Abstract
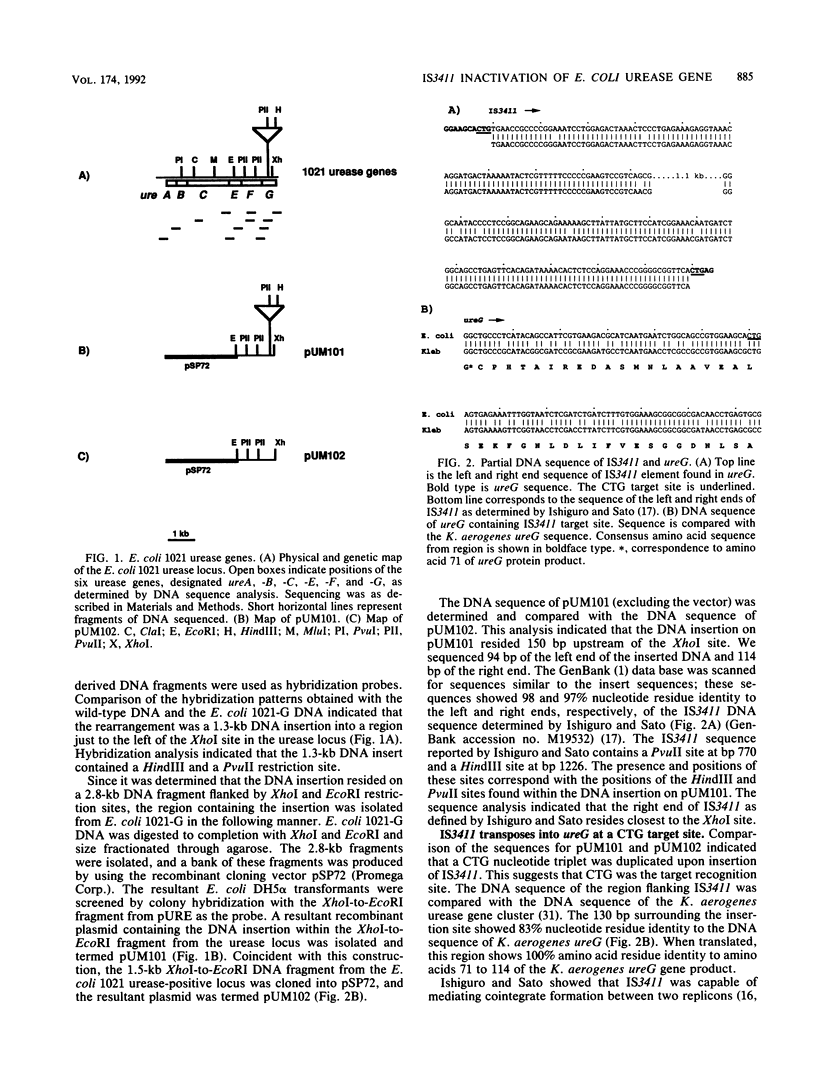
Ureolytic Escherichia coli are unusual clinical isolates that are found at various extraintestinal sites of infection, predominantly the urinary tract. The urease-positive phenotype is unstable in approximately 25% of these isolates, and urease-negative segregants are produced at a high frequency. We have studied the nature of the urease-positive-to-negative transition in one of these isolates, designated E. coli 1021. Southern hybridization experiments with genomic DNA extracted from seven independent E. coli 1021 urease-negative segregants revealed the presence of a 1.3-kb DNA insertion in the urease gene cluster. A DNA fragment containing the DNA insertion was cloned from one of the urease-negative segregants. This cloned DNA fragment was capable of mediating cointegrate formation with the conjugative plasmid pOX38, suggesting that the DNA insertion was a transposable element. The insert was identified as an IS3411 element in ureG by DNA sequence analysis. A 3-bp target duplication (CTG) flanking the insertion element was found. DNA spanning the insertion site was amplified from the other six urease-negative segregants by using the polymerase chain reaction. The DNA sequence of the amplified fragments indicated that an IS3411 element was found in an identical site in all urease-negative segregants examined. These data suggest that in E. coli 1021, IS3411 transposes at a high frequency into ureG at a CTG site, disrupting this gene and eliminating urease activity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRAUDE A. I., SIEMIENSKI J. Role of bacterial urease in experimental pyelonephritis. J Bacteriol. 1960 Aug;80:171–179. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.2.171-179.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilofsky H. S., Burks C. The GenBank genetic sequence data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1861–1863. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard A., Barile M. F. Cloning of Ureaplasma urealyticum DNA sequences showing genetic homology with urease genes from gram-negative bacteria. Res Microbiol. 1989 May-Jun;140(4-5):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(89)90020-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard A. Ureaplasma urealyticum urease genes; use of a UGA tryptophan codon. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Apr;4(4):669–676. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00636.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton C. L., Pallen M. J., Kleanthous H., Wren B. W., Tabaqchali S. Nucleotide sequence of two genes from Helicobacter pylori encoding for urease subunits. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 25;18(2):362–362. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.2.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins C. M., Falkow S. Genetic analysis of Escherichia coli urease genes: evidence for two distinct loci. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7138–7144. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7138-7144.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins C. M., Falkow S. Genetic analysis of an Escherichia coli urease locus: evidence of DNA rearrangement. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1041–1045. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1041-1045.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn B. E., Campbell G. P., Perez-Perez G. I., Blaser M. J. Purification and characterization of urease from Helicobacter pylori. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9464–9469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatermann S., John J., Marre R. Staphylococcus saprophyticus urease: characterization and contribution to uropathogenicity in unobstructed urinary tract infection of rats. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):110–116. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.110-116.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatermann S., Marre R. Cloning and expression of Staphylococcus saprophyticus urease gene sequences in Staphylococcus carnosus and contribution of the enzyme to virulence. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):2998–3002. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.2998-3002.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith D. P., Musher D. M., Itin C. Urease. The primary cause of infection-induced urinary stones. Invest Urol. 1976 Mar;13(5):346–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausinger R. P. Nickel utilization by microorganisms. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Mar;51(1):22–42. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.1.22-42.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu L. T., Nicholson E. B., Jones B. D., Lynch M. J., Mobley H. L. Morganella morganii urease: purification, characterization, and isolation of gene sequences. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3073–3080. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3073-3080.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro N., Sato G. Nucleotide sequence of insertion sequence IS3411, which flanks the citrate utilization determinant of transposon Tn3411. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1902–1906. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1902-1906.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro N., Sato G., Sasakawa C., Danbara H., Yoshikawa M. Identification of citrate utilization transposon Tn3411 from a naturally occurring citrate utilization plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):961–968. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.961-968.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro N., Sato G. Spontaneous deletion of citrate-utilizing ability promoted by insertion sequences. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):642–650. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.642-650.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. D., Lockatell C. V., Johnson D. E., Warren J. W., Mobley H. L. Construction of a urease-negative mutant of Proteus mirabilis: analysis of virulence in a mouse model of ascending urinary tract infection. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1120–1123. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1120-1123.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. D., Mobley H. L. Proteus mirabilis urease: genetic organization, regulation, and expression of structural genes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3342–3349. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3342-3349.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. D., Mobley H. L. Proteus mirabilis urease: nucleotide sequence determination and comparison with jack bean urease. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6414–6422. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6414-6422.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan E., Saedler H., Starlinger P. O0 and strong-polar mutations in the gal operon are insertions. Mol Gen Genet. 1968;102(4):353–363. doi: 10.1007/BF00433726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyce C. M., Grindley N. D. Method for determining whether a gene of Escherichia coli is essential: application to the polA gene. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):636–643. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.636-643.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labigne A., Cussac V., Courcoux P. Shuttle cloning and nucleotide sequences of Helicobacter pylori genes responsible for urease activity. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(6):1920–1931. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.6.1920-1931.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J. Duplication and amplification of toxin genes in Vibrio cholerae. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley H. L., Hausinger R. P. Microbial ureases: significance, regulation, and molecular characterization. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Mar;53(1):85–108. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.1.85-108.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley H. L., Jones B. D., Jerse A. E. Cloning of urease gene sequences from Providencia stuartii. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):161–169. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.161-169.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulrooney S. B., Hausinger R. P. Sequence of the Klebsiella aerogenes urease genes and evidence for accessory proteins facilitating nickel incorporation. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5837–5843. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5837-5843.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulrooney S. B., Lynch M. J., Mobley H. L., Hausinger R. P. Purification, characterization, and genetic organization of recombinant Providencia stuartii urease expressed by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 May;170(5):2202–2207. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.5.2202-2207.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulrooney S. B., Pankratz H. S., Hausinger R. P. Regulation of gene expression and cellular localization of cloned Klebsiella aerogenes (K. pneumoniae) urease. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Jun;135(6):1769–1776. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-6-1769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M., Griffith D. P., Yawn D., Rossen R. D. Role of urease in pyelonephritis resulting from urinary tract infection with Proteus. J Infect Dis. 1975 Feb;131(2):177–181. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.2.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mörsdorf G., Kaltwasser H. Cloning of the genes encoding urease from Proteus vulgaris and sequencing of the structural genes. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Jan 1;54(1-3):67–73. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90260-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson E. B., Concaugh E. A., Mobley H. L. Proteus mirabilis urease: use of a ureA-lacZ fusion demonstrates that induction is highly specific for urea. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3360–3365. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3360-3365.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd M. J., Hausinger R. P. Competitive inhibitors of Klebsiella aerogenes urease. Mechanisms of interaction with the nickel active site. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):15835–15842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd M. J., Hausinger R. P. Purification and characterization of the nickel-containing multicomponent urease from Klebsiella aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):5963–5967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsmuth I. K., Davis B. R., Allen S. D. Ureolytic Escherichia coli of human origin: serological, epidemiological, and genetic analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Dec;10(6):897–902. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.6.897-902.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz S. E., Wray S. K., Hull S. I., Hull R. A. Multiple proteins encoded within the urease gene complex of Proteus mirabilis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1027–1033. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1027-1033.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]