Abstract
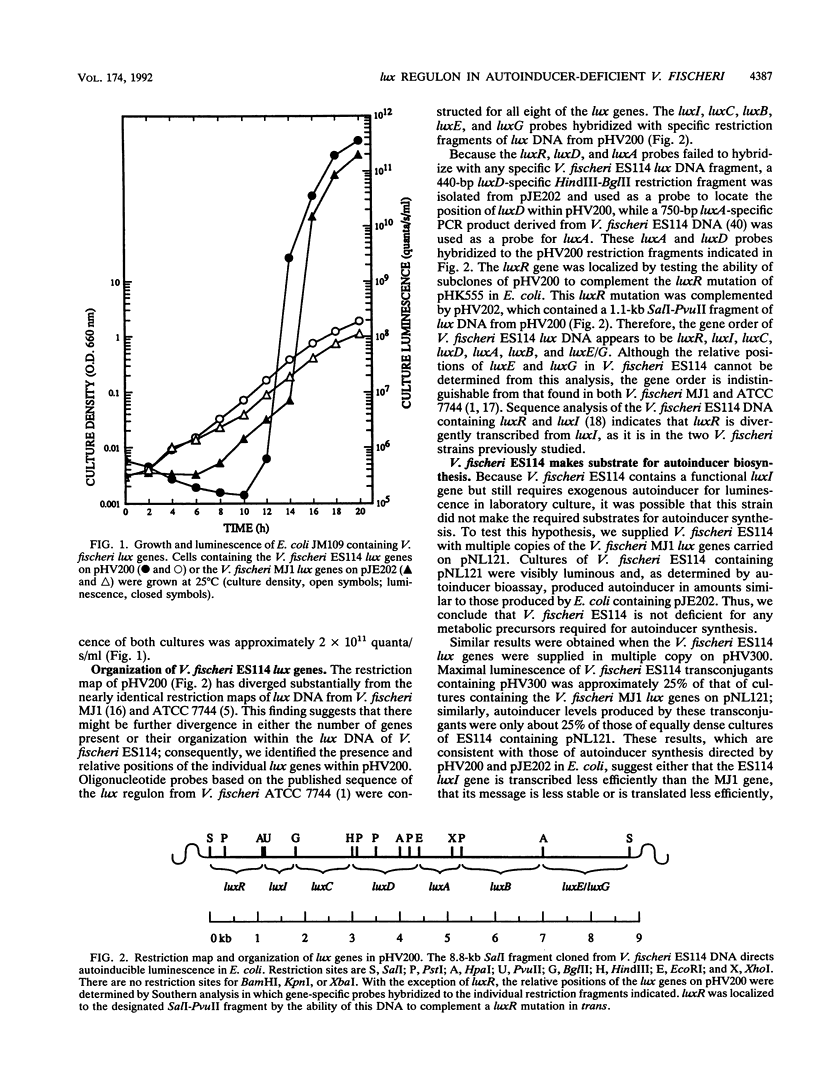
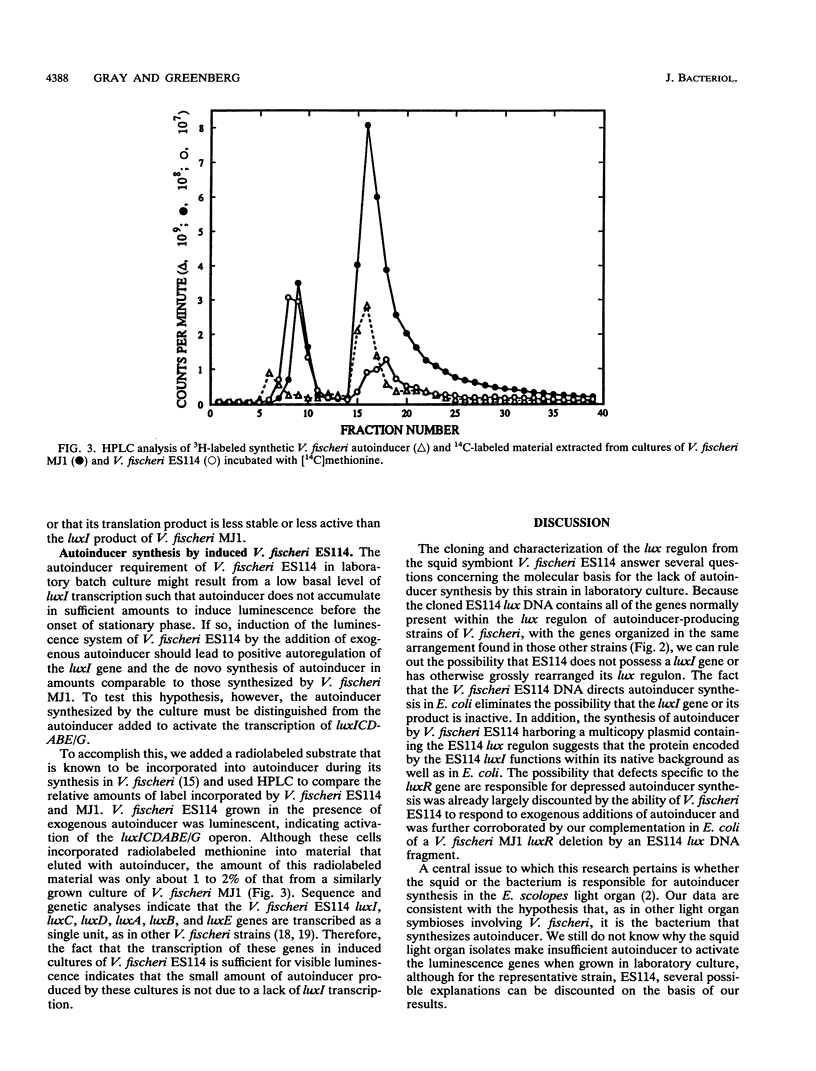
Vibrio fischeri ES114 is an isolate representing the specific bacterial light organ symbiont of the squid Euprymna scolopes. An interesting feature of this strain of V. fischeri is that it is visibly luminous within the light organ of the squid host but is nonluminous when grown under standard laboratory conditions. Luminescence can be restored in laboratory culture, however, by the addition of autoinducer, a species-specific inducer of the V. fischeri luminescence (lux) genes. Most other isolates of V. fischeri produce autoinducer in sufficient quantities to induce luminescence in laboratory culture. We have cloned an 8.8-kb DNA fragment from V. fischeri ES114 that encodes all of the functions necessary for luminescence in Escherichia coli in the absence of exogenous autoinducer. This DNA contains both of the recognized V. fischeri lux regulatory genes, one of which (luxI) directs E. coli to synthesize autoinducer. The organization of the individual lux genes within this DNA fragment appears to be the same as that in the other strains of V. fischeri studied; the restriction map of the V. fischeri ES114 lux DNA has diverged substantially, however, from the largely conserved maps of V. fischeri MJ1 and ATCC 7744. Although E. coli containing the V. fischeri ES114 lux DNA synthesizes considerable amounts of autoinducer, V. fischeri ES114 synthesizes autoinducer only in small amounts, even when transcription of the lux genes, including luxI, is activated by the addition of exogenous autoinducer. Nonetheless, transconjugants of V. fischeri ES114 that contain multicopy plasmids bearing the ES114 lux genes synthesize sufficient autoinducer to induce luminescence. These results suggest that V. fischeri ES11r does not lack a functional luxl, nor is it deficient in the ability to synthesize metabolic precursors for autoinducer synthesis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin T. O., Devine J. H., Heckel R. C., Lin J. W., Shadel G. S. The complete nucleotide sequence of the lux regulon of Vibrio fischeri and the luxABN region of Photobacterium leiognathi and the mechanism of control of bacterial bioluminescence. J Biolumin Chemilumin. 1989 Jul;4(1):326–341. doi: 10.1002/bio.1170040145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boettcher K. J., Ruby E. G. Depressed light emission by symbiotic Vibrio fischeri of the sepiolid squid Euprymna scolopes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3701–3706. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3701-3706.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan M., Graham A. F., Meighen E. A. Functional identification of the fatty acid reductase components encoded in the luminescence operon of Vibrio fischeri. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1186–1190. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1186-1190.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhme H., Haselkorn R. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence analysis of the gene coding for heterocyst ferredoxin from the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Oct;214(2):278–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00337722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Effect of growth conditions on the formation of the relaxation complex of supercoiled ColE1 deoxyribonucleic acid and protein in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):1135–1146. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.1135-1146.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dower W. J., Miller J. F., Ragsdale C. W. High efficiency transformation of E. coli by high voltage electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6127–6145. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap P. V., Greenberg E. P. Control of Vibrio fischeri luminescence gene expression in Escherichia coli by cyclic AMP and cyclic AMP receptor protein. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):45–50. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.45-50.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard A., Burlingame A. L., Eberhard C., Kenyon G. L., Nealson K. H., Oppenheimer N. J. Structural identification of autoinducer of Photobacterium fischeri luciferase. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 28;20(9):2444–2449. doi: 10.1021/bi00512a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard A. Inhibition and activation of bacterial luciferase synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):1101–1105. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.1101-1105.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engebrecht J., Nealson K., Silverman M. Bacterial bioluminescence: isolation and genetic analysis of functions from Vibrio fischeri. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engebrecht J., Silverman M. Identification of genes and gene products necessary for bacterial bioluminescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4154–4158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan H. B., Greenberg E. P. Diffusion of autoinducer is involved in regulation of the Vibrio fischeri luminescence system. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1210–1214. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1210-1214.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan H. B., Greenberg E. P. Overproduction and purification of the luxR gene product: Transcriptional activator of the Vibrio fischeri luminescence system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6639–6643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. Y., Rasheed S. A simple procedure for maximum yield of high-quality plasmid DNA. Biotechniques. 1990 Dec;9(6):676–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFall-Ngai M. J., Ruby E. G. Symbiont recognition and subsequent morphogenesis as early events in an animal-bacterial mutualism. Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1491–1494. doi: 10.1126/science.1962208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nealson K. H. Autoinduction of bacterial luciferase. Occurrence, mechanism and significance. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Feb 4;112(1):73–79. doi: 10.1007/BF00446657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nealson K. H., Hastings J. W. Bacterial bioluminescence: its control and ecological significance. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Dec;43(4):496–518. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.4.496-518.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby E. G., Greenberg E. P., Hastings J. W. Planktonic marine luminous bacteria: species distribution in the water column. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Feb;39(2):302–306. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.2.302-306.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby E. G., Nealson K. H. Symbiotic association of Photobacterium fischeri with the marine luminous fish Monocentris japonica; a model of symbiosis based on bacterial studies. Biol Bull. 1976 Dec;151(3):574–586. doi: 10.2307/1540507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R., O'Connell M., Labes M., Pühler A. Plasmid vectors for the genetic analysis and manipulation of rhizobia and other gram-negative bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1986;118:640–659. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)18106-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. S., Lubinsky-Mink S., Jackson C. G., Cassel A., Kuhn J. pHG165: a pBR322 copy number derivative of pUC8 for cloning and expression. Plasmid. 1986 May;15(3):172–181. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(86)90035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart V., Parales J., Jr Identification and expression of genes narL and narX of the nar (nitrate reductase) locus in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1589–1597. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1589-1597.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartzman A., Kapoor S., Graham A. F., Meighen E. A. A new Vibrio fischeri lux gene precedes a bidirectional termination site for the lux operon. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6797–6802. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6797-6802.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimpee C. F., Nadeau T. L., Nealson K. H. Development of species-specific hybridization probes for marine luminous bacteria by using in vitro DNA amplification. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 May;57(5):1319–1324. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.5.1319-1324.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


