Abstract
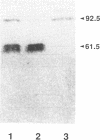
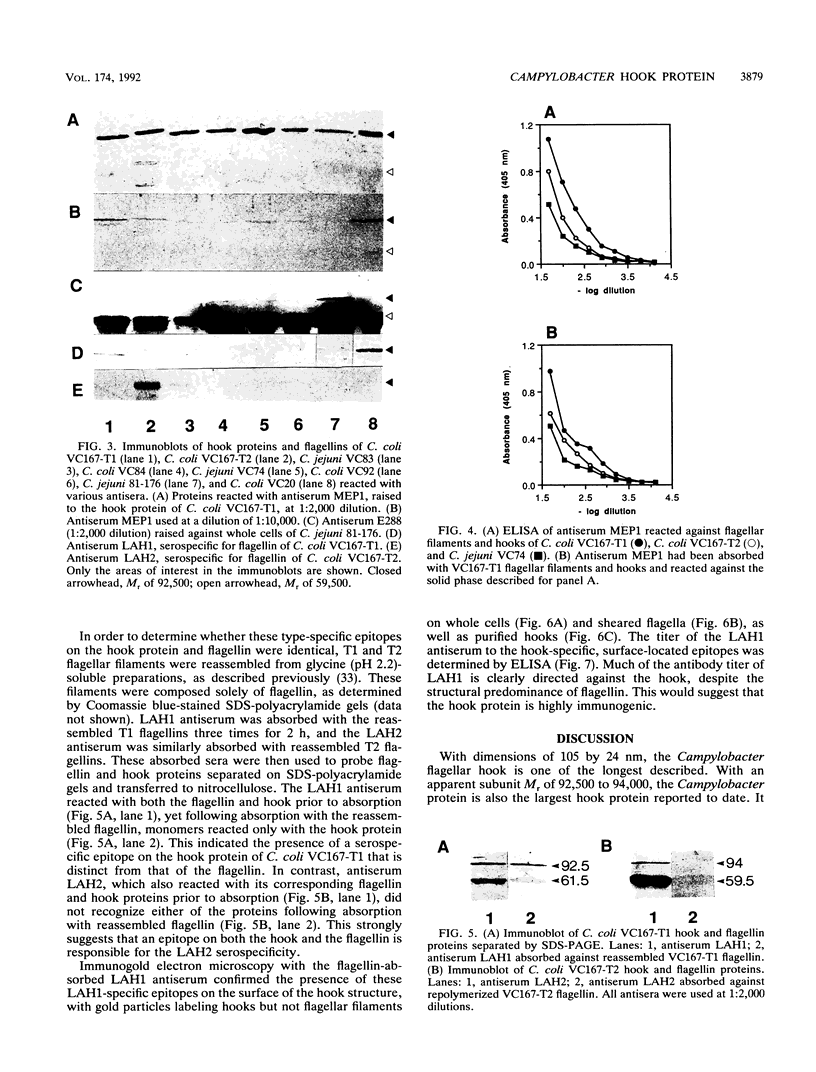
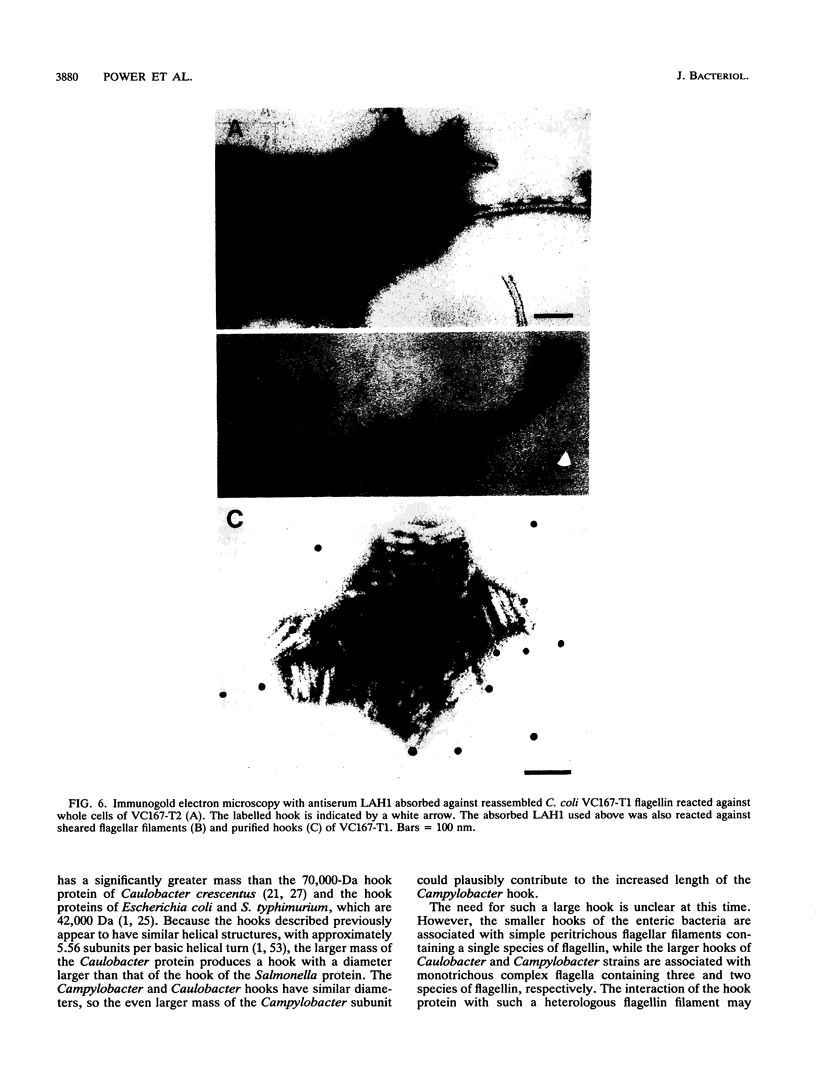
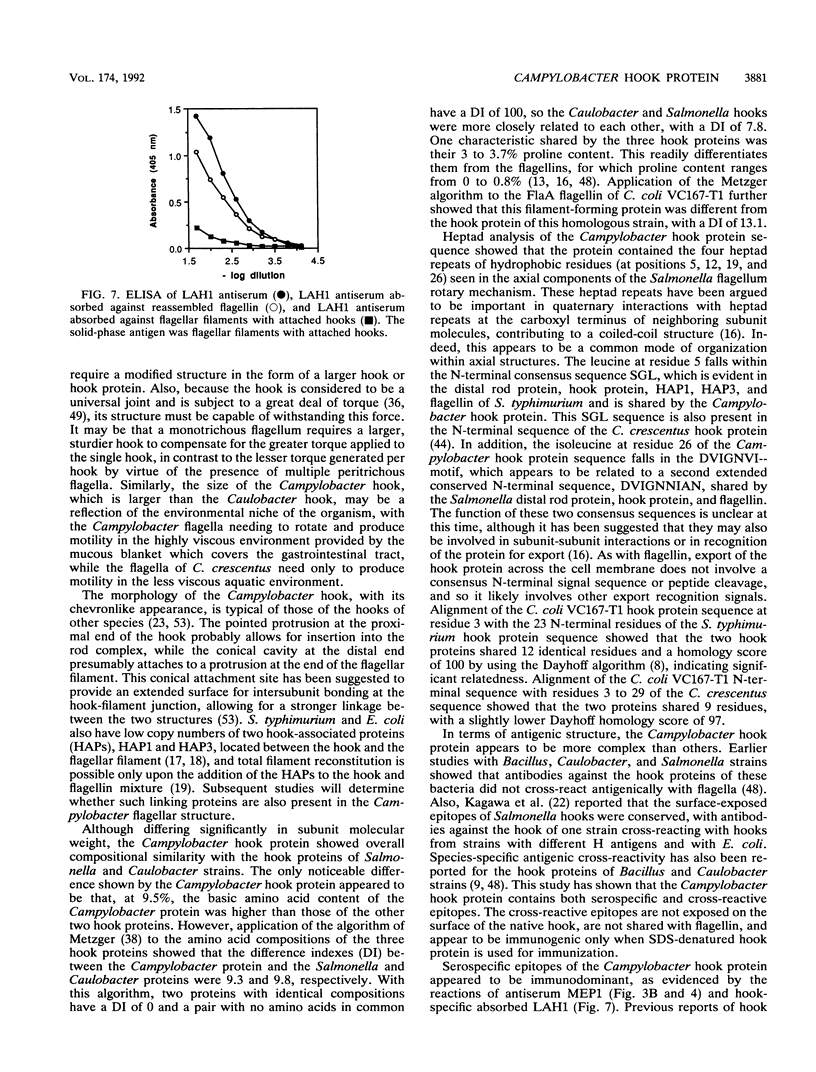
The flagellar filament-hook complex was removed from Campylobacter cells by shearing and was purified by differential solubilization and ultracentrifugation at pH 11 followed by cesium chloride buoyant density ultracentrifugation. Flagellar filaments were then dissociated in 0.2 M glycine-HCl (pH 2.2), and purified hooks were collected by ultracentrifugation. The hooks (105 by 24 nm) each displayed a conical protrusion at the proximal end, a concave cavity at the distal end, and helically arranged subunits. The apparent subunit molecular weight of the hook protein of seven of the eight Campylobacter strains studied was 92,500, while that of the other was 94,000. N-terminal amino acid analysis of the hook protein of two strains of Campylobacter coli and one strain of Campylobacter jejuni demonstrated that the first 15 residues were identical. Amino acid composition analysis showed that the Campylobacter hook protein contained 35.7% hydrophobic and 9.5% basic residues. Isoelectric focusing determined that the hook protein was acidic, with a pI of 4.9. Comparisons with the Salmonella and Caulobacter hook protein compositions and N-terminal amino acid sequences indicated that the Campylobacter protein was related, but more distantly than these two proteins were to each other. Immunochemical analysis with four different antisera and a panel of eight strains showed that serospecific epitopes were immunodominant. The Campylobacter hook proteins carried both cross-reactive and specific non-surface-exposed epitopes, as well as serospecific epitopes which were exposed on the surface of the assembled hook. One class of these surface-exposed hook epitopes was shared with serospecific flagellin epitopes and may involve posttranslational modification, while the second class of epitopes was hook specific and not shared with flagellin.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aizawa S. I., Dean G. E., Jones C. J., Macnab R. M., Yamaguchi S. Purification and characterization of the flagellar hook-basal body complex of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):836–849. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.836-849.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alm R. A., Guerry P., Power M. E., Lior H., Trust T. J. Analysis of the role of flagella in the heat-labile Lior serotyping scheme of thermophilic Campylobacters by mutant allele exchange. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2438–2445. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2438-2445.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black R. E., Levine M. M., Clements M. L., Hughes T. P., Blaser M. J. Experimental Campylobacter jejuni infection in humans. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):472–479. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Hopkins J. A., Berka R. M., Vasil M. L., Wang W. L. Identification and characterization of Campylobacter jejuni outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):276–284. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.276-284.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis. Clin Gastroenterol. 1979 Sep;8(3):737–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell M. B., Guerry P., Lee E. C., Burans J. P., Walker R. I. Reversible expression of flagella in Campylobacter jejuni. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):941–943. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.941-943.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimmitt K., Simon M. Antigenic nature of bacterial flagellar hook structures. Infect Immun. 1970 Feb;1(2):212–213. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.2.212-213.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrero R. L., Lee A. Motility of Campylobacter jejuni in a viscous environment: comparison with conventional rod-shaped bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jan;134(1):53–59. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-1-53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., Alm R. A., Power M. E., Logan S. M., Trust T. J. Role of two flagellin genes in Campylobacter motility. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4757–4764. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4757-4764.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., Logan S. M., Thornton S., Trust T. J. Genomic organization and expression of Campylobacter flagellin genes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):1853–1860. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.1853-1860.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris L. A., Logan S. M., Guerry P., Trust T. J. Antigenic variation of Campylobacter flagella. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5066–5071. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5066-5071.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., DeRosier D. J., Macnab R. M. Flagellar hook and hook-associated proteins of Salmonella typhimurium and their relationship to other axial components of the flagellum. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):819–832. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80266-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Iino T. Locations of hook-associated proteins in flagellar structures of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):183–189. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.183-189.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Kutsukake K., Iino T., Yamaguchi S. Hook-associated proteins essential for flagellar filament formation in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):100–108. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.100-108.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda T., Asakura S., Kamiya R. Total reconstitution of Salmonella flagellar filaments from hook and purified flagellin and hook-associated proteins in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1989 Sep 5;209(1):109–114. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90174-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin T., Penner J. L. Role of the 92.5-kilodalton outer membrane protein of Campylobacter jejuni in serological reactions. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Dec;26(12):2480–2483. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.12.2480-2483.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Walsh M. P., Ely B., Shapiro L. Flagellar hook and basal complex of Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):984–989. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.984-989.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagawa H., Asakura S., Iino T. Serological study of bacterial flagellar hooks. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1474–1481. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1474-1481.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato S., Aizawa S., Asakura S. Reconstruction in vitro of the flagellar polyhook from Salmonella. J Mol Biol. 1982 Nov 15;161(4):551–560. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90407-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Khan I. H., Reese T. S. New structural features of the flagellar base in Salmonella typhimurium revealed by rapid-freeze electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(9):2888–2896. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.9.2888-2896.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komeda Y., Silverman M., Simon M. Identification of the structural gene for the hook subunit protein of Escherichia coli flagella. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):364–371. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.364-371.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagenaur C., DeMartini M., Agabian N. Isolation and characterization of Caulobacter crescentus flagellar hooks. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):795–798. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.795-798.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeGendre N., Matsudaira P. Direct protein microsequencing from Immobilon-P Transfer Membrane. Biotechniques. 1988 Feb;6(2):154–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A., O'Rourke J. L., Barrington P. J., Trust T. J. Mucus colonization as a determinant of pathogenicity in intestinal infection by Campylobacter jejuni: a mouse cecal model. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):536–546. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.536-546.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lior H., Woodward D. L., Edgar J. A., Laroche L. J., Gill P. Serotyping of Campylobacter jejuni by slide agglutination based on heat-labile antigenic factors. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):761–768. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.761-768.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan S. M., Guerry P., Rollins D. M., Burr D. H., Trust T. J. In vivo antigenic variation of Campylobacter flagellin. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2583–2585. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2583-2585.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan S. M., Harris L. A., Trust T. J. Isolation and characterization of Campylobacter flagellins. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5072–5077. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5072-5077.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan S. M., Trust T. J., Guerry P. Evidence for posttranslational modification and gene duplication of Campylobacter flagellin. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3031–3038. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3031-3038.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan S. M., Trust T. J. Location of epitopes on Campylobacter jejuni flagella. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):739–745. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.739-745.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan S. M., Trust T. J. Molecular identification of surface protein antigens of Campylobacter jejuni. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):675–682. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.675-682.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall T., Williams K. M., Vesterberg O. Two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins in human serum: improved resolution by use of narrow pH gradients and prolonged electrophoresis. Clin Chem. 1984 Dec;30(12 Pt 1):2008–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger H., Shapiro M. B., Mosimann J. E., Vinton J. E. Assessment of compositional relatedness between proteins. Nature. 1968 Sep 14;219(5159):1166–1168. doi: 10.1038/2191166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills S. D., Bradbury W. C. Human antibody response to outer membrane proteins of Campylobacter jejuni during infection. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):739–743. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.739-743.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morooka T., Umeda A., Amako K. Motility as an intestinal colonization factor for Campylobacter jejuni. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Aug;131(8):1973–1980. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-8-1973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell D. G. Monoclonal antibodies directed against the flagella of Campylobacter jejuni: production, characterization and lack of effect on the colonization of infant mice. J Hyg (Lond) 1986 Apr;96(2):131–141. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400065906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuijten P. J., van der Zeijst B. A., Newell D. G. Localization of immunogenic regions on the flagellin proteins of Campylobacter jejuni 81116. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):1100–1105. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.1100-1105.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta N., Chen L. S., Swanson E., Newton A. Transcriptional regulation of a periodically controlled flagellar gene operon in Caulobacter crescentus. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):107–115. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90261-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hennessy J. N., Congi R. V. Serotyping of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli on the basis of thermostable antigens. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;2(4):378–383. doi: 10.1007/BF02019474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. G., Blaser M. J., Sarmiento J. I., Fox J. Experimental Campylobacter jejuni infection in Macaca nemestrina. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1438–1444. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1438-1444.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster S. C., Baeuerlein E. Location of the basal disk and a ringlike cytoplasmic structure, two additional structures of the flagellar apparatus of Wolinella succinogenes. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):263–268. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.263-268.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffery M., Newton A. Purification and characterization of a polyhook protein from Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):575–583. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.575-583.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. I. Bacterial flagella. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:397–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis: a "new" disease. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 2;2(6078):9–11. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6078.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueki Y., Fujimoto S., Umeda A., Amako K. Purification and antigenic analysis of flagella of Campylobacter jejuni. Microbiol Immunol. 1988;32(4):327–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1988.tb01393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagenknecht T., DeRosier D. J., Aizawa S., Macnab R. M. Flagellar hook structures of Caulobacter and Salmonella and their relationship to filament structure. J Mol Biol. 1982 Nov 25;162(1):69–87. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90162-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. I., Caldwell M. B., Lee E. C., Guerry P., Trust T. J., Ruiz-Palacios G. M. Pathophysiology of Campylobacter enteritis. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Mar;50(1):81–94. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.1.81-94.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenman W. M., Chai J., Louie T. J., Goudreau C., Lior H., Newell D. G., Pearson A. D., Taylor D. E. Antigenic analysis of Campylobacter flagellar protein and other proteins. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):108–112. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.108-112.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]