Abstract
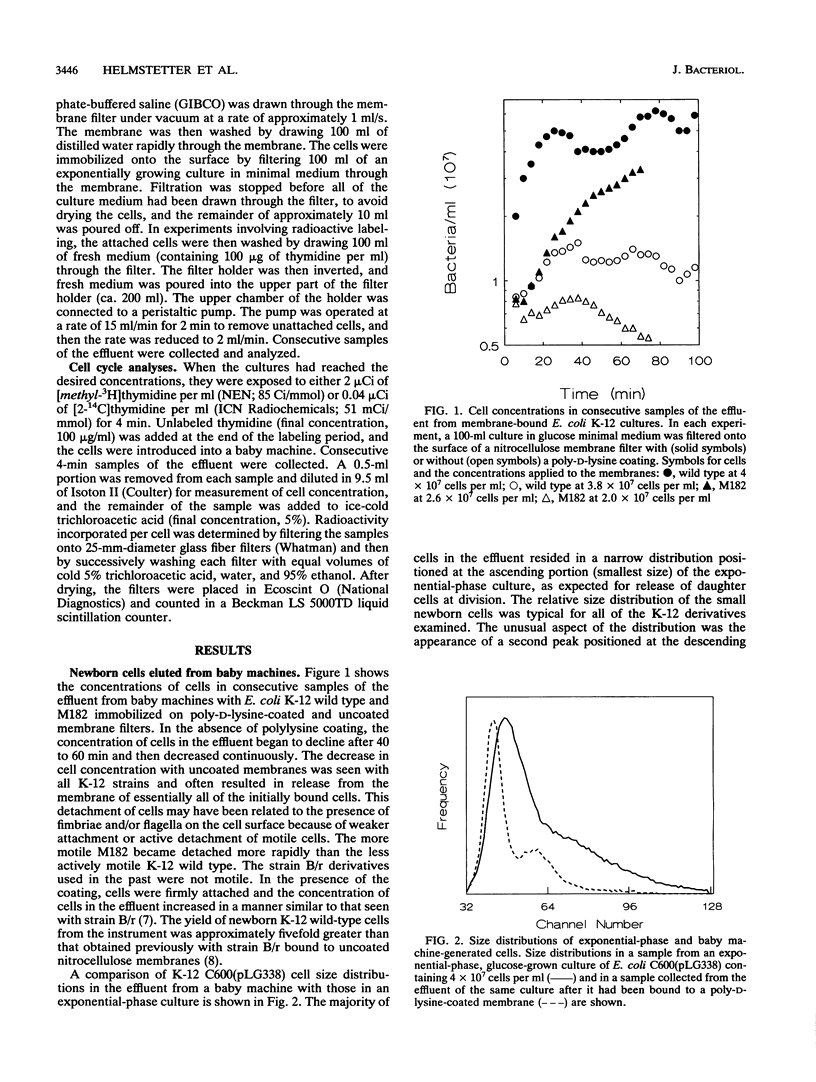
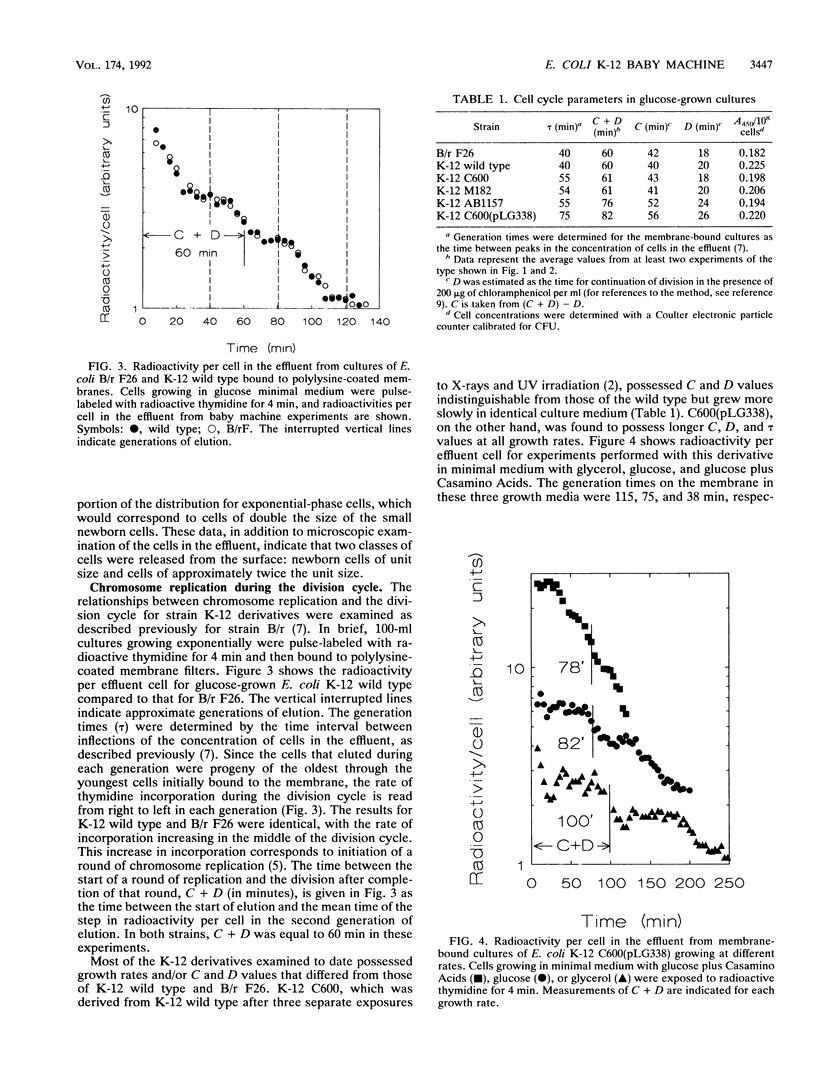
Exponentially growing derivatives of Escherichia coli K-12 were immobilized onto the surfaces of nitrocellulose membrane filters which had been coated with poly-D-lysine. The cells attached firmly to the surfaces, and when flushed with culture medium, the immobilized cells continued to divide and newborn cells were released into the effluent. Cell cycle parameters were examined with the technique, and it was found that K-12 derivatives possessed differing values for interdivision times, C, D, and average cell sizes when grown in the same culture media. It was also found that the cells released from immobilized populations of one culture consisted of two predominant size classes: newborn cells of unit size with single nucleoids and newborn cells of double this unit size. The results demonstrated that K-12 derivatives can be used in the baby machine culture technique to examine all aspects of the cell cycle of this organism. Furthermore, the yield of newborn cells was about fivefold greater than that obtained previously with cultures of strain B/r immobilized onto uncoated membranes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allman R., Schjerven T., Boye E. Cell cycle parameters of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(24):7970–7974. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.24.7970-7974.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S., Helmstetter C. E. Chromosome replication and the division cycle of Escherichia coli B/r. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):519–540. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90425-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings D. J. Synchronization of E. coli K 12 by membrane selection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Oct 23;41(2):471–476. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90529-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELMSTETTER C. E., CUMMINGS D. J. AN IMPROVED METHOD FOR THE SELECTION OF BACTERIAL CELLS AT DIVISION. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Mar 16;82:608–610. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90453-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmstetter C. E. Description of a baby machine for Saccharomyces cerevisiae. New Biol. 1991 Nov;3(11):1089–1096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shehata T. E., Marr A. G. Synchronous growth of enteric bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):789–792. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.789-792.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker N. G., Fairweather N. F., Spratt B. G. Versatile low-copy-number plasmid vectors for cloning in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):335–341. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90172-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


