Abstract
The phytopathogenic bacterium Erwinia chrysanthemi, unlike other members of the family Enterobacteriaceae, is able to metabolize the beta-glucosides, arbutin, and salicin. A previous genetic analysis of the E. chrysanthemi arb genes, which mediate beta-glucoside metabolism, suggested that they were homologous to the Escherichia coli K-12 bgl genes. We have now determined the nucleotide sequence of a 5,065-bp DNA fragment containing three genes, arbG, arbF, and arbB. Deletion analysis, expression in minicell systems, and comparison with sequences of other proteins suggest that arbF and arbB encode a beta-glucoside-specific phosphotransferase system-dependent permease and a phospho-beta-glucosidase, respectively. The ArbF amino acid sequence shares 55% identity with that of the E. coli BglF permease and contains most residues thought to be important for a phosphotransferase. One change, however, was noted, since BglF Arg-625, presumably involved in phosphoryl transfer, was replaced by a Cys residue in ArbF. An analysis of the ArbB sequence led to the definition of a protein family which contained enzymes classified as phospho-beta-glucosidases, phospho-beta-galactosidases, beta-glucosidases, and beta-galactosidases and originating from gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, archebacteria, and mammals, including humans. An analysis of this family allowed us (i) to speculate on the ways that these enzymes evolved, (ii) to identify a glutamate residue likely to be a key amino acid in the catalytic activity of each protein, and (iii) to predict that domain II of the human lactate-phlorizin hydrolase, which is involved in lactose intolerance, is catalytically nonactive. A comparison between the untranslated regions of the E. chrysanthemi arb cluster and the E. coli bgl operon revealed the conservation of two regions which, in the latter, are known to terminate transcription under noninducing conditions and be the target of the BglG transcriptional antiterminator under inducing conditions. ArbG was found to share a high level of similarity with the BglG antiterminator as well as with Bacillus subtilis SacT and SacY antiterminators, suggesting that ArbG functions as an antiterminator in regulating the expression of the E. chrysanthemi arb genes.
Full text
PDF

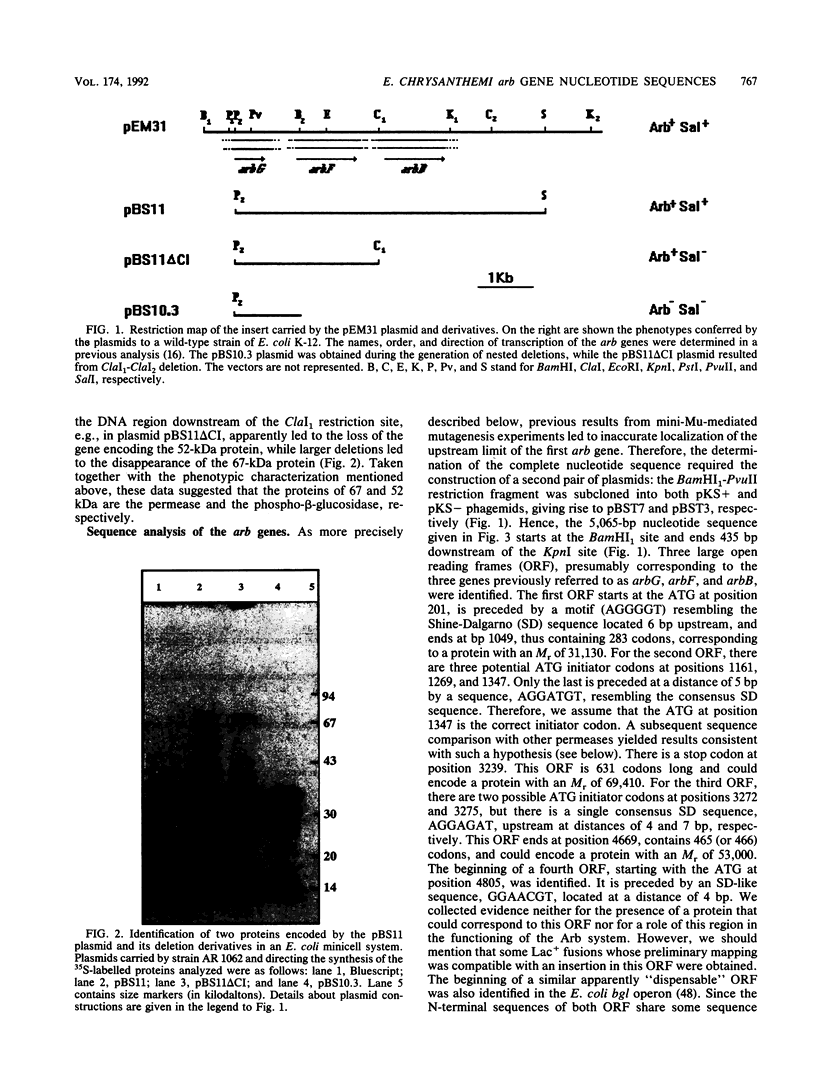


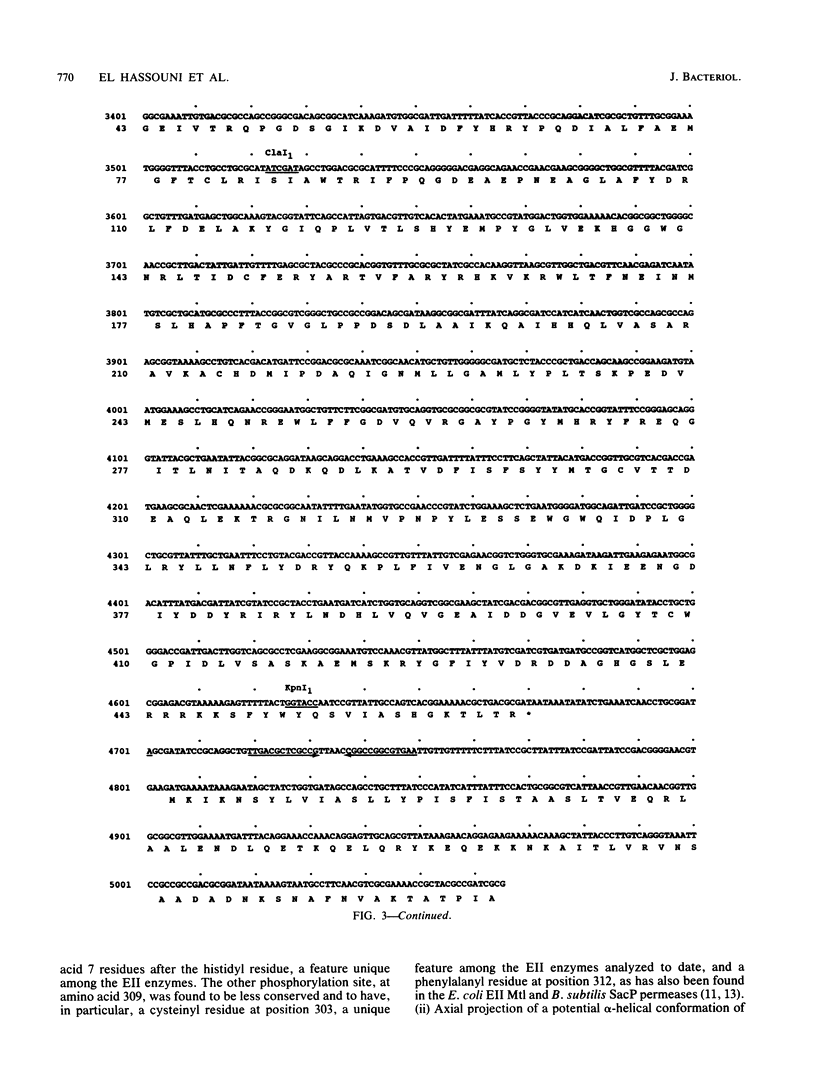



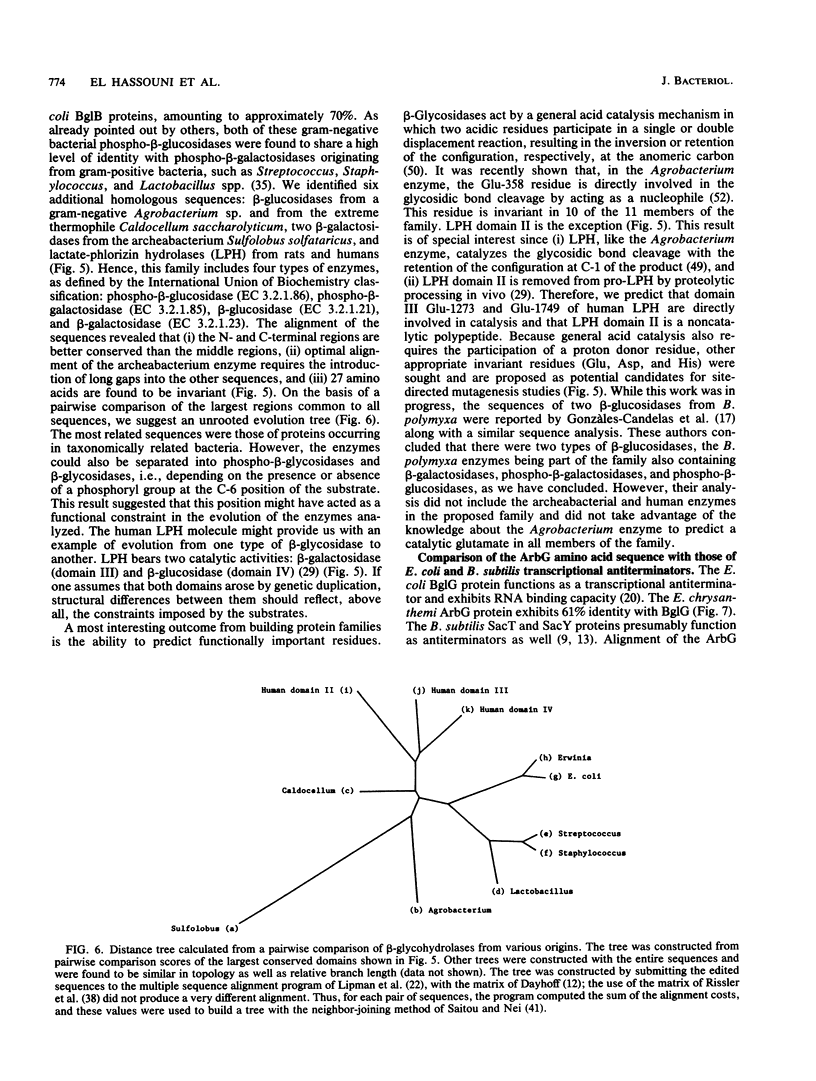



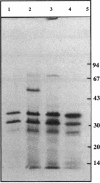
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amster-Choder O., Houman F., Wright A. Protein phosphorylation regulates transcription of the beta-glucoside utilization operon in E. coli. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):847–855. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90937-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amster-Choder O., Wright A. Regulation of activity of a transcriptional anti-terminator in E. coli by phosphorylation in vivo. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):540–542. doi: 10.1126/science.2200123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barras F., el Hassouni M., Chambost J. P., Chippaux M. The beta-glucosides metabolism in Erwinia chrysanthemi: preliminary analysis and comparison to Escherichia coli systems. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;5(1-2):143–147. doi: 10.1016/0168-6445(89)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boizet B., Villeval D., Slos P., Novel M., Novel G., Mercenier A. Isolation and structural analysis of the phospho-beta-galactosidase gene from Streptococcus lactis Z268. Gene. 1988;62(2):249–261. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90563-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breidt F., Jr, Stewart G. C. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of the Staphylococcus aureus phospho-beta-galactosidase gene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):969–973. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.969-973.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung C. T., Miller R. H. A rapid and convenient method for the preparation and storage of competent bacterial cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3580–3580. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crutz A. M., Steinmetz M., Aymerich S., Richter R., Le Coq D. Induction of levansucrase in Bacillus subtilis: an antitermination mechanism negatively controlled by the phosphotransferase system. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):1043–1050. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.1043-1050.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubellis M. V., Rozzo C., Montecucchi P., Rossi M. Isolation and sequencing of a new beta-galactosidase-encoding archaebacterial gene. Gene. 1990 Sep 28;94(1):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90472-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis T., Yamada M., Elgort M., Saier M. H., Jr Nucleotide sequence of the mannitol (mtl) operon in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1988 May;2(3):405–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00045.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debarbouille M., Arnaud M., Fouet A., Klier A., Rapoport G. The sacT gene regulating the sacPA operon in Bacillus subtilis shares strong homology with transcriptional antiterminators. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3966–3973. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3966-3973.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiNardo S., Voelkel K. A., Sternglanz R., Reynolds A. E., Wright A. Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase I mutants have compensatory mutations in DNA gyrase genes. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):43–51. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90403-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Candelas L., Ramón D., Polaina J. Sequences and homology analysis of two genes encoding beta-glucosidases from Bacillus polymyxa. Gene. 1990 Oct 30;95(1):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90410-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrissat B. A classification of glycosyl hydrolases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem J. 1991 Dec 1;280(Pt 2):309–316. doi: 10.1042/bj2800309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Sharp P. M. CLUSTAL: a package for performing multiple sequence alignment on a microcomputer. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houman F., Diaz-Torres M. R., Wright A. Transcriptional antitermination in the bgl operon of E. coli is modulated by a specific RNA binding protein. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1153–1163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90392-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemesle-Varloot L., Henrissat B., Gaboriaud C., Bissery V., Morgat A., Mornon J. P. Hydrophobic cluster analysis: procedures to derive structural and functional information from 2-D-representation of protein sequences. Biochimie. 1990 Aug;72(8):555–574. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(90)90120-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Altschul S. F., Kececioglu J. D. A tool for multiple sequence alignment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4412–4415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little S., Cartwright P., Campbell C., Prenneta A., McChesney J., Mountain A., Robinson M. Nucleotide sequence of a thermostable beta-galactosidase from Sulfolobus solfataricus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7980–7980. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love D. R., Fisher R., Bergquist P. L. Sequence structure and expression of a cloned beta-glucosidase gene from an extreme thermophile. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jul;213(1):84–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00333402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan S., Reynolds A. E., Wright A. Positive and negative regulation of the bgl operon in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2570–2578. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2570-2578.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan S., Wright A. A bacterial gene involved in transcription antitermination: regulation at a rho-independent terminator in the bgl operon of E. coli. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):485–494. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90502-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantei N., Villa M., Enzler T., Wacker H., Boll W., James P., Hunziker W., Semenza G. Complete primary structure of human and rabbit lactase-phlorizin hydrolase: implications for biosynthesis, membrane anchoring and evolution of the enzyme. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2705–2713. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03124.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meagher R. B., Tait R. C., Betlach M., Boyer H. W. Protein expression in E. coli minicells by recombinant plasmids. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):521–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy N., McConnell D. J., Cantwell B. A. The DNA sequence of the gene and genetic control sites for the excreted B. subtilis enzyme beta-glucanase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5355–5367. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker L. L., Hall B. G. A fourth Escherichia coli gene system with the potential to evolve beta-glucoside utilization. Genetics. 1988 Jul;119(3):485–490. doi: 10.1093/genetics/119.3.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker L. L., Hall B. G. Characterization and nucleotide sequence of the cryptic cel operon of Escherichia coli K12. Genetics. 1990 Mar;124(3):455–471. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.3.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter E. V., Chassy B. M. Nucleotide sequence of the beta-D-phosphogalactoside galactohydrolase gene of Lactobacillus casei: comparison to analogous pbg genes of other gram-positive organisms. Gene. 1988;62(2):263–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90564-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. E., Felton J., Wright A. Insertion of DNA activates the cryptic bgl operon in E. coli K12. Nature. 1981 Oct 22;293(5834):625–629. doi: 10.1038/293625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. E., Mahadevan S., LeGrice S. F., Wright A. Enhancement of bacterial gene expression by insertion elements or by mutation in a CAP-cAMP binding site. J Mol Biol. 1986 Sep 5;191(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90424-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risler J. L., Delorme M. O., Delacroix H., Henaut A. Amino acid substitutions in structurally related proteins. A pattern recognition approach. Determination of a new and efficient scoring matrix. J Mol Biol. 1988 Dec 20;204(4):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Werner P. K., Müller M. Insertion of proteins into bacterial membranes: mechanism, characteristics, and comparisons with the eucaryotic process. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Sep;53(3):333–366. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.3.333-366.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Yamada M., Erni B., Suda K., Lengeler J., Ebner R., Argos P., Rak B., Schnetz K., Lee C. A. Sugar permeases of the bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system: sequence comparisons. FASEB J. 1988 Mar 1;2(3):199–208. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.3.2832233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou N., Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jul;4(4):406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefler S. Inducible system for the utilization of beta-glucosides in Escherichia coli. I. Active transport and utilization of beta-glucosides. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):254–263. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.254-263.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefler S., Maas W. K. Inducible system for the utilization of beta-glucosides in Escherichia coli. II. Description of mutant types and genetic analysis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):264–272. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.264-272.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefler S., Malamy A. Taxonomic investigations on expressed and cryptic phospho-beta-glucosidases in Enterobacteriaceae. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):422–433. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.422-433.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnetz K., Rak B. Regulation of the bgl operon of Escherichia coli by transcriptional antitermination. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3271–3277. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03194.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnetz K., Sutrina S. L., Saier M. H., Jr, Rak B. Identification of catalytic residues in the beta-glucoside permease of Escherichia coli by site-specific mutagenesis and demonstration of interdomain cross-reactivity between the beta-glucoside and glucose systems. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13464–13471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnetz K., Toloczyki C., Rak B. Beta-glucoside (bgl) operon of Escherichia coli K-12: nucleotide sequence, genetic organization, and possible evolutionary relationship to regulatory components of two Bacillus subtilis genes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2579–2590. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2579-2590.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakarchuk W. W., Greenberg N. M., Kilburn D. G., Miller R. C., Jr, Warren R. A. Structure and transcription analysis of the gene encoding a cellobiase from Agrobacterium sp. strain ATCC 21400. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):301–307. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.301-307.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Hassouni M., Chippaux M., Barras F. Analysis of the Erwinia chrysanthemi arb genes, which mediate metabolism of aromatic beta-glucosides. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6261–6267. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6261-6267.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]