredoxin reductase involved in biphenyl and polychlorinated biphenyl degradation in Pseudomonas sp. strain KKS102. J Bacteriol. 1994 Mar;176(6):1689–1694. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.6.1689-1694.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimbara K., Hashimoto T., Fukuda M., Koana T., Takagi M., Oishi M., Yano K. Cloning and sequencing of two tandem genes involved in degradation of 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl to benzoic acid in the polychlorinated biphenyl-degrading soil bacterium Pseudomonas sp. strain KKS102. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2740–2747. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2740-2747.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powlowski J., Sahlman L., Shingler V. Purification and properties of the physically associated meta-cleavage pathway enzymes 4-hydroxy-2-ketovalerate aldolase and aldehyde dehydrogenase (acylating) from Pseudomonas sp. strain CF600. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jan;175(2):377–385. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.2.377-385.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala-Trepat J. M., Murray K., Williams P. A. The metabolic divergence in the meta cleavage of catechols by Pseudomonas putida NCIB 10015. Physiological significance and evolutionary implications. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 24;28(3):347–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. Determinant of cistron specificity in bacterial ribosomes. Nature. 1975 Mar 6;254(5495):34–38. doi: 10.1038/254034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shingler V., Powlowski J., Marklund U. Nucleotide sequence and functional analysis of the complete phenol/3,4-dimethylphenol catabolic pathway of Pseudomonas sp. strain CF600. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):711–724. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.711-724.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R. The biodegradation of aromatic hydrocarbons by bacteria. Biodegradation. 1990;1(2-3):191–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00058836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira K., Hirose J., Hayashida S., Furukawa K. Analysis of bph operon from the polychlorinated biphenyl-degrading strain of Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes KF707. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4844–4853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira K., Hirose J., Hayashida S., Furukawa K. Analysis of bph operon from the polychlorinated biphenyl-degrading strain of Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes KF707. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4844–4853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada I., Kwon S. T., Miyata Y., Matsuzawa H., Ohta T. Unique precursor structure of an extracellular protease, aqualysin I, with NH2- and COOH-terminal pro-sequences and its processing in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6576–6581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thöny B., Hennecke H. The -24/-12 promoter comes of age. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;5(4):341–357. doi: 10.1016/0168-6445(89)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen K. M., Gunsalus I. C. Plasmid gene organization: naphthalene/salicylate oxidation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):874–878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meer J. R., de Vos W. M., Harayama S., Zehnder A. J. Molecular mechanisms of genetic adaptation to xenobiotic compounds. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Dec;56(4):677–694. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.4.677-694.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]