Abstract
In gram-negative bacteria, numerous cell functions, including respiration-linked electron transport, have been ascribed to the cytoplasmic membrane. Gram-negative bacteria which use solid substrates (e.g., oxidized manganese or iron) as terminal electron acceptors for anaerobic respiration are presented with a unique problem: they must somehow establish an electron transport link across the outer membrane between large particulate metal oxides and the electron transport chain in the cytoplasmic membrane. When the metal-reducing bacterium Shewanella putrefaciens MR-1 is grown under anaerobic conditions and membrane fractions are purified from cells lysed by an EDTA-lysozyme-polyoxyethylene cetyl ether (Brij 58) protocol, approximately 80% of its membrane-bound cytochromes are localized in its outer membrane. These outer membrane cytochromes could not be dislodged by treatment with chaotropic agents or by increased concentrations of the nonionic detergent Brij 58, suggesting that they are integral membrane proteins. Cytochrome distribution in cells lysed by a French press protocol confirm the localization of cytochromes to the outer membrane of anaerobically grown cells. This novel cytochrome distribution could play a key role in the anaerobic respiratory capabilities of this bacterium, especially in its ability to mediate manganese and iron reduction.
Full text
PDF

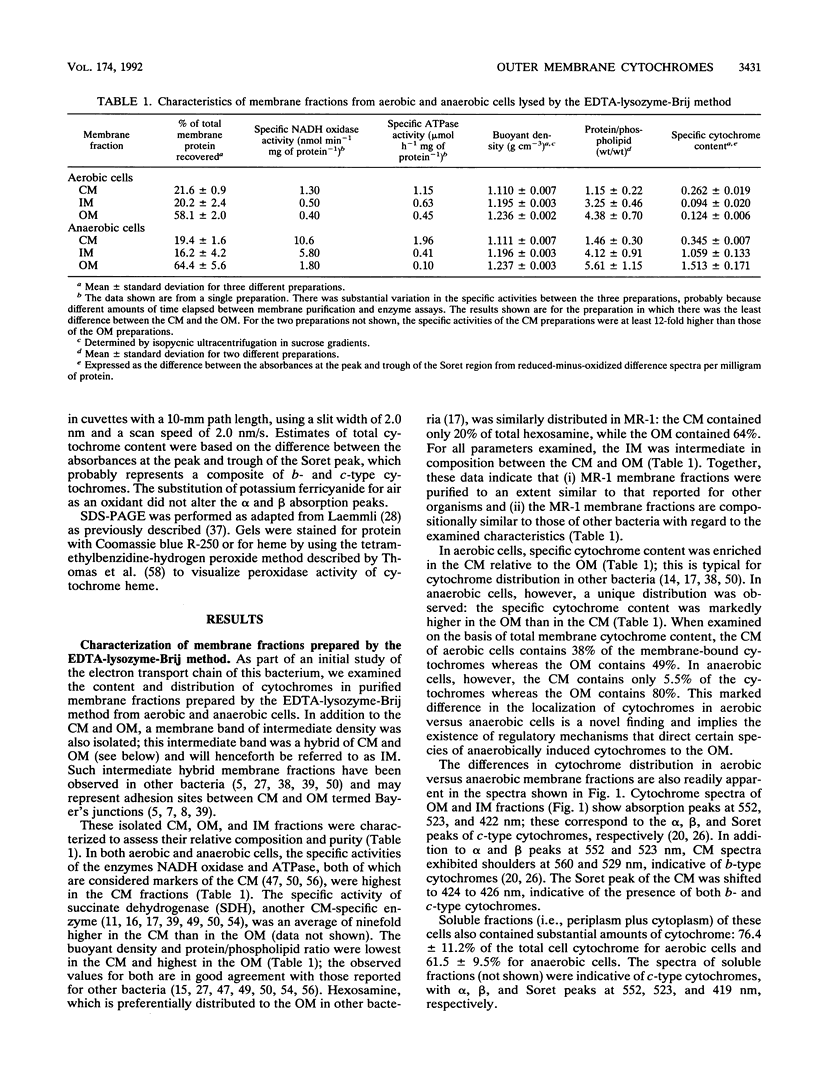





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
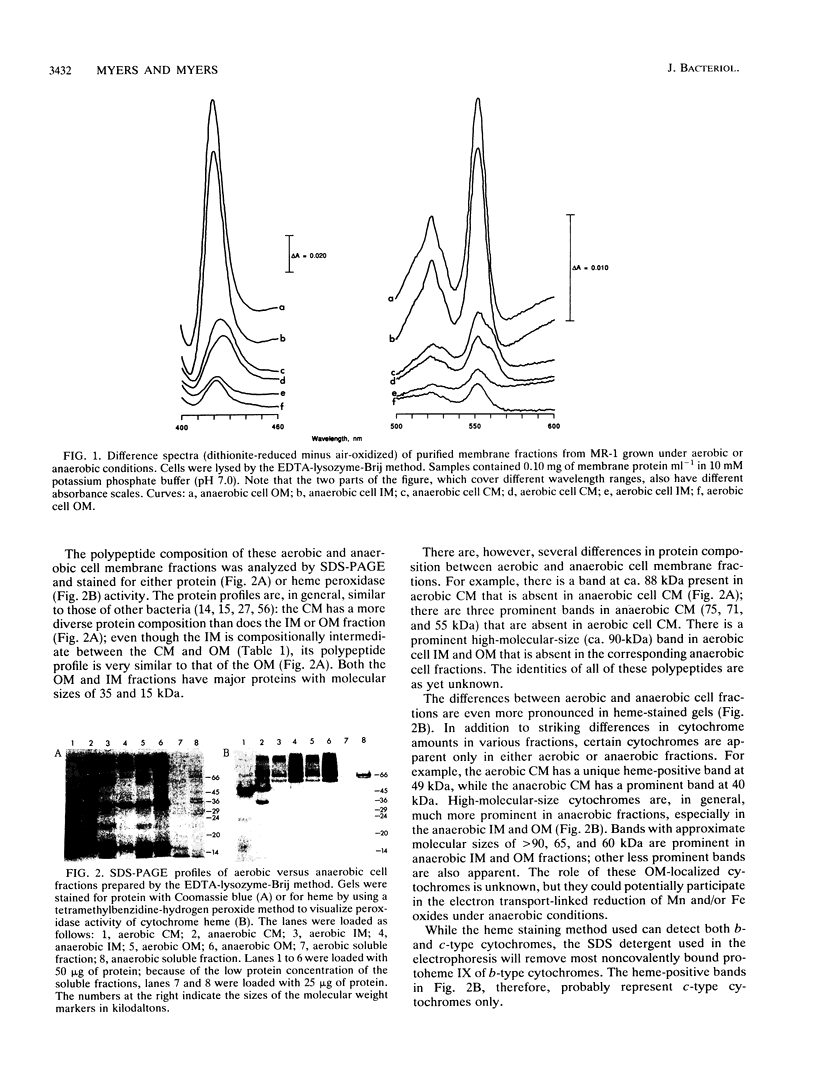
- Ames G. F. Lipids of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli: structure and metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):833–843. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.833-843.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony C. Bacterial oxidation of methane and methanol. Adv Microb Physiol. 1986;27:113–210. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60305-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbas J. A., Díaz J., Rodríguez-Tébar A., Vázquez D. Specific location of penicillin-binding proteins within the cell envelope of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):269–275. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.269-275.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E. Adsorption of bacteriophages to adhesions between wall and membrane of Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1968 Apr;2(4):346–356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.4.346-356.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E. Areas of adhesion between wall and membrane of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Oct;53(3):395–404. doi: 10.1099/00221287-53-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma G., Braster M., Stouthamer A. H., van Verseveld H. W. Subfractionation and characterization of soluble c-type cytochromes from Paracoccus denitrificans cultured under various limiting conditions in the chemostat. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jun 15;165(3):665–670. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
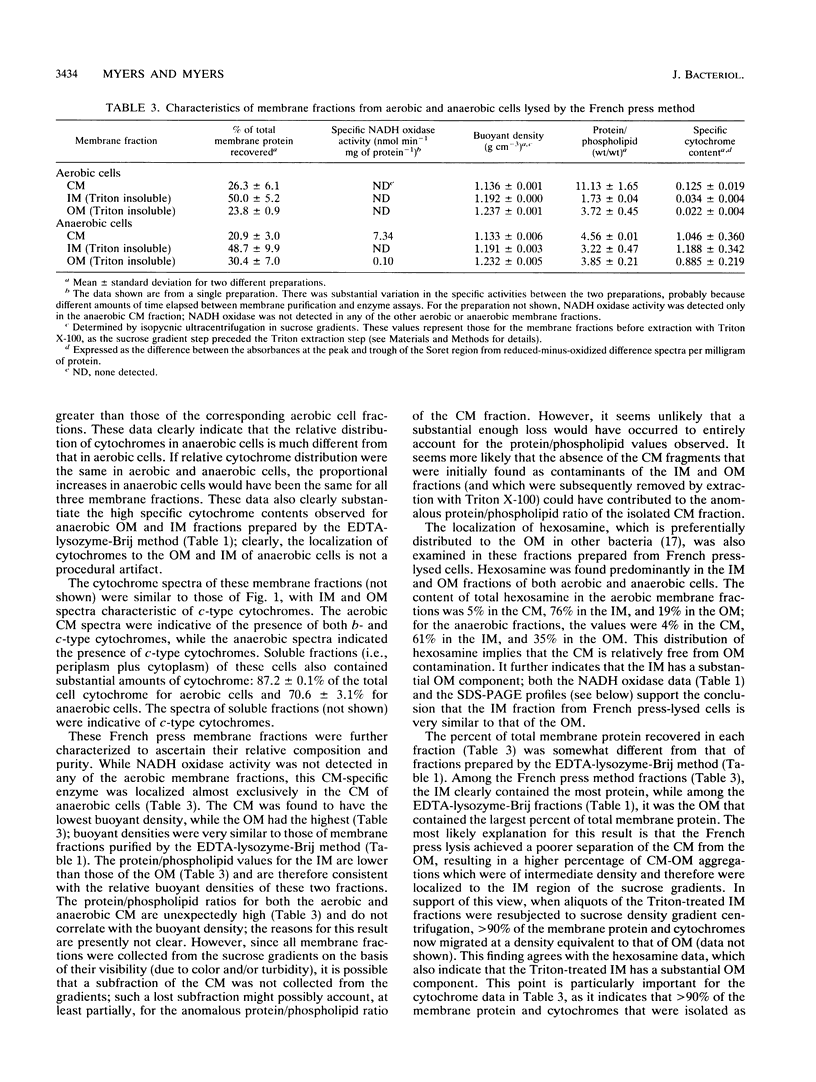
- Cain B. D., Donohue T. J., Shepherd W. D., Kaplan S. Localization of phospholipid biosynthetic enzyme activities in cell-free fractions derived from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):942–948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. L., Niederman R. A. Membranes of Rhodospirillum rubrum: isolation and physicochemical properties of membranes from aerobically grown cells. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1316–1325. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1316-1325.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. L., Salton M. R. Preparation and crossed immunoelectrophoretic analysis of cytoplasmic and outer membrane fractions from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):281–288. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.281-288.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper C. L., Lueking D. R. Localization and characterization of the sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase in Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Lipid Res. 1984 Nov;25(11):1222–1232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiSpirito A. A., Lipscomb J. D., Lidstrom M. E. Soluble cytochromes from the marine methanotroph Methylomonas sp. strain A4. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5360–5367. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5360-5367.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding D. H., Kaplan S. Separation of inner and outer membranes of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Prep Biochem. 1976;6(1):61–79. doi: 10.1080/00327487608061599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatefi Y., Hanstein W. G. Solubilization of particulate proteins and nonelectrolytes by chaotropic agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1129–1136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle B., Beveridge T. J. Binding of metallic ions to the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):749–752. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.749-752.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingledew W. J. Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. The bioenergetics of an acidophilic chemolithotroph. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 30;683(2):89–117. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(82)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent N. E., Wisnieski B. J. Heat modifiability and detergent solubility of outer membrane proteins of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):956–961. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.956-961.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Phillips E. J. Novel mode of microbial energy metabolism: organic carbon oxidation coupled to dissimilatory reduction of iron or manganese. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1472–1480. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1472-1480.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lueking D. R., Fraley R. T., Kaplan S. Intracytoplasmic membrane synthesis in synchronous cell populations of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Fate of "old" and "new" membrane. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):451–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Van Alphen L. Molecular architecture and functioning of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli and other gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):51–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Cannac V., Fitch J., Bartsch R. G., Tollin D., Tollin G., Cusanovich M. A. Soluble cytochromes and ferredoxins from the marine purple phototrophic bacterium, Rhodopseudomonas marina. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 1;1017(2):125–138. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(90)90143-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris C. J., Gibson D. M., Ward F. B. Influence of respiratory substrate on the cytochrome content of Shewanella putrefaciens. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Jun 1;57(3):259–262. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90077-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers C. R., Collins M. L. Cell-cycle-specific fluctuation in cytoplasmic membrane composition in aerobically grown Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5445–5451. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5445-5451.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers C. R., Collins M. L. Cell-cycle-specific oscillation in the composition of chromatophore membrane in Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):818–823. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.818-823.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers C. R., Nealson K. H. Bacterial manganese reduction and growth with manganese oxide as the sole electron acceptor. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1319–1321. doi: 10.1126/science.240.4857.1319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers C. R., Nealson K. H. Respiration-linked proton translocation coupled to anaerobic reduction of manganese(IV) and iron(III) in Shewanella putrefaciens MR-1. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6232–6238. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6232-6238.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Siderophores of bacteria and fungi. Microbiol Sci. 1984 Apr;1(1):9–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Nakae T. The outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol. 1979;20:163–250. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60208-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obinger C., Knepper J. C., Zimmermann U., Peschek G. A. Identification of a periplasmic C-type cytochrome as electron donor to the plasma membrane-bound cytochrome oxidase of the cyanobacterium Nostoc Mac. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jun 15;169(2):492–501. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90358-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oelze J., Golecki J. R., Kleinig H., Weckesser J. Characterization of two cell-envelope fractions from chemotrophically grown Rhodospirillum rubrum. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1975;41(3):273–286. doi: 10.1007/BF02565063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salton M. R. Bacterial membranes. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1971 May;1(1):161–197. doi: 10.3109/10408417109104480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato A., Fukumori Y., Yano T., Kai M., Yamanaka T. Thiobacillus ferrooxidans cytochrome c-552: purification and some of its molecular features. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Sep 28;976(2-3):129–134. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(89)80221-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Protein composition of the cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):890–901. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.890-901.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by Triton X-100. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):545–552. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.545-552.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott C. C., Makula S. R., Finnerty W. R. Isolation and characterization of membranes from a hydrocarbon-oxidizing Acinetobacter sp. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):469–480. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.469-480.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soe G., Nishi N., Kakuno T., Yamashita J., Horio T. Purification and identification of the factor capable of converting Ca2+-ATPase into Mg2+-ATPase present in Rhodospirillum rubrum chromatophores. J Biochem. 1980 Feb;87(2):473–481. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. E., Ryan D., Levin W. An improved staining procedure for the detection of the peroxidase activity of cytochrome P-450 on sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1976 Sep;75(1):168–176. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]