Abstract
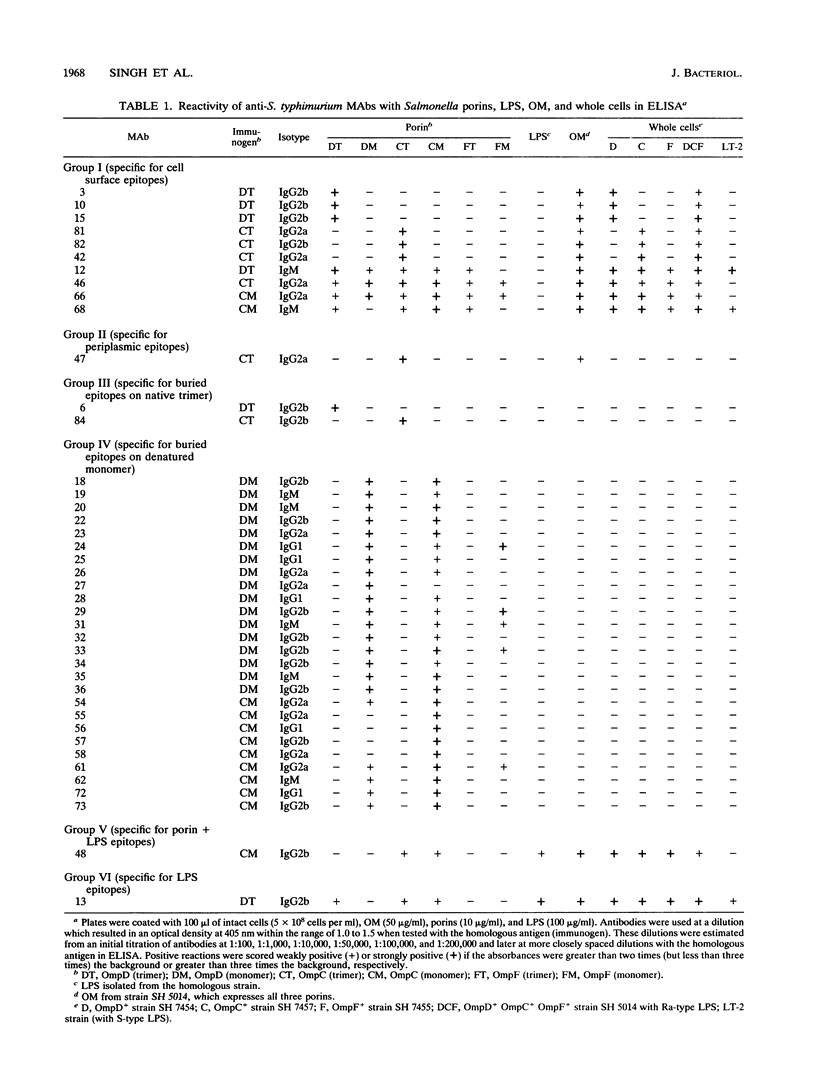
The immunochemistry and structure of enteric bacterial porins are critical to the understanding of the immune response to bacterial infection. We raised 41 monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) to Salmonella typhimurium OmpD and OmpC porin trimers and monomers. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays, immunoprecipitations, and/or Western immunoblot techniques indicated that 39 MAbs (11 anti-trimer and 28 anti-monomer) in the panel are porin specific and one binds to the lipopolysaccharide; the specificity of the remaining MAb probably lies in the porin-lipopolysaccharide complex. Among the porin-specific MAbs, 10 bound cell-surface-exposed epitopes, one reacted with a periplasmic epitope, and the remaining 28 recognized determinants that are buried within the outer membrane bilayer. Many of the MAbs reacting with surface-exposed epitopes were highly specific, recognizing only the homologous porin trimers; this suggests that the cell-surface-exposed regions of porins tends to be quite different among S. typhimurium OmpF, OmpC, and OmpD porins. Immunological cross-reaction showed that S. typhimurium OmpD was very closely related to Escherichia coli NmpC and to the Lc porin of bacteriophage PA-2. Immunologically, E. coli OmpG and protein K also appear to belong to the family of closely related porins including E. coli OmpF, OmpC, PhoE, and NmpC and S. typhimurium OmpF, OmpC, and OmpD. It appears, however, that S. typhimurium "PhoE" is not closely related to this group. Finally, about one-third of the MAbs that presumably recognize buried epitopes reacted with porin domains that are widely conserved in 13 species of the family Enterobacteriaceae, but apparently not in the seven nonenterobacterial species tested. These data are evaluated in relation to host immune response to infection by gram-negative bacteria.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer K., Benz R., Brass J., Boos W. Salmonella typhimurium contains an anion-selective outer membrane porin induced by phosphate starvation. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):813–816. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.813-816.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley A. T., Klebba P. E. Effect of lipopolysaccharide structure on reactivity of antiporin monoclonal antibodies with the bacterial cell surface. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1063–1068. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1063-1068.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasband A. J., Marcotte W. R., Jr, Schnaitman C. A. Structure of the lc and nmpC outer membrane porin protein genes of lambdoid bacteriophage. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12723–12732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouzoubaa K., Nagaraja K. V., Newman J. A., Pomeroy B. S. Use of membrane proteins from Salmonella gallinarum for prevention of fowl typhoid infection in chickens. Avian Dis. 1987 Oct-Dec;31(4):699–704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brauner A., Källenius G., Wrangsell G., Wretlind B., Svenson S. B. Antibody responses to Escherichia coli J5 lipopolysaccharide and to Salmonella porin in patients with bacteremia. Microb Pathog. 1986 Oct;1(5):475–481. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., Fanning G. R., Steigerwalt A. G., Sodd M. A., Doctor B. P. Conservation of transfer ribonucleic acid and 5S ribonucleic acid cistrons in Enterobacteriaceae. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1435–1439. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1435-1439.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderón I., Lobos S. R., Rojas H. A., Palomino C., Rodríguez L. H., Mora G. C. Antibodies to porin antigens of Salmonella typhi induced during typhoid infection in humans. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):209–212. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.209-212.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloeckaert A., Jacques I., Bosseray N., Limet J. N., Bowden R., Dubray G., Plommet M. Protection conferred on mice by monoclonal antibodies directed against outer-membrane-protein antigens of Brucella. J Med Microbiol. 1991 Mar;34(3):175–180. doi: 10.1099/00222615-34-3-175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocks G. T., Wilson A. C. Enzyme evolution in the Enterobacteriaceae. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):793–802. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.793-802.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn D. L. Antibody immunotherapy of gram-negative bacterial sepsis. Pharmacotherapy. 1987;7(2):S31–S35. doi: 10.1002/j.1875-9114.1987.tb03511.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick B. W., Cullor J. S., Osburn B. I., Olander H. J. Mechanisms involved in protection provided by immunization against core lipopolysaccharides of Escherichia coli J5 from lethal Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae infections in swine. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):298–304. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.298-304.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Beros M. E., Gonzalez C., McIntosh M. A., Cabello F. C. Immune response to the iron-deprivation-induced proteins of Salmonella typhi in typhoid fever. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1271–1275. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1271-1275.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring K. B., Nikaido H. Existence and purification of porin heterotrimers of Escherichia coli K12 OmpC, OmpF, and PhoE proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2810–2815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerbl-Rieger S., Peters J., Kellermann J., Lottspeich F., Baumeister W. Nucleotide and derived amino acid sequences of the major porin of Comamonas acidovorans and comparison of porin primary structures. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(7):2196–2205. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.7.2196-2205.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilleland H. E., Jr, Matthews-Greer J. M. Perspectives on the potential for successful development of outer membrane protein vaccines. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jun;6(3):231–233. doi: 10.1007/BF02017606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen A. Z., Maeland J. A. A conserved domain on enterobacterial porin protein analysed by monoclonal antibody. APMIS. 1991 Jan;99(1):49–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1991.tb05117.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstra H., Dankert J. Porin from the outer membrane of Escherichia coli: immunological characterization of native and heat-dissociated forms. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Aug;125(2):285–292. doi: 10.1099/00221287-125-2-285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzenburg A., Engel A., Kessler R., Manz H. J., Lustig A., Aebi U. Rapid isolation of OmpF porin-LPS complexes suitable for structure-function studies. Biochemistry. 1989 May 16;28(10):4187–4193. doi: 10.1021/bi00436a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isibasi A., Ortiz V., Vargas M., Paniagua J., González C., Moreno J., Kumate J. Protection against Salmonella typhi infection in mice after immunization with outer membrane proteins isolated from Salmonella typhi 9,12,d, Vi. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2953–2959. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2953-2959.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jap B. K., Walian P. J. Biophysics of the structure and function of porins. Q Rev Biophys. 1990 Nov;23(4):367–403. doi: 10.1017/s003358350000559x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebba P. E., Benson S. A., Bala S., Abdullah T., Reid J., Singh S. P., Nikaido H. Determinants of OmpF porin antigenicity and structure. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6800–6810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korteland J., Tommassen J., Lugtenberg B. PhoE protein pore of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli K12 is a particularly efficient channel for organic and inorganic phosphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 9;690(2):282–289. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90332-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusi N., Nurminen M., Saxen H., Valtonen M., Mäkelä P. H. Immunization with major outer membrane proteins in experimental salmonellosis of mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):857–862. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.857-862.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusi N., Nurminen M., Saxén H., Mäkelä P. H. Immunization with major outer membrane protein (porin) preparations in experimental murine salmonellosis: effect of lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):328–332. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.328-332.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. R., Schnaitman C. A. Comparison of outer membrane porin proteins produced by Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):1019–1022. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.1019-1022.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Peters R., Bernheimer H., Berendsen W. Influence of cultural conditions and mutations on the composition of the outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Sep 23;147(3):251–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00582876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Van Alphen L. Molecular architecture and functioning of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli and other gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):51–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupi N., Bourgois A., Bernadac A., Laboucarié S., Pagès J. M. Immunological analysis of porin polymorphism in Escherichia coli B and K-12. Mol Immunol. 1989 Nov;26(11):1027–1036. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(89)90067-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui K., Arai T. Protective immunity induced by porin in experimental mouse salmonellosis. Microbiol Immunol. 1989;33(9):699–708. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1989.tb00957.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra R., Benson S. A. A novel mutation, cog, which results in production of a new porin protein (OmpG) of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4105–4111. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4105-4111.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Chou M. Y., Inouye M. A comparative study on the genes for three porins of the Escherichia coli outer membrane. DNA sequence of the osmoregulated ompC gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6932–6940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy C. K., Kalve V. I., Klebba P. E. Surface topology of the Escherichia coli K-12 ferric enterobactin receptor. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2736–2746. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2736-2746.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutharia L. M., Hancock R. E. Surface localization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane porin protein F by using monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1027–1033. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1027-1033.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H. Proteins forming large channels from bacterial and mitochondrial outer membranes: porins and phage lambda receptor protein. Methods Enzymol. 1983;97:85–100. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)97122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Rosenberg E. Y., Foulds J. Porin channels in Escherichia coli: studies with beta-lactams in intact cells. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):232–240. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.232-240.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Vaara M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.1-32.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurminen M., Lounatmaa K., Sarvas M., Mäkelä P. H., Nakae T. Bacteriophage-resistant mutants of Salmonella typhimurium deficient in two major outer membrane proteins. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):941–955. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.941-955.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz V., Isibasi A., García-Ortigoza E., Kumate J. Immunoblot detection of class-specific humoral immune response to outer membrane proteins isolated from Salmonella typhi in humans with typhoid fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1640–1645. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1640-1645.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbeeke N., Van Scharrenburg G., Lugtenberg B. Antigenic relationships between pore proteins of Escherichia coli K12. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Sep;110(1):247–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04862.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paakkanen J., Gotschlich E. C., Mäkelä P. H. Protein K: a new major outer membrane protein found in encapsulated Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):835–841. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.835-841.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pages J. M., Bolla J. M., Bernadac A., Fourel D. Immunological approach of assembly and topology of OmpF, an outer membrane protein of Escherichia coli. Biochimie. 1990 Feb-Mar;72(2-3):169–176. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(90)90142-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puente J. L., Alvarez-Scherer V., Gosset G., Calva E. Comparative analysis of the Salmonella typhi and Escherichia coli ompC genes. Gene. 1989 Nov 30;83(2):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90105-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Schnaitman C. A. Identification of three genes controlling production of new outer membrane pore proteins in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):1118–1129. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.1118-1129.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutz J. M., Abdullah T., Singh S. P., Kalve V. I., Klebba P. E. Evolution of the ferric enterobactin receptor in gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):5964–5974. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.5964-5974.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxén H., Nurminen M., Kuusi N., Svenson S. B., Mäkelä P. H. Evidence for the importance of O antigen specific antibodies in mouse-protective Salmonella outer membrane protein (porin) antisera. Microb Pathog. 1986 Oct;1(5):433–441. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma P., Ganguly N. K., Sharma B. K., Sharma S., Rawal I. J., Saxena S. N., Sehgal R. Humoral and cell mediated immune responses to porins of Salmonella typhi. Jpn J Exp Med. 1989 Apr;59(2):73–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit J., Kamio Y., Nikaido H. Outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium: chemical analysis and freeze-fracture studies with lipopolysaccharide mutants. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):942–958. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.942-958.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukupolvi S., Vaara M., Helander I. M., Viljanen P., Mäkelä P. H. New Salmonella typhimurium mutants with altered outer membrane permeability. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):704–712. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.704-712.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udhayakumar V., Muthukkaruppan V. R. Protective immunity induced by outer membrane proteins of Salmonella typhimurium in mice. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):816–821. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.816-821.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef C., Benz R., Poon A. P., Tommassen J. New pore protein produced in cells lysogenic for Escherichia coli phage HK253hrk. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Apr 1;164(1):141–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel H., Jähnig F. Models for the structure of outer-membrane proteins of Escherichia coli derived from raman spectroscopy and prediction methods. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jul 20;190(2):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90292-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. S., Wacker T., Weckesser J., Welte W., Schulz G. E. The three-dimensional structure of porin from Rhodobacter capsulatus at 3 A resolution. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jul 16;267(2):268–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80942-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada H., Oshima N., Mizuno T., Matsui H., Kai Y., Noguchi H., Mizushima S. Use of a series of ompF-ompC chimeric proteins for locating antigenic determinants recognized by monoclonal antibodies against the ompC and ompF proteins of the Escherichia coli outer membrane. J Biochem. 1987 Sep;102(3):455–464. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Ley P., Amesz H., Tommassen J., Lugtenberg B. Monoclonal antibodies directed against the cell-surface-exposed part of PhoE pore protein of the Escherichia coli K-12 outer membrane. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Mar 1;147(2):401–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08764.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]