Abstract
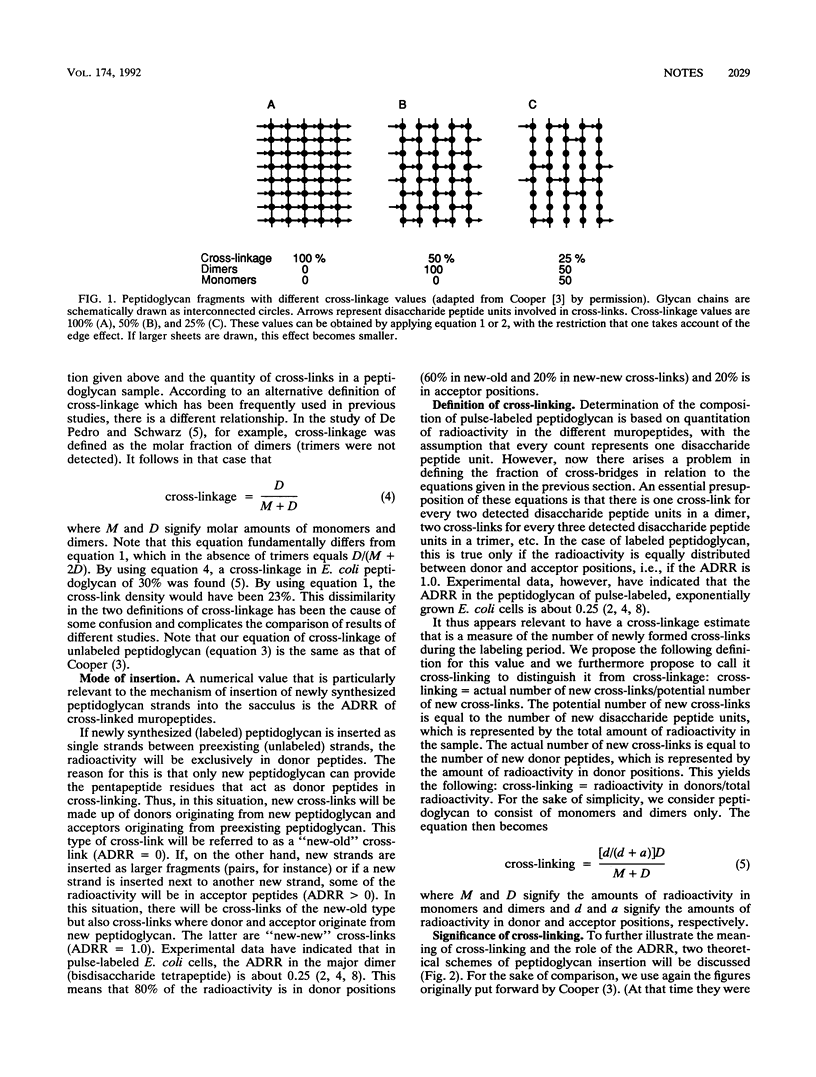
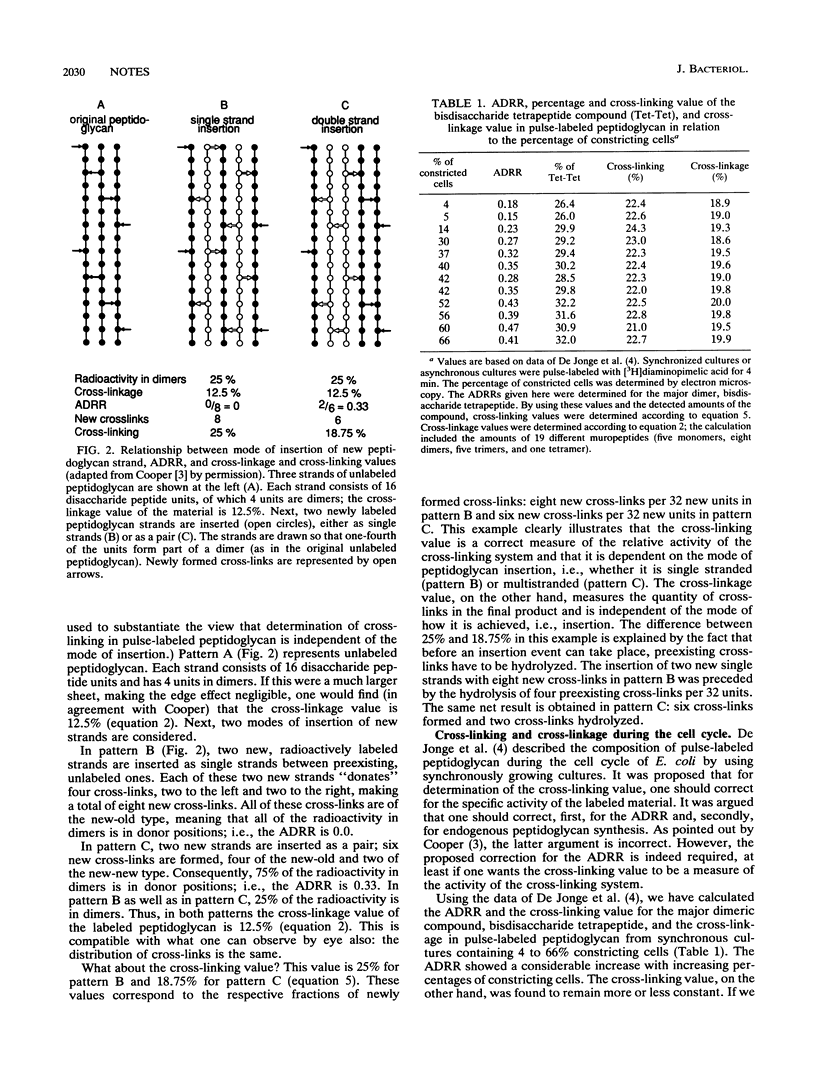
The glycan chains in peptidoglycan or murein are cross-linked by transpeptidation of the peptide side chains. To assess the fraction of side chains involved in cross-bridges, distinction has been made between cross-linkage and cross-linking. The first expression refers to the situation in unlabeled (or fully labeled) peptidoglycan, and the second refers to pulse-labeled peptidoglycan. It is argued that for the determination of the cross-linking value, the mode of insertion as denoted by the so-called acceptor/donor radioactivity ratio should be taken into account.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burman L. G., Park J. T. Changes in the composition of Escherichia coli murein as it ages during exponential growth. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):447–453. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.447-453.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burman L. G., Park J. T. Molecular model for elongation of the murein sacculus of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1844–1848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S. Relationship between the acceptor/donor radioactivity ratio and cross-linking in bacterial peptidoglycan: application to surface synthesis during the division cycle. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5506–5510. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5506-5510.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driehuis F., Wouters J. T. Effect of growth rate and cell shape on the peptidoglycan composition in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):97–101. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.97-101.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glauner B. Separation and quantification of muropeptides with high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1988 Aug 1;172(2):451–464. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90468-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmeiner J., Kroll H. P. Murein biosynthesis and O-acetylation of N-acetylmuramic acid during the cell-division cycle of Proteus mirabilis. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jun;117(1):171–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06317.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lear A. L., Perkins H. R. O-acetylation of peptidoglycan in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Investigation of lipid-linked intermediates and glycan chains newly incorporated into the cell wall. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Sep;132(9):2413–2420. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-9-2413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jonge B. L., Wientjes F. B., Jurida I., Driehuis F., Wouters J. T., Nanninga N. Peptidoglycan synthesis during the cell cycle of Escherichia coli: composition and mode of insertion. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):5783–5794. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.5783-5794.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Pedro M. A., Schwarz U. Heterogeneity of newly inserted and preexisting murein in the sacculus of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5856–5860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


