Abstract
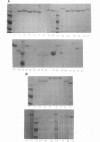
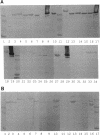
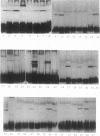
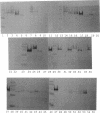
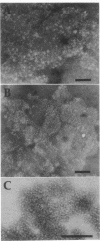
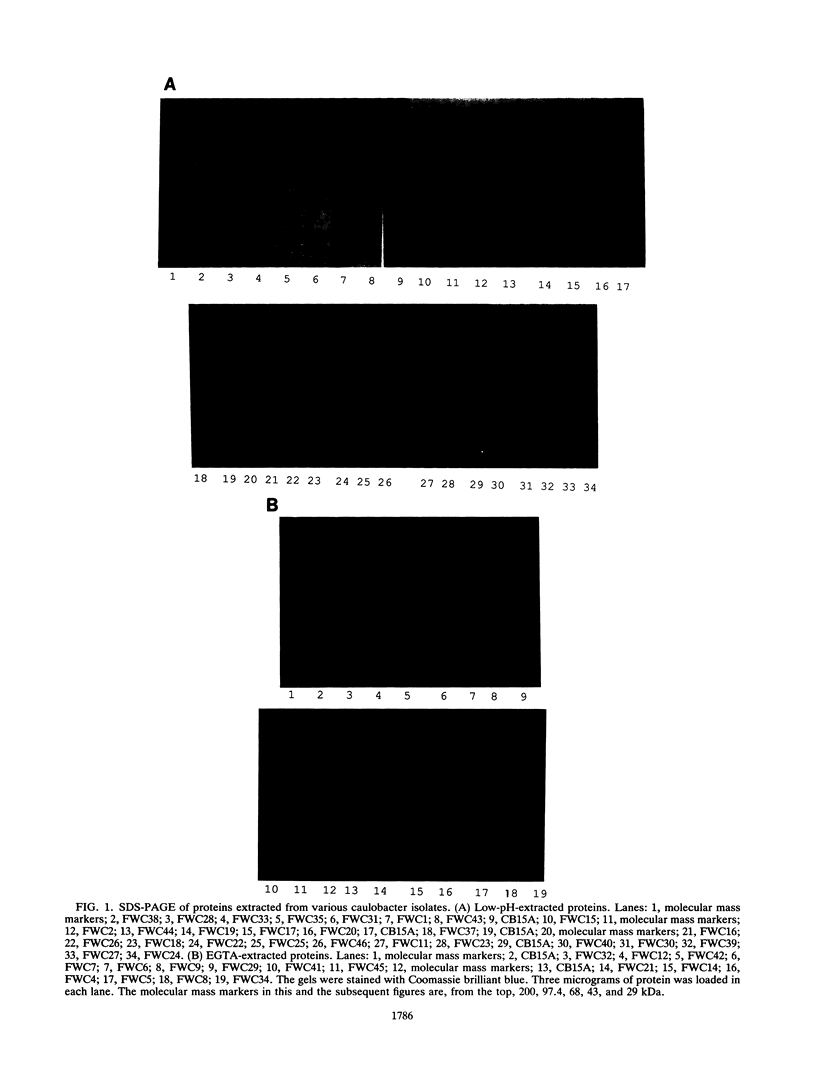
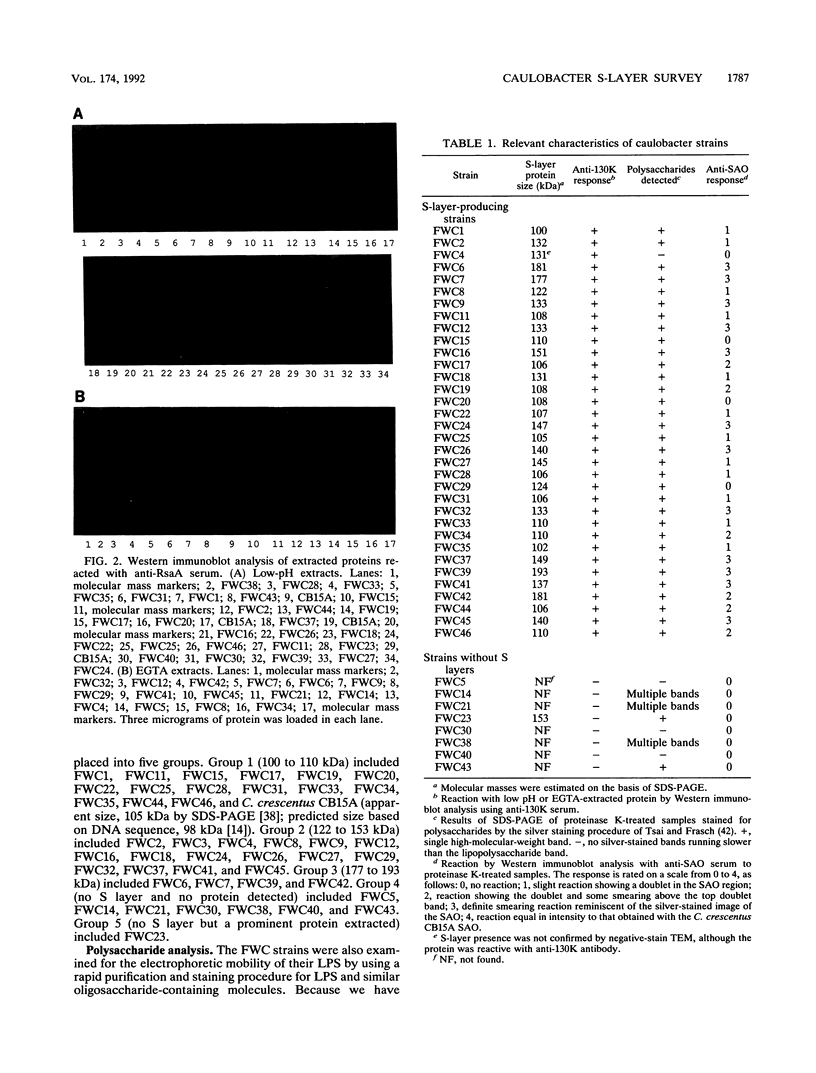
Several methods for isolation of the paracrystalline surface (S) layer protein (RsaA) of Caulobacter crescentus CB15A were evaluated. Treatment of cells with HEPES (N-2-hydroxyethylpiperazine-N'-2-ethanesulfonic acid) buffer at pH 2 was the most effective means of selectively removing RsaA from cells, and after neutralization, the protein was capable of reassembling into a paracrystalline structure. Ethylene glycol-bis(beta-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid treatment could also be used to extract RsaA and yielded protein capable of reassembly. The success of the methods was likely related to disruption of calcium-mediated bonding; calcium was required for recrystallization, while magnesium and strontium ions were ineffective. Antibody was raised against purified RsaA and, along with the S-layer extraction techniques, was used to evaluate 42 strains of caulobacters isolated from a variety of aquatic and wastewater treatment locations. A single characteristic protein could be isolated from the 35 strains that produced an S layer; with one exception, no proteins were extracted from strains that had no S layer. The presumed S-layer proteins ranged in size from 100 to 193 kDa. All of these proteins specifically reacted with anti-RsaA serum by Western immunoblot analysis. In strain CB15A, a specific S-layer-associated oligosaccharide has been proposed to be involved in a calcium-mediated attachment of the S layer to the cell surface. This molecule was detected by Western immunoblotting with a specific antiserum and on polyacrylamide gels stained for polysaccharides. A comparable band was found in all S-layer-producing strains and for most, S-layer-associated oligosaccharide-specific antibody reacted with them in Western analysis. Overall, in freshwater caulobacters at least portions of their S-layer structures appear to be strongly conserved entities, as well as the means of attachment to the cell surface.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anast Nick, Smit John. Isolation and Characterization of Marine Caulobacters and Assessment of Their Potential for Genetic Experimentation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Mar;54(3):809–817. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.3.809-817.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Murray R. G. Dependence of the superficial layers of Spirillum putridiconchylium on Ca2+ or Sr2+. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Sep;22(9):1233–1244. doi: 10.1139/m76-183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Murray R. G. Reassembly in vitro of the superficial cell wall components of Spirillum putridiconcyhylium. J Ultrastruct Res. 1976 Apr;55(1):105–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(76)80086-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Murray R. G. Superficial cell-wall layers on Spirillum "Ordal" and their in vitro reassembly. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Apr;22(4):567–582. doi: 10.1139/m76-085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chart H., Shaw D. H., Ishiguro E. E., Trust T. J. Structural and immunochemical homogeneity of Aeromonas salmonicida lipopolysaccharide. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):16–22. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.16-22.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley J. S., Lallier R., Shaw D. H., Trust T. J. Electrophoretic and immunochemical analyses of the lipopolysaccharides from various strains of Aeromonas hydrophila. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):263–269. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.263-269.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley J. S., Trust T. J. Surface protein composition of Aeromonas hydrophila strains virulent for fish: identification of a surface array protein. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):499–506. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.499-506.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubreuil J. D., Kostrzynska M., Austin J. W., Trust T. J. Antigenic differences among Campylobacter fetus S-layer proteins. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5035–5043. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5035-5043.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards P., Smit J. A transducing bacteriophage for Caulobacter crescentus uses the paracrystalline surface layer protein as a receptor. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(17):5568–5572. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.17.5568-5572.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovmöller S., Sjögren A., Wang D. N. The structure of crystalline bacterial surface layers. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1988;51(2):131–163. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(88)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karkhanis Y. D., Zeltner J. Y., Jackson J. J., Carlo D. J. A new and improved microassay to determine 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate in lipopolysaccharide of Gram-negative bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):595–601. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90260-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay W. W., Phipps B. M., Ishiguro E. E., Olafson R. W., Trust T. J. Surface layer virulence A-proteins from Aeromonas salmonicida strains. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;62(11):1064–1071. doi: 10.1139/o84-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koval S. F., Hynes S. H. Effect of paracrystalline protein surface layers on predation by Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(7):2244–2249. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.7.2244-2249.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koval S. F., Murray R. G. The isolation of surface array proteins from bacteria. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;62(11):1181–1189. doi: 10.1139/o84-152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis L. O., Yousten A. A., Murray R. G. Characterization of the surface protein layers of the mosquito-pathogenic strains of Bacillus sphaericus. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):72–79. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.72-79.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacRae J. D., Smit J. Characterization of caulobacters isolated from wastewater treatment systems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Mar;57(3):751–758. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.3.751-758.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCoy E. C., Doyle D., Burda K., Corbeil L. B., Winter A. J. Superficial antigens of Campylobacter (Vibrio) fetus: characterization of antiphagocytic component. Infect Immun. 1975 Mar;11(3):517–525. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.3.517-525.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray R. G., Dooley J. S., Whippey P. W., Trust T. J. Structure of an S layer on a pathogenic strain of Aeromonas hydrophila. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2625–2630. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2625-2630.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POINDEXTER J. S. BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES AND CLASSIFICATION OF THE CAULOBACTER GROUP. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Sep;28:231–295. doi: 10.1128/br.28.3.231-295.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A. A., McGroarty E. J. High-molecular-weight components in lipopolysaccharides of Salmonella typhimurium, Salmonella minnesota, and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):738–745. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.738-745.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B., Messner P. Crystalline surface layers in procaryotes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):2891–2897. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.2891-2897.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B., Messner P. Crystalline surface layers on bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:311–339. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.001523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B., Sára M., Küpcü Z., Messner P. Structural and chemical characterization of S-layers of selected strains of Bacillus stearothermophilus and Desulfotomaculum nigrificans. Arch Microbiol. 1986 Oct;146(1):19–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00690152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit J., Agabian N. Cloning of the major protein of the Caulobacter crescentus periodic surface layer: detection and characterization of the cloned peptide by protein expression assays. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):1137–1145. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.1137-1145.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit J., Grano D. A., Glaeser R. M., Agabian N. Periodic surface array in Caulobacter crescentus: fine structure and chemical analysis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):1135–1150. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.1135-1150.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. H., Murray R. G. The structure and associations of the double S layer on the cell wall of Aquaspirillum sinuosum. Can J Microbiol. 1990 May;36(5):327–335. doi: 10.1139/m90-057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]