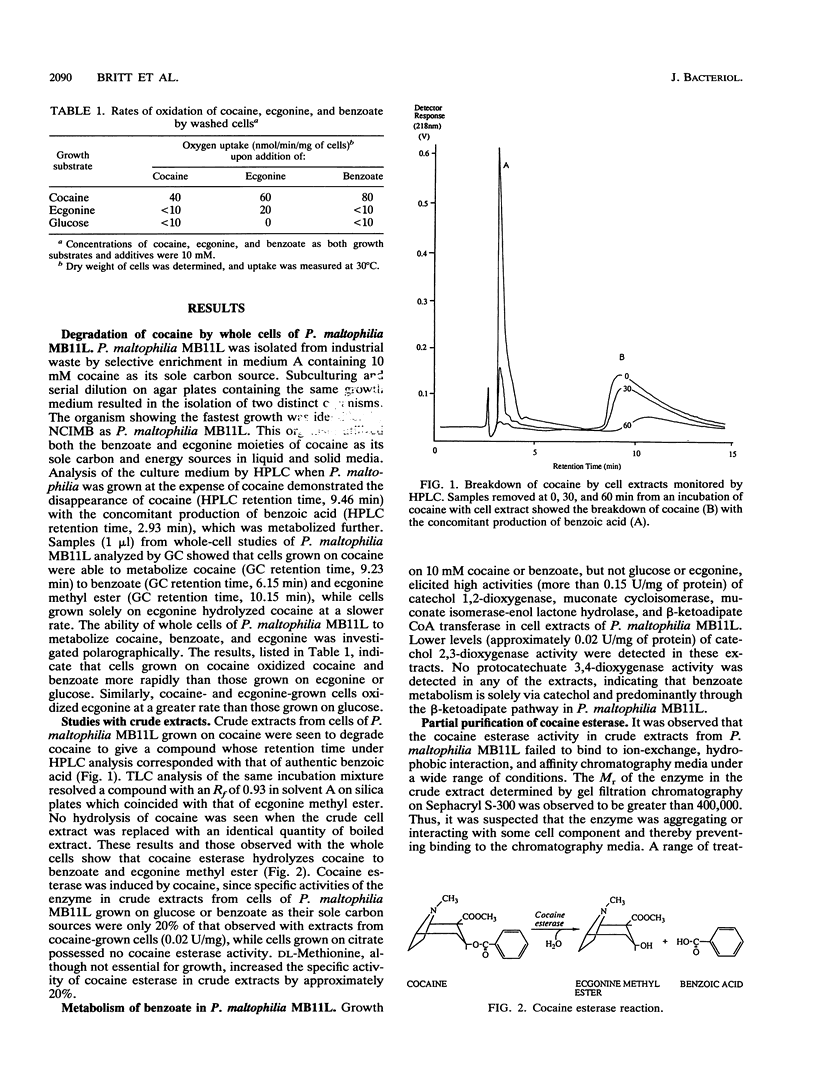
Abstract
A strain of Pseudomonas maltophilia (termed MB11L) which was capable of using cocaine as its sole carbon and energy source was isolated by selective enrichment. An inducible esterase catalyzing the hydrolysis of cocaine to ecgonine methyl ester and benzoic acid was identified and purified 22-fold. In the presence of the solubilizing agent cholate, cocaine esterase had a native Mr of 110,000 and was shown by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis to be a monomer. In the absence of cholate, cocaine esterase had a native Mr of 410,000 and probably existed as a tetramer. The pH optimum of the enzyme was 8.0, and the Km values for cocaine, ethyl benzoate, and ethyl 2-hydroxybenzoate were 0.36, 1.89, and 1.75 mM, respectively. Inhibition studies indicated that the enzyme was a serine esterase, possibly possessing a cation-binding site similar to those of mammalian acetylcholinesterase and the atropine esterase of Pseudomonas putida PMBL-1. The cocaine esterase of P. maltophilia MB11L showed no activity with atropine, despite the structural similarity of cocaine and atropine.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman H. A., Leonard K. Ligand exclusion on acetylcholinesterase. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 27;29(47):10640–10649. doi: 10.1021/bi00499a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain R. B., Bilton R. F., Darrah J. A. The metabolism of aromatic acids by micro-organisms. Metabolic pathways in the fungi. Biochem J. 1968 Aug;108(5):797–828. doi: 10.1042/bj1080797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calame K. B., Gallo L., Cheriathundam E., Vahouny G. V., Treadwell C. R. Purification and properties of subunits of sterol ester hydrolase from rat pancreas. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 May;168(1):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90227-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton R. W., Ribbons D. W. Metabolism of dibutylphthalate and phthalate by Micrococcus sp. strain 12B. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):48–57. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.48-57.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhardt G., Wallnöfer P. R. Metabolism of Di- and Mono-n-Butyl Phthalate by Soil Bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Feb;35(2):243–246. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.2.243-246.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara M., Golovleva L. A., Saeki Y., Nozaki M., Hayaishi O. Extradiol cleavage of 3-substituted catechols by an intradiol dioxygenase, pyrocatechase, from a Pseudomonad. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):4848–4855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goullet P., Picard B. Characterization of enterobacteria by esterase specific-activity profiles. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Mar;136(3):431–440. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-3-431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATAGIRI M., HAYAISHI O. Enzymatic degradation of beta-ketoadipic acid. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):439–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima Y., Fujisawa H., Nakazawa A., Nakazawa T., Kanetsuna F., Taniuchi H., Nozaki M., Hayaishi O. Studies on pyrocatechase. I. Purification and spectral properties. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jul 25;242(14):3270–3278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masound A. N. Systematic identification of drugs of abuse I: spot tests. J Pharm Sci. 1975 May;64(5):841–844. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600640526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra A. L., Pontani R. B., Mulé S. J. Separation of cocaine, some of its metabolites and congeners on glass fibre sheets. J Chromatogr. 1973 Jun 27;81(1):167–169. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)82333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIEMER H., BUCHERER H., KOHLER A. [On the decomposition of atropine by Corynebacterium belladonnae]. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1959;317:238–242. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1959.317.1.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIEMER H., BUCHERER H. [On the degradation of atropine by Corynebacterium belladonnae. II]. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1961 Oct 25;326:9–12. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1961.326.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa T., Yokota T. Benzoate metabolism in Pseudomonas putida(arvilla) mt-2: demonstration of two benzoate pathways. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):262–267. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.262-267.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noggle F. T., Jr, Clark C. R. Liquid chromatographic identification of cis- and trans-cinnamoylcocaine in illicit cocaine. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1982 May;65(3):756–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosterbaan R. A., Berends F. A comparative study of the atropinesterases of nine Pseudomonas strains. Proc K Ned Akad Wet C. 1971;74(2):158–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacaud M. Identification and localization of two membrane-bound esterases from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):6–14. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.6-14.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENBERGER R. F., ELSDEN S. R. The yields of Streptococcus faecalis grown in continuous culture. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Jun;22:726–739. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-3-726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rörsch A., Berends F., Bartlema H. C., Stevens W. F. The isolation and properties of Pseudomonas strains growing on atropine and producing atropinesterase. Proc K Ned Akad Wet C. 1971;74(2):132–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shum A. C., Markovetz A. J. Purification and properties of undecyl acetate esterase from Pseudomonas cepacia grown on 2-tridecanone. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):880–889. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.880-889.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobek H., Görisch H. Purification and characterization of a heat-stable esterase from the thermoacidophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 1;250(2):453–458. doi: 10.1042/bj2500453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujita T., Mizuno N. K., Brockman H. L. Nonspecific high affinity binding of bile salts to carboxylester lipases. J Lipid Res. 1987 Dec;28(12):1434–1443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veeraragavan K. A simple and sensitive method for the estimation of microbial lipase activity. Anal Biochem. 1990 May 1;186(2):301–305. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90084-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Drift A. C., Beck H. C., Dekker W. H., Hulst A. G., Wils E. R. P NMR and mass spectrometry of atropinesterase and some serine proteases phosphorylated with a transition-state analogue. Biochemistry. 1985 Nov 19;24(24):6894–6903. doi: 10.1021/bi00345a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Drift A. C., Moes G. W., van der Drift E., Rousseeuw B. A. Comparison of the active sites of atropinesterase and some serine proteases by spin-labeling. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5333–5342. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Drift A. C., Sluiter W., Berends F. Hydrodynamic characterization of the size and shape of atropinesterase from Pseudomonas putida. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Apr 8;912(2):167–177. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(87)90085-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


