Abstract
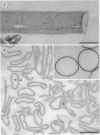
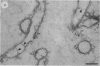
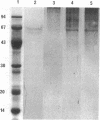
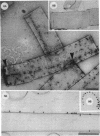
Treatment of the Methanospirillum hungatei GP1 sheath with 90% (wt/vol) phenol resulted in the solubilization of a novel phenol-soluble group of polypeptides. These polypeptides were purified by the removal of insoluble material by ultracentrifugation and represented approximately 19% of the mass of the sheath. The phenol-insoluble material resembled untreated sheath but had lost its rigidity and cylindrical form. Recombination of phenol-soluble and phenol-insoluble fractions by dialysis to remove phenol resulted in cylindrical reassembly products. Although bona fide sheath (complete with the 2.8-nm lattice) was not produced, a role for the phenol-soluble polypeptides in the maintenance of sheath rigidity is implied. The phenol-soluble polypeptides have limited surface exposure as detected by antibodies on intact sheath; therefore, they are not responsible for the 2.8-nm repeat occurring on the outer face of the sheath. However, longitudinal and transverse linear labeling by protein A-colloidal gold on the outer and inner faces, respectively, occurred with monoclonal antibodies specific to the phenol-soluble polypeptides. Restricted surface exposure of phenol-soluble polypeptides on the sheath highlighted molecular defects in sheath architecture. These lattice faults may indicate sites of sheath growth to accommodate cell growth or division (longitudinal immunogold label) and filament division (transverse immunogold label). The identification of a second group of polypeptides within the infrastructure of the sheath suggests that the sheath is a trilaminar structure in which phenol-soluble polypeptides are sandwiched between sodium dodecyl sulfate-beta-mercaptoethanol-EDTA-soluble polypeptides (G. Southam and T. J. Beveridge, J. Bacteriol. 173:6213-6222, 1991) (phenol-insoluble material).
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bendayan M. Double immunocytochemical labeling applying the protein A-gold technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Jan;30(1):81–85. doi: 10.1177/30.1.6172469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Southam G., Jericho M. H., Blackford B. L. High-resolution topography of the S-layer sheath of the archaebacterium Methanospirillum hungatei provided by scanning tunneling microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6589–6595. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6589-6595.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Sprott G. D., Whippey P. Ultrastructure, inferred porosity, and gram-staining character of Methanospirillum hungatei filament termini describe a unique cell permeability for this archaeobacterium. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):130–140. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.130-140.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Stewart M., Doyle R. J., Sprott G. D. Unusual stability of the Methanospirillum hungatei sheath. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):728–737. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.728-737.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard L. V., Dalton D. D., McCoubrey W. K., Jr Expansion of the tetragonally arrayed cell wall protein layer during growth of Bacillus sphaericus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):748–757. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.748-757.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koval S. F., Murray R. G. The isolation of surface array proteins from bacteria. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;62(11):1181–1189. doi: 10.1139/o84-152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel G. B., Roth L. A., van den Berg L., Clark D. S. Characterization of a strain of Methanospirillum hungatti. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Sep;22(9):1404–1410. doi: 10.1139/m76-208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. J., Hills G. J., Henwood J. A., Harris J. E., Archer D. B. Three-dimensional architecture of the cell sheath and septa of Methanospirillum hungatei. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):750–757. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.750-757.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B., Messner P. Crystalline surface layers in procaryotes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):2891–2897. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.2891-2897.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southam G., Beveridge T. J. Dissolution and immunochemical analysis of the sheath of the archaeobacterium Methanospirillum hungatei GP1. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):6213–6222. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.6213-6222.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprott G. D., Colvin J. R., McKellar R. C. Spheroplasts of Methanospirillum hungatii formed upon treatment with dithiothreitol. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Jun;25(6):730–738. doi: 10.1139/m79-106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprott G. D., McKellar R. C. Composition and properties of the cell wall of Methanospirillum hungatii. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Feb;26(2):115–120. doi: 10.1139/m80-017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M., Beveridge T. J., Sprott G. D. Crystalline order to high resolution in the sheath of Methanospirillum hungatei: a cross-beta structure. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 5;183(3):509–515. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorun W., Mehl E. Determination of molecular weights of microgram quantities of protein components from biological membranes and other complex mixtures: gel electrophoresis across linear gradients of acrylamide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 May 6;160(1):132–134. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]