Abstract
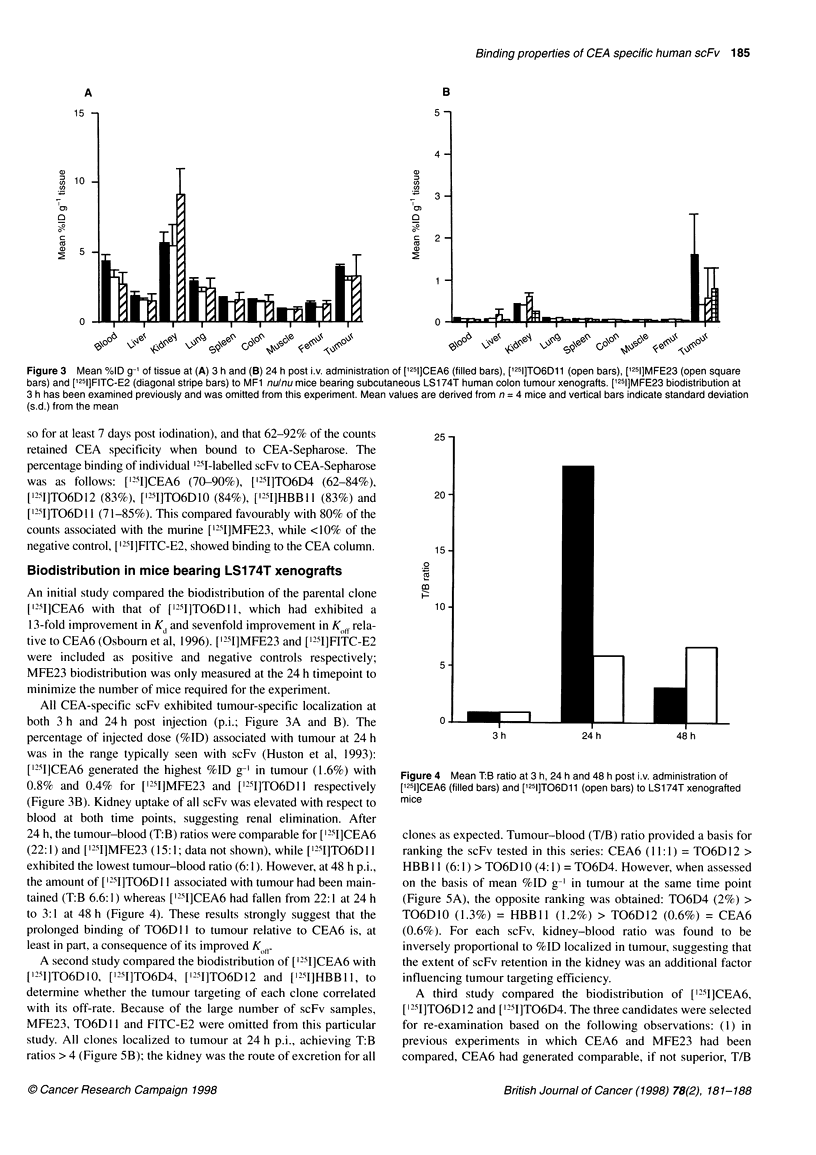
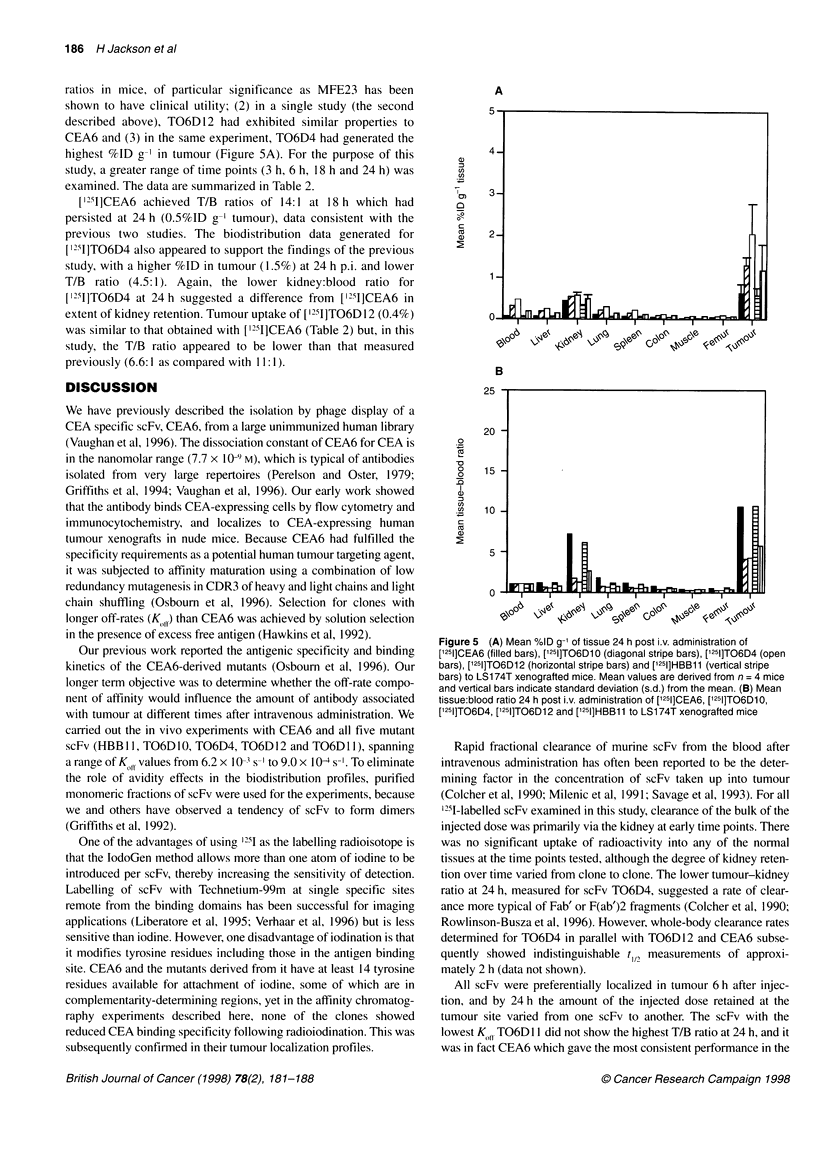
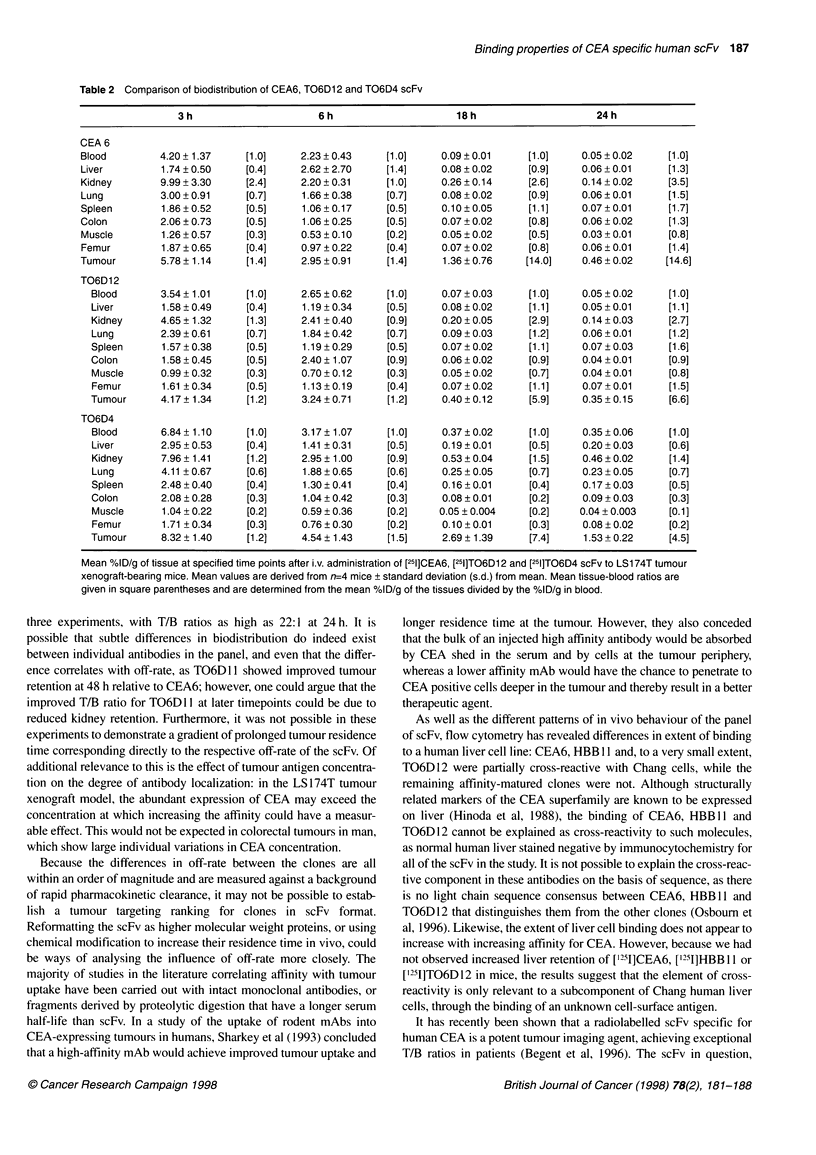
We have examined the biological properties of CEA6, a human carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)-specific single-chain Fv (scFv) isolated by phage display, and five related clones derived by affinity maturation and selected for improved off-rate (Koff). All clones bind strongly and specifically to CEA-positive human tumours by immunocytochemistry and show negligible cross-reactivity with normal colon. Flow cytometry of scFv on human liver cells indicates a shift in fine epitope specificity resulting from mutagenesis. All monomeric scFv have been radioiodinated, retaining effectively full binding activity. A single intravenous injection into nude mice bearing human colon tumour xenografts confirms tumour targeting in all cases. As reported in other studies, the kidney is the main route of elimination of scFv at early time points. Tumour binding of the parental antibody CEA6 consistently gives the highest tumour-blood ratios at 24 h (mean 16:1). Clone TO6D11, which has a sevenfold reduced Koff relative to CEA6, showed no difference in tumour uptake at 24 h but persisted at the tumour site for longer than CEA6. This study demonstrates a possible correlation between binding affinity and tumour residence time when examined in this model.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Begent R. H., Verhaar M. J., Chester K. A., Casey J. L., Green A. J., Napier M. P., Hope-Stone L. D., Cushen N., Keep P. A., Johnson C. J. Clinical evidence of efficient tumor targeting based on single-chain Fv antibody selected from a combinatorial library. Nat Med. 1996 Sep;2(9):979–984. doi: 10.1038/nm0996-979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chester K. A., Begent R. H., Robson L., Keep P., Pedley R. B., Boden J. A., Boxer G., Green A., Winter G., Cochet O. Phage libraries for generation of clinically useful antibodies. Lancet. 1994 Feb 19;343(8895):455–456. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)92695-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colcher D., Bird R., Roselli M., Hardman K. D., Johnson S., Pope S., Dodd S. W., Pantoliano M. W., Milenic D. E., Schlom J. In vivo tumor targeting of a recombinant single-chain antigen-binding protein. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 Jul 18;82(14):1191–1197. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.14.1191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg D. M., Goldenberg H., Sharkey R. M., Lee R. E., Horowitz J. A., Hall T. C., Hansen H. J. In-vivo antibody imaging for the detection of human tumors. Cancer Treat Res. 1990;51:273–292. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-1497-4_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths A. D., Malmqvist M., Marks J. D., Bye J. M., Embleton M. J., McCafferty J., Baier M., Holliger K. P., Gorick B. D., Hughes-Jones N. C. Human anti-self antibodies with high specificity from phage display libraries. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):725–734. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05706.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood P. J., Boden J., Pedley R. B., Rawlins G., Rogers G. T., Bagshawe K. D. Comparative tumour localization of antibody fragments and intact IgG in nude mice bearing a CEA-producing human colon tumour xenograft. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1985 Dec;21(12):1515–1522. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(85)90247-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins R. E., Russell S. J., Winter G. Selection of phage antibodies by binding affinity. Mimicking affinity maturation. J Mol Biol. 1992 Aug 5;226(3):889–896. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90639-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinoda Y., Neumaier M., Hefta S. A., Drzeniek Z., Wagener C., Shively L., Hefta L. J., Shively J. E., Paxton R. J. Molecular cloning of a cDNA coding biliary glycoprotein I: primary structure of a glycoprotein immunologically crossreactive with carcinoembryonic antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6959–6963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S., Shively L., Raubitschek A., Sherman M., Williams L. E., Wong J. Y., Shively J. E., Wu A. M. Minibody: A novel engineered anti-carcinoembryonic antigen antibody fragment (single-chain Fv-CH3) which exhibits rapid, high-level targeting of xenografts. Cancer Res. 1996 Jul 1;56(13):3055–3061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huston J. S., McCartney J., Tai M. S., Mottola-Hartshorn C., Jin D., Warren F., Keck P., Oppermann H. Medical applications of single-chain antibodies. Int Rev Immunol. 1993;10(2-3):195–217. doi: 10.3109/08830189309061696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langmuir V. K., Mendonca H. L., Woo D. V. Comparisons between two monoclonal antibodies that bind to the same antigen but have differing affinities: uptake kinetics and 125I-antibody therapy efficacy in multicell spheroids. Cancer Res. 1992 Sep 1;52(17):4728–4734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberatore M., Neri D., Neri G., Pini A., Iurilli A. P., Ponzo F., Spampinato G., Padula F., Pala A., Colella A. C. Efficient one-step direct labelling of recombinant antibodies with technetium-99m. Eur J Nucl Med. 1995 Nov;22(11):1326–1329. doi: 10.1007/BF00801622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milenic D. E., Yokota T., Filpula D. R., Finkelman M. A., Dodd S. W., Wood J. F., Whitlow M., Snoy P., Schlom J. Construction, binding properties, metabolism, and tumor targeting of a single-chain Fv derived from the pancarcinoma monoclonal antibody CC49. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6363–6371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. An Hsp70-like protein in the ER: identity with the 78 kd glucose-regulated protein and immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90746-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osbourn J. K., Field A., Wilton J., Derbyshire E., Earnshaw J. C., Jones P. T., Allen D., McCafferty J. Generation of a panel of related human scFv antibodies with high affinities for human CEA. Immunotechnology. 1996 Sep;2(3):181–196. doi: 10.1016/s1380-2933(96)00046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons H. L., Earnshaw J. C., Wilton J., Johnson K. S., Schueler P. A., Mahoney W., McCafferty J. Directing phage selections towards specific epitopes. Protein Eng. 1996 Nov;9(11):1043–1049. doi: 10.1093/protein/9.11.1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley R. B., Boden J. A., Boden R., Dale R., Begent R. H. Comparative radioimmunotherapy using intact or F(ab')2 fragments of 131I anti-CEA antibody in a colonic xenograft model. Br J Cancer. 1993 Jul;68(1):69–73. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perelson A. S., Oster G. F. Theoretical studies of clonal selection: minimal antibody repertoire size and reliability of self-non-self discrimination. J Theor Biol. 1979 Dec 21;81(4):645–670. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(79)90275-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimm M. V., Gribben S. J. Influence of syngeneic (anti-idiotypic) antibody responses on biodistribution and tumour localisation of murine monoclonal antibodies and fragments. Anticancer Res. 1993 Jan-Feb;13(1):241–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage P., Rowlinson-Busza G., Verhoeyen M., Spooner R. A., So A., Windust J., Davis P. J., Epenetos A. A. Construction, characterisation and kinetics of a single chain antibody recognising the tumour associated antigen placental alkaline phosphatase. Br J Cancer. 1993 Oct;68(4):738–742. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schier R., McCall A., Adams G. P., Marshall K. W., Merritt H., Yim M., Crawford R. S., Weiner L. M., Marks C., Marks J. D. Isolation of picomolar affinity anti-c-erbB-2 single-chain Fv by molecular evolution of the complementarity determining regions in the center of the antibody binding site. J Mol Biol. 1996 Nov 8;263(4):551–567. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlom J., Eggensperger D., Colcher D., Molinolo A., Houchens D., Miller L. S., Hinkle G., Siler K. Therapeutic advantage of high-affinity anticarcinoma radioimmunoconjugates. Cancer Res. 1992 Mar 1;52(5):1067–1072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharkey R. M., Goldenberg D. M., Murthy S., Pinsky H., Vagg R., Pawlyk D., Siegel J. A., Wong G. Y., Gascon P., Izon D. O. Clinical evaluation of tumor targeting with a high-affinity, anticarcinoembryonic-antigen-specific, murine monoclonal antibody, MN-14. Cancer. 1993 Mar 15;71(6):2082–2096. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19930315)71:6<2082::aid-cncr2820710625>3.0.co;2-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Pope T., Tung J. S., Chan C., Hollis G., Mark G., Johnson K. S. Affinity maturation of a high-affinity human monoclonal antibody against the third hypervariable loop of human immunodeficiency virus: use of phage display to improve affinity and broaden strain reactivity. J Mol Biol. 1996 Feb 16;256(1):77–88. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan T. J., Williams A. J., Pritchard K., Osbourn J. K., Pope A. R., Earnshaw J. C., McCafferty J., Hodits R. A., Wilton J., Johnson K. S. Human antibodies with sub-nanomolar affinities isolated from a large non-immunized phage display library. Nat Biotechnol. 1996 Mar;14(3):309–314. doi: 10.1038/nbt0396-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhaar M. J., Chester K. A., Keep P. A., Robson L., Pedley R. B., Boden J. A., Hawkins R. E., Begent R. H. A single chain Fv derived from a filamentous phage library has distinct tumor targeting advantages over one derived from a hybridoma. Int J Cancer. 1995 May 16;61(4):497–501. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910610412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota T., Milenic D. E., Whitlow M., Schlom J. Rapid tumor penetration of a single-chain Fv and comparison with other immunoglobulin forms. Cancer Res. 1992 Jun 15;52(12):3402–3408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]