Abstract
Sequence analysis of a 6.3-kbp genomic EcoRI-fragment of Alcaligenes eutrophus, which was recently identified by using a dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase-specific DNA probe (A. Pries, S. Hein, and A. Steinbüchel, FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 97:227-234, 1992), and of an adjacent 1.0-kbp EcoRI fragment revealed the structural genes of the A. eutrophus pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, pdhA (2,685 bp), pdhB (1,659 bp), and pdhL (1,782 bp), encoding the pyruvate dehydrogenase (E1), the dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase (E2), and the dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (E3) components, respectively. Together with a 675-bp open reading frame (ORF3), the function of which remained unknown, these genes occur colinearly in one gene cluster in the order pdhA, pdhB, ORF3, and pdhL. The A. eutrophus pdhA, pdhB, and pdhL gene products exhibited significant homologies to the E1, E2, and E3 components, respectively, of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes of Escherichia coli and other organisms. Heterologous expression of pdhA, pdhB, and pdhL in E. coli K38(pGP1-2) and in the aceEF deletion mutant E. coli YYC202 was demonstrated by the occurrence of radiolabeled proteins in electropherograms, by spectrometric detection of enzyme activities, and by phenotypic complementation, respectively. A three-step procedure using chromatography on DEAE-Sephacel, chromatography on the triazine dye affinity medium Procion Blue H-ERD, and heat precipitation purified the E3 component of the A. eutrophus pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from the recombinant E. coli K38(pGP1-2, pT7-4SH7.3) 60-fold, recovering 41.5% of dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase activity. Microsequencing of the purified E3 component revealed an amino acid sequence which corresponded to the N-terminal amino acid sequence deduced from the nucleotide sequence of pdhL. The N-terminal region of PdhL comprising amino acids 1 to 112 was distinguished from all other known dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenases. It resembled the N terminus of dihydrolipoamide acyltransferases, and it contained one single lipoyl domain which was separated by an adjacent hinge region from the C-terminal region of the protein that exhibited high homology to classical dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenases.
Full text
PDF












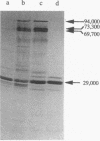
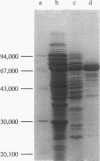
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appleyard R K. Segregation of New Lysogenic Types during Growth of a Doubly Lysogenic Strain Derived from Escherichia Coli K12. Genetics. 1954 Jul;39(4):440–452. doi: 10.1093/genetics/39.4.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson T., Hammond P. M., Hartwell R. D., Hughes P., Scawen M. D., Sherwood R. F., Small D. A., Bruton C. J., Harvey M. J., Lowe C. R. Triazine-dye affinity; chromatography. Biochem Soc Trans. 1981 Aug;9(4):290–293. doi: 10.1042/bst0090290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausubel F. M. Regulation of nitrogen fixation genes. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90294-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Findlay P. R., Johnson M. W. The relationship between base composition and codon usage in bacterial genes and its use for the simple and reliable identification of protein-coding sequences. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borges A., Hawkins C. F., Packman L. C., Perham R. N. Cloning and sequence analysis of the genes encoding the dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase and dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase components of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Bacillus stearothermophilus. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 26;194(1):95–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19432.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browner M. F., Taroni F., Sztul E., Rosenberg L. E. Sequence analysis, biogenesis, and mitochondrial import of the alpha-subunit of rat liver propionyl-CoA carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12680–12685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carothers D. J., Pons G., Patel M. S. Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase: functional similarities and divergent evolution of the pyridine nucleotide-disulfide oxidoreductases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Feb 1;268(2):409–425. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90309-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. Y., Cronan J. E., Jr Genetic and biochemical analyses of Escherichia coli strains having a mutation in the structural gene (poxB) for pyruvate oxidase. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):756–762. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.756-762.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. Y., Cronan J. E., Jr Mapping nonselectable genes of Escherichia coli by using transposon Tn10: location of a gene affecting pyruvate oxidase. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1279–1289. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1279-1289.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrichs D., Andreesen J. R. Purification and comparative studies of dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenases from the anaerobic, glycine-utilizing bacteria Peptostreptococcus glycinophilus, Clostridium cylindrosporum, and Clostridium sporogenes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):243–251. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.243-251.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fründ C., Priefert H., Steinbüchel A., Schlegel H. G. Biochemical and genetic analyses of acetoin catabolism in Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6539–6548. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6539-6548.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTSCHALK G. DIE BIOSYNTHESE DER POLY-BETA-HYDROXYBUTTERSAEURE DURCH KNALLGASBAKTERIEN. II. VERWERTUNG ORGANISCHER SAEUREN. Arch Mikrobiol. 1964 Feb 21;47:230–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guest J. R., Cole S. T., Jeyaseelan K. Organization and expression of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex genes of Escherichia coli K12. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Nov;127(1):65–79. doi: 10.1099/00221287-127-1-65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guest J. R. Gene-protein relationships of the alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes of Escherichia coli K12: Chromosomal location of the lipoamide dehydrogenase gene. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Feb;80(2):523–532. doi: 10.1099/00221287-80-2-523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanemaaijer R., Janssen A., de Kok A., Veeger C. The dihydrolipoyltransacetylase component of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from Azotobacter vinelandii. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jul 1;174(4):593–599. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins C. F., Borges A., Perham R. N. A common structural motif in thiamin pyrophosphate-binding enzymes. FEBS Lett. 1989 Sep 11;255(1):77–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81064-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Collins J. A small cosmid for efficient cloning of large DNA fragments. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. In vitro packaging of lambda and cosmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:299–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Murray K. Packaging recombinant DNA molecules into bacteriophage particles in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3259–3263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JUNI E., HEYM G. A. A cyclic pathway for the bacterial dissimilation of 2, 3-butanediol, acetylmethylcarbinol, and diacetyl. I. General aspects of the 2, 3-butanediol cycle. J Bacteriol. 1956 Apr;71(4):425–432. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.4.425-432.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauf V. C., Nester E. W. Wide host range cloning vectors: a cosmid clone bank of an Agrobacterium Ti plasmid. Plasmid. 1982 Jul;8(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krüger N., Oppermann F. B., Lorenzl H., Steinbüchel A. Biochemical and molecular characterization of the Clostridium magnum acetoin dehydrogenase enzyme system. J Bacteriol. 1994 Jun;176(12):3614–3630. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.12.3614-3630.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krüger N., Steinbüchel A. Identification of acoR, a regulatory gene for the expression of genes essential for acetoin catabolism in Alcaligenes eutrophus H16. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(13):4391–4400. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.13.4391-4400.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leary J. J., Brigati D. J., Ward D. C. Rapid and sensitive colorimetric method for visualizing biotin-labeled DNA probes hybridized to DNA or RNA immobilized on nitrocellulose: Bio-blots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machado R. S., Clark D. P., Guest J. R. Construction and properties of pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes with up to nine lipoyl domains per lipoate acetyltransferase chain. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Dec 15;100(1-3):243–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb14047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizusawa S., Nishimura S., Seela F. Improvement of the dideoxy chain termination method of DNA sequencing by use of deoxy-7-deazaguanosine triphosphate in place of dGTP. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1319–1324. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niu X. D., Browning K. S., Behal R. H., Reed L. J. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the gene for dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7546–7550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann F. B., Schmidt B., Steinbüchel A. Purification and characterization of acetoin:2,6-dichlorophenolindophenol oxidoreductase, dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase, and dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase of the Pelobacter carbinolicus acetoin dehydrogenase enzyme system. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):757–767. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.757-767.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann F. B., Steinbüchel A. Identification and molecular characterization of the aco genes encoding the Pelobacter carbinolicus acetoin dehydrogenase enzyme system. J Bacteriol. 1994 Jan;176(2):469–485. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.2.469-485.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann F. B., Steinbüchel A., Schlegel H. G. Evidence for oxidative thiolytic cleavage of acetoin in Pelobacter carbinolicus analogous to aerobic oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jul 1;51(1):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perham R. N., Packman L. C. 2-Oxo acid dehydrogenase multienzyme complexes: domains, dynamics, and design. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;573:1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb14983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perham R. N., Packman L. C., Radford S. E. 2-Oxo acid dehydrogenase multi-enzyme complexes: in the beginning and halfway there. Biochem Soc Symp. 1987;54:67–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priefert H., Hein S., Krüger N., Zeh K., Schmidt B., Steinbüchel A. Identification and molecular characterization of the Alcaligenes eutrophus H16 aco operon genes involved in acetoin catabolism. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(13):4056–4071. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.13.4056-4071.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priefert H., Steinbüchel A. Identification and molecular characterization of the acetyl coenzyme A synthetase gene (acoE) of Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(20):6590–6599. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.20.6590-6599.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pries A., Hein S., Steinbüchel A. Identification of a lipoamide dehydrogenase gene as second locus affected in poly(3-hydroxybutyric acid)-leaky mutants of Alcaligenes eutrophus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Oct 15;76(3):227–233. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90341-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed L. J., Hackert M. L. Structure-function relationships in dihydrolipoamide acyltransferases. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):8971–8974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez H., Kohr W. J., Harkins R. N. Design and operation of a completely automated Beckman microsequencer. Anal Biochem. 1984 Aug 1;140(2):538–547. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHINDLER J. DIE SYNTHESE VON POLY-BETA-HYDROXYBUTTERSAEURE DURCH HYDROGENOMONAS H-16 DIE ZU BETA-HYDROXYBUTYRYL-COENZYM A FUEHRENDEN REAKTIONSSCHRITTE. Arch Mikrobiol. 1964 Oct 2;49:236–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLEGEL H. G., KALTWASSER H., GOTTSCHALK G. [A submersion method for culture of hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria: growth physiological studies]. Arch Mikrobiol. 1961;38:209–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert P., Krüger N., Steinbüchel A. Molecular analysis of the Alcaligenes eutrophus poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) biosynthetic operon: identification of the N terminus of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) synthase and identification of the promoter. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):168–175. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.168-175.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiert P. S., Stauffer L. T., Stauffer G. V. The lpd gene product functions as the L protein in the Escherichia coli glycine cleavage enzyme system. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):6142–6144. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.6142-6144.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens P. E., Darlison M. G., Lewis H. M., Guest J. R. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli K12. Nucleotide sequence encoding the dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase component. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;133(3):481–489. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07490.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens P. E., Darlison M. G., Lewis H. M., Guest J. R. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli K12. Nucleotide sequence encoding the pyruvate dehydrogenase component. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):155–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07441.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss E. C., Kobori J. A., Siu G., Hood L. E. Specific-primer-directed DNA sequencing. Anal Biochem. 1986 Apr;154(1):353–360. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90536-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Lerner S. A., Lin E. C. Replacement of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase by a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-linked dehydrogenase for the utilization of mannitol. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):642–648. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.642-648.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trüper H. G. Tricarboxylic acid cycle and related enzymes in Hydrogenomonas strain H16G+ grown on various carbon sources. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Dec 16;111(2):565–568. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wexler I. D., Hemalatha S. G., Patel M. S. Sequence conservation in the alpha and beta subunits of pyruvate dehydrogenase and its similarity to branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 22;282(1):209–213. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80479-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]