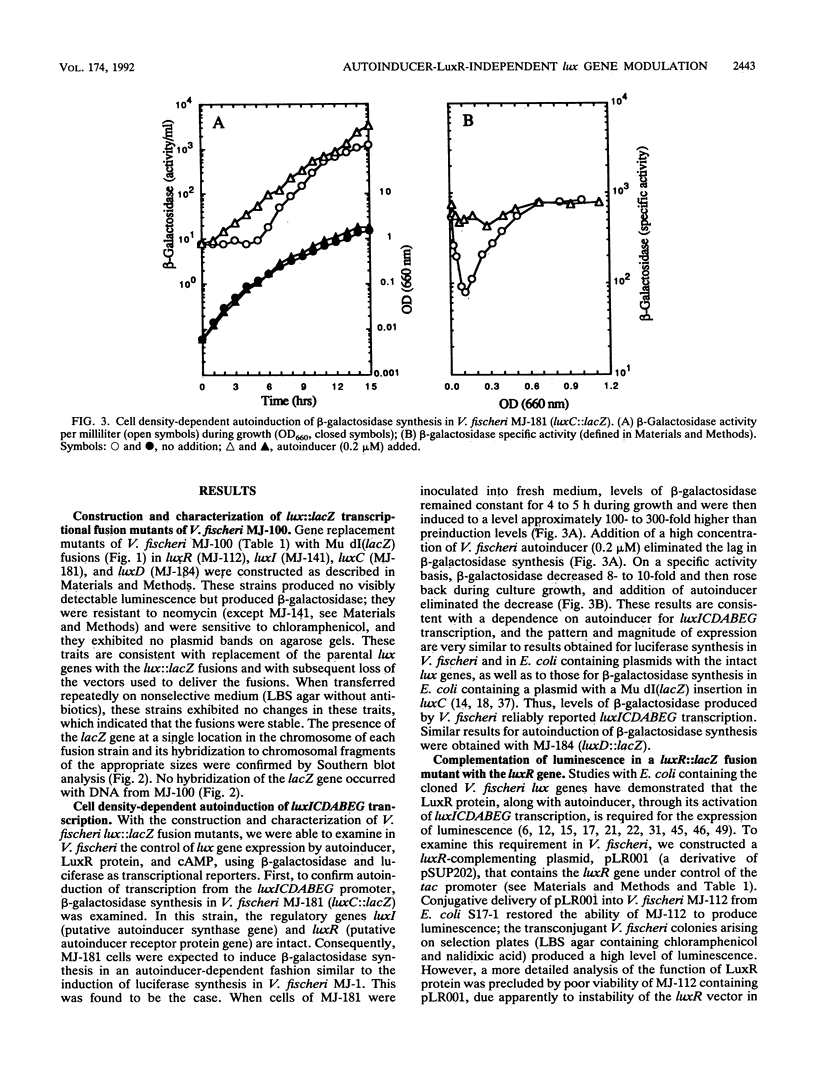
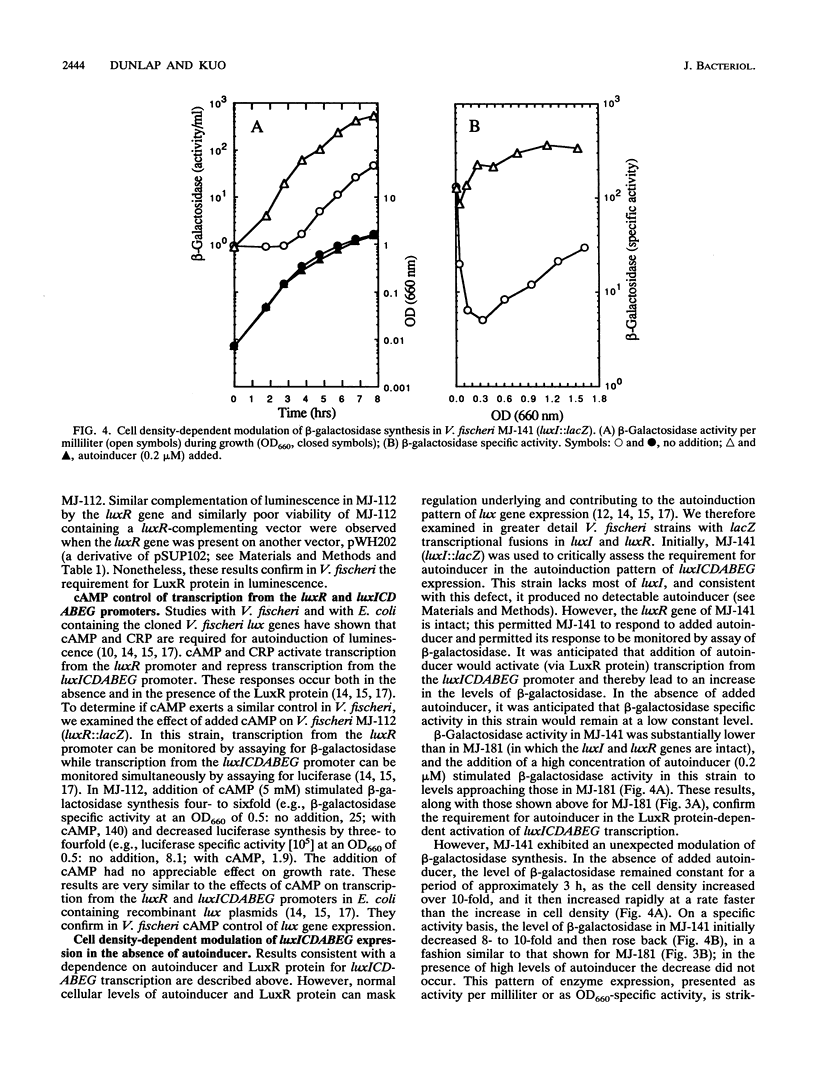
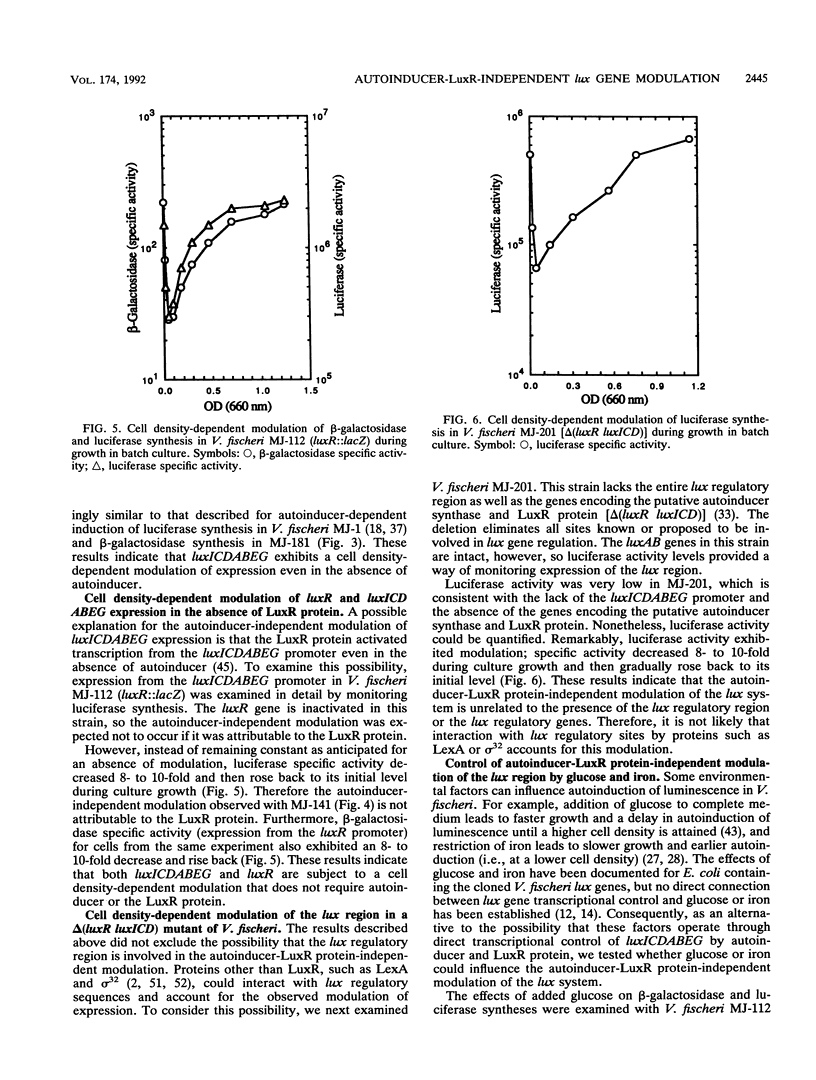
Abstract
Expression of the Vibrio fischeri luminescence genes (luxR and luxICDABEG) in Escherichia coli requires autoinducer (N-3-oxohexanoyl homoserine lactone) and LuxR protein, which activate transcription of luxICDABEG (genes for autoinducer synthase and the luminescence enzymes), and cyclic AMP (cAMP) and cAMP receptor protein (CRP), which activate transcription of the divergently expressed luxR gene. In E. coli and in V. fischeri, the autoinducer-LuxR protein-dependent induction of luxICDABEG transcription (called autoinduction) is delayed by glucose, whereas it is promoted by iron restriction, but the mechanisms for these effects are not clear. To examine in V. fischeri control of lux gene expression by autoinducer, cAMP, glucose, and iron, lux::Mu dI(lacZ) and lux deletion mutants of V. fischeri were constructed by conjugation and gene replacement procedures. beta-Galactosidase synthesis in a luxC::lacZ mutant exhibited autoinduction. In a luxR::lacZ mutant, complementation by the luxR gene was necessary for luminescence, and addition of cAMP increased beta-galactosidase activity four- to sixfold. Furthermore, a luxI::lacZ mutant produced no detectable autoinducer but responded to its addition with induced synthesis of beta-galactosidase. These results confirm in V. fischeri key features of lux gene regulation derived from studies with E. coli. However, beta-galactosidase specific activity in the luxI::lacZ mutant, without added autoinducer, exhibited an eight- to tenfold decrease and rise back during growth, as did beta-galactosidase and luciferase specific activities in the luxR::lacZ mutant and luciferase specific activity in a delta(luxR luxICD) mutant. The presence of glucose delayed the rise back in beta-galactosidase and luciferase specific activities in these strains, whereas iron restriction promoted it. Thus, in addition to transcriptional control by autoinducer and LuxR protein, the V. fischeri lux system exhibits a cell density-dependent modulation of expression that does not require autoinducer, LuxR protein, or known lux regulatory sites. The response of autoinducer-LuxR protein-independent modulation to glucose and iron may account for how these environmental factors control lux gene expressions.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin T. O., Devine J. H., Heckel R. C., Lin J. W., Shadel G. S. The complete nucleotide sequence of the lux regulon of Vibrio fischeri and the luxABN region of Photobacterium leiognathi and the mechanism of control of bacterial bioluminescence. J Biolumin Chemilumin. 1989 Jul;4(1):326–341. doi: 10.1002/bio.1170040145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird R. E., Louarn J., Martuscelli J., Caro L. Origin and sequence of chromosome replication in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1972 Oct 14;70(3):549–566. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90559-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan M., Graham A. F., Meighen E. A. Functional identification of the fatty acid reductase components encoded in the luminescence operon of Vibrio fischeri. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1186–1190. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1186-1190.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castilho B. A., Olfson P., Casadaban M. J. Plasmid insertion mutagenesis and lac gene fusion with mini-mu bacteriophage transposons. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):488–495. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.488-495.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi S. H., Greenberg E. P. The C-terminal region of the Vibrio fischeri LuxR protein contains an inducer-independent lux gene activating domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11115–11119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchward G., Estiva E., Bremer H. Growth rate-dependent control of chromosome replication initiation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1232–1238. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1232-1238.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorman C. J., Ni Bhriain N., Higgins C. F. DNA supercoiling and environmental regulation of virulence gene expression in Shigella flexneri. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):789–792. doi: 10.1038/344789a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap P. V., Greenberg E. P. Control of Vibrio fischeri luminescence gene expression in Escherichia coli by cyclic AMP and cyclic AMP receptor protein. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):45–50. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.45-50.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap P. V., Greenberg E. P. Control of Vibrio fischeri lux gene transcription by a cyclic AMP receptor protein-luxR protein regulatory circuit. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4040–4046. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4040-4046.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap P. V., Ray J. M. Requirement for autoinducer in transcriptional negative autoregulation of the Vibrio fischeri luxR gene in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3549–3552. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3549-3552.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap P. V. Regulation of luminescence by cyclic AMP in cya-like and crp-like mutants of Vibrio fischeri. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):1199–1202. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.1199-1202.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard A., Burlingame A. L., Eberhard C., Kenyon G. L., Nealson K. H., Oppenheimer N. J. Structural identification of autoinducer of Photobacterium fischeri luciferase. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 28;20(9):2444–2449. doi: 10.1021/bi00512a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard A. Inhibition and activation of bacterial luciferase synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):1101–1105. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.1101-1105.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engebrecht J., Nealson K., Silverman M. Bacterial bioluminescence: isolation and genetic analysis of functions from Vibrio fischeri. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engebrecht J., Silverman M. Identification of genes and gene products necessary for bacterial bioluminescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4154–4158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engebrecht J., Silverman M. Nucleotide sequence of the regulatory locus controlling expression of bacterial genes for bioluminescence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10455–10467. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haygood M. G., Nealson K. H. Mechanisms of iron regulation of luminescence in Vibrio fischeri. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):209–216. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.209-216.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Kumada Y., Beppu T. Unstable genetic determinant of A-factor biosynthesis in streptomycin-producing organisms: cloning and characterization. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):481–487. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.481-487.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan H. B., Greenberg E. P. Diffusion of autoinducer is involved in regulation of the Vibrio fischeri luminescence system. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1210–1214. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1210-1214.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan H. B., Greenberg E. P. Overproduction and purification of the luxR gene product: Transcriptional activator of the Vibrio fischeri luminescence system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6639–6643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khokhlov A. S., Anisova L. N., Tovarova I. I., Kleiner E. M., Kovalenko I. V., Krasilnikova O. I., Kornitskaya E. Y., Pliner S. A. Effect of A-factor on the growth of asporogenous mutants of Streptomyces griseus, not producing this factor. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1973;13(8):647–655. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630130803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters M., Broda P. Evidence for the bidirectional replications of the Escherichia coli chromosome. Nat New Biol. 1971 Aug 4;232(31):137–140. doi: 10.1038/newbio232137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nealson K. H. Autoinduction of bacterial luciferase. Occurrence, mechanism and significance. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Feb 4;112(1):73–79. doi: 10.1007/BF00446657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nealson K. H., Hastings J. W. Low oxygen is optimal for luciferase synthesis in some bacteria. Ecological implications. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Feb 4;112(1):9–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00446648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J. Iron-Binding Catechols and Virulence in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):445–456. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.445-456.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby E. G., Nealson K. H. Symbiotic association of Photobacterium fischeri with the marine luminous fish Monocentris japonica; a model of symbiosis based on bacterial studies. Biol Bull. 1976 Dec;151(3):574–586. doi: 10.2307/1540507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadel G. S., Baldwin T. O. The Vibrio fischeri LuxR protein is capable of bidirectional stimulation of transcription and both positive and negative regulation of the luxR gene. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):568–574. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.568-574.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showalter R. E., Martin M. O., Silverman M. R. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of luxR, a regulatory gene controlling bioluminescence in Vibrio harveyi. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):2946–2954. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.2946-2954.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R., O'Connell M., Labes M., Pühler A. Plasmid vectors for the genetic analysis and manipulation of rhizobia and other gram-negative bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1986;118:640–659. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)18106-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slock J., VanRiet D., Kolibachuk D., Greenberg E. P. Critical regions of the Vibrio fischeri luxR protein defined by mutational analysis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3974–3979. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3974-3979.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartzman A., Kapoor S., Graham A. F., Meighen E. A. A new Vibrio fischeri lux gene precedes a bidirectional termination site for the lux operon. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6797–6802. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6797-6802.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulitzur S., Kuhn J. The transcription of bacterial luminescence is regulated by sigma 32. J Biolumin Chemilumin. 1988 Apr-Jun;2(2):81–93. doi: 10.1002/bio.1170020205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulitzur S. The regulatory control of the bacterial luminescence system--a new view. J Biolumin Chemilumin. 1989 Jul;4(1):317–325. doi: 10.1002/bio.1170040144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]