Abstract
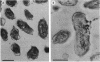
AlgP, a protein with an unusual carboxy-terminal domain resembling the tails of eukaryotic H1 histones, was detected in whole-cell extracts and within the cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by using immunoblotting and immunoelectron microscopy analyses. One known function of AlgP is its participation in the transcriptional activation of the algD gene. This is a pivotal step in the establishment of mucoidy in P. aeruginosa; mucoidy is a critical virulence factor expressed during respiratory infections in patients with cystic fibrosis. Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies were raised against a synthetic 50-mer peptide containing two sets of six tandem repeats of the motif Lys-Pro-Ala-Ala (and its single-amino-acid substitution variants), based on the sequence of the algP gene from the standard genetic strain PAO. Western immunoblots with these antibodies and total protein extracts from P. aeruginosa revealed two polypeptides that reacted with the antibodies in all of the P. aeruginosa strains tested. The detected polypeptides displayed strain-dependent variability in their electrophoretic mobility, in accordance with the previously noted variability of the algP repeats at the DNA level. In strain PAO, the recognized polypeptides had apparent masses of 46.4 and 41.6 kDa. Immunoelectron microscopy revealed that AlgP is an intracellular protein with a wide distribution suggestive of its more general role. To indicate that fact, AlgP is given here an alternative name, Hp1. Since AlgP (Hp1) is a eubacterial histonelike element displaying sequence and domanial similarity with eukaryotic H1 histones, these findings may have implications on the understanding of the organization of the prokaryotic nucleoid and its role in the control of gene expression and bacterial virulence.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan J., Mitchell T., Harborne N., Bohm L., Crane-Robinson C. Roles of H1 domains in determining higher order chromatin structure and H1 location. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 20;187(4):591–601. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90337-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croston G. E., Kerrigan L. A., Lira L. M., Marshak D. R., Kadonaga J. T. Sequence-specific antirepression of histone H1-mediated inhibition of basal RNA polymerase II transcription. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):643–649. doi: 10.1126/science.1899487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deretic D., Hamm H. E. Topographic analysis of antigenic determinants recognized by monoclonal antibodies to the photoreceptor guanyl nucleotide-binding protein, transducin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10839–10847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deretic V., Gill J. F., Chakrabarty A. M. Gene algD coding for GDPmannose dehydrogenase is transcriptionally activated in mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):351–358. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.351-358.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deretic V., Govan J. R., Konyecsni W. M., Martin D. W. Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis: mutations in the muc loci affect transcription of the algR and algD genes in response to environmental stimuli. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Feb;4(2):189–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00586.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deretic V., Konyecsni W. M. A procaryotic regulatory factor with a histone H1-like carboxy-terminal domain: clonal variation of repeats within algP, a gene involved in regulation of mucoidy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5544–5554. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5544-5554.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deretic V., Konyecsni W. M. Control of mucoidy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: transcriptional regulation of algR and identification of the second regulatory gene, algQ. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3680–3688. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3680-3688.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deretic V., Mohr C. D., Martin D. W. Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis: signal transduction and histone-like elements in the regulation of bacterial virulence. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jul;5(7):1577–1583. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01903.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K., Rouviere-Yaniv J. Histonelike proteins of bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Sep;51(3):301–319. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.3.301-319.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürrenberger M., Bjornsti M. A., Uetz T., Hobot J. A., Kellenberger E. Intracellular location of the histonelike protein HU in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4757–4768. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4757-4768.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn J. L., Ohman D. E. Use of a gene replacement cosmid vector for cloning alginate conversion genes from mucoid and nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains: algS controls expression of algT. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3228–3236. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3228-3236.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franssen H. J., Nap J. P., Gloudemans T., Stiekema W., Van Dam H., Govers F., Louwerse J., Van Kammen A., Bisseling T. Characterization of cDNA for nodulin-75 of soybean: A gene product involved in early stages of root nodule development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4495–4499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freytag J. W., Noelken M. E., Hudson B. G. Physical properties of collagen--sodium dodecyl sulfate complexes. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4761–4768. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyfe J. A., Govan J. R. Alginate synthesis in mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a chromosomal locus involved in control. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Aug;119(2):443–450. doi: 10.1099/00221287-119-2-443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobot J. A., Villiger W., Escaig J., Maeder M., Ryter A., Kellenberger E. Shape and fine structure of nucleoids observed on sections of ultrarapidly frozen and cryosubstituted bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):960–971. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.960-971.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover T. R., Santero E., Porter S., Kustu S. The integration host factor stimulates interaction of RNA polymerase with NIFA, the transcriptional activator for nitrogen fixation operons. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90284-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høiby N., Döring G., Schiøtz P. O. Pathogenic mechanisms of chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in cystic fibrosis patients. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1987;39:60–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Chakrabarty A. M. Purification of the regulatory protein AlgR1 and its binding in the far upstream region of the algD promoter in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1760–1764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Misra T. K., Chakrabarty A. M. AlgR3, a protein resembling eukaryotic histone H1, regulates alginate synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2887–2891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konyecsni W. M., Deretic V. DNA sequence and expression analysis of algP and algQ, components of the multigene system transcriptionally regulating mucoidy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: algP contains multiple direct repeats. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2511–2520. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2511-2520.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Nakane P. K. Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1077–1083. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr C. D., Deretic V. Gene-scrambling mutagenesis: generation and analysis of insertional mutations in the alginate regulatory region of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6252–6260. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6252-6260.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr C. D., Hibler N. S., Deretic V. AlgR, a response regulator controlling mucoidy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, binds to the FUS sites of the algD promoter located unusually far upstream from the mRNA start site. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):5136–5143. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.5136-5143.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr C. D., Martin D. W., Konyecsni W. M., Govan J. R., Lory S., Deretic V. Role of the far-upstream sites of the algD promoter and the algR and rpoN genes in environmental modulation of mucoidy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6576–6580. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6576-6580.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr C. D., Rust L., Albus A. M., Iglewski B. H., Deretic V. Expression patterns of genes encoding elastase and controlling mucoidy: co-ordinate regulation of two virulence factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from cystic fibrosis. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Dec;4(12):2103–2110. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00571.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettijohn D. E. Histone-like proteins and bacterial chromosome structure. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):12793–12796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Matthews W. J., Jr, Eardley D. D. Immunochemical characterization of the mucoid exopolysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1983 Mar;147(3):494–503. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.3.494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid M. B. More than just "histone-like" proteins. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):451–453. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90438-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods J. P., Spinola S. M., Strobel S. M., Cannon J. G. Conserved lipoprotein H.8 of pathogenic Neisseria consists entirely of pentapeptide repeats. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jan;3(1):43–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]