Abstract
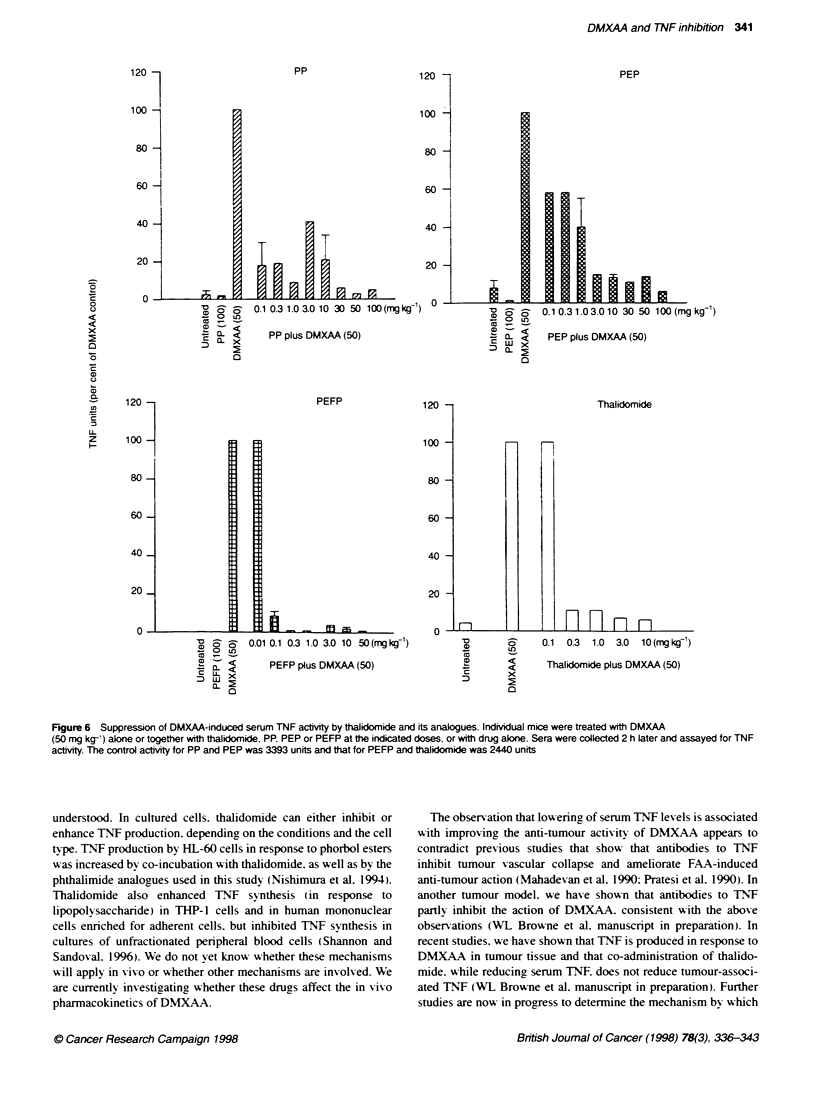
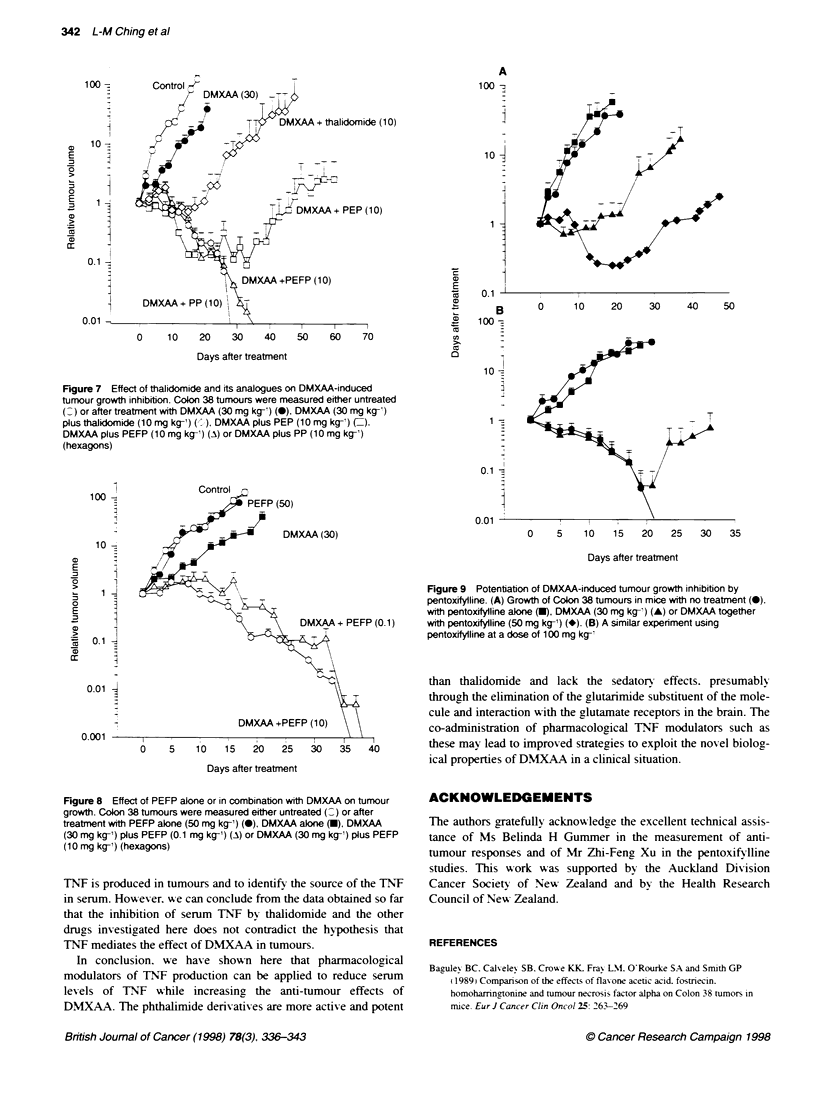
DMXAA (5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid), a novel anti-tumour agent currently undergoing clinical evaluation, appears to mediate its anti-tumour effects through immune modulation and the production of the cytokine tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF). Our previous studies have shown that thalidomide, a potent inhibitor of TNF biosynthesis that has numerous biological effects, including inhibition of tumour angiogenesis, unexpectedly augments the anti-tumour response in mice to DMXAA. We show here that thalidomide (100 mg kg(-1)) has no effect when administered with inactive doses of DMXAA, and that it must be given simultaneously with an active dose of DMXAA to have its maximum potentiating effect on the growth of the murine Colon 38 adenocarcinoma. To address the issue of whether inhibition of serum TNF production is important for potentiation of anti-tumour activity, we have tested three potent analogues of thalidomide. All three analogues, when co-administered with DMXAA to mice at doses lower than those used with thalidomide, inhibited TNF production and were effective in potentiating the anti-tumour activity of DMXAA against transplanted Colon 38 tumours. One of the analogues, N-phenethyltetrafluorophthalimide, was 1000-fold more potent than thalidomide and at a dose of 0.1 mg kg(-1) in combination with DMXAA (30 mg kg(-1)) cured 100% of mice, compared with 67% for the group treated with DMXAA alone. We also tested pentoxifylline and found it to suppress TNF production in response to DMXAA and to potentiate the anti-tumour effect of DMXAA. The results are compatible with the hypothesis that pharmacological reduction of serum TNF levels might benefit the anti-tumour effects of DMXAA and suggest new strategies for therapy using this agent.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baguley B. C., Calveley S. B., Crowe K. K., Fray L. M., O'Rourke S. A., Smith G. P. Comparison of the effects of flavone acetic acid, fostriecin, homoharringtonine and tumour necrosis factor alpha on colon 38 tumours in mice. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1989 Feb;25(2):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(89)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
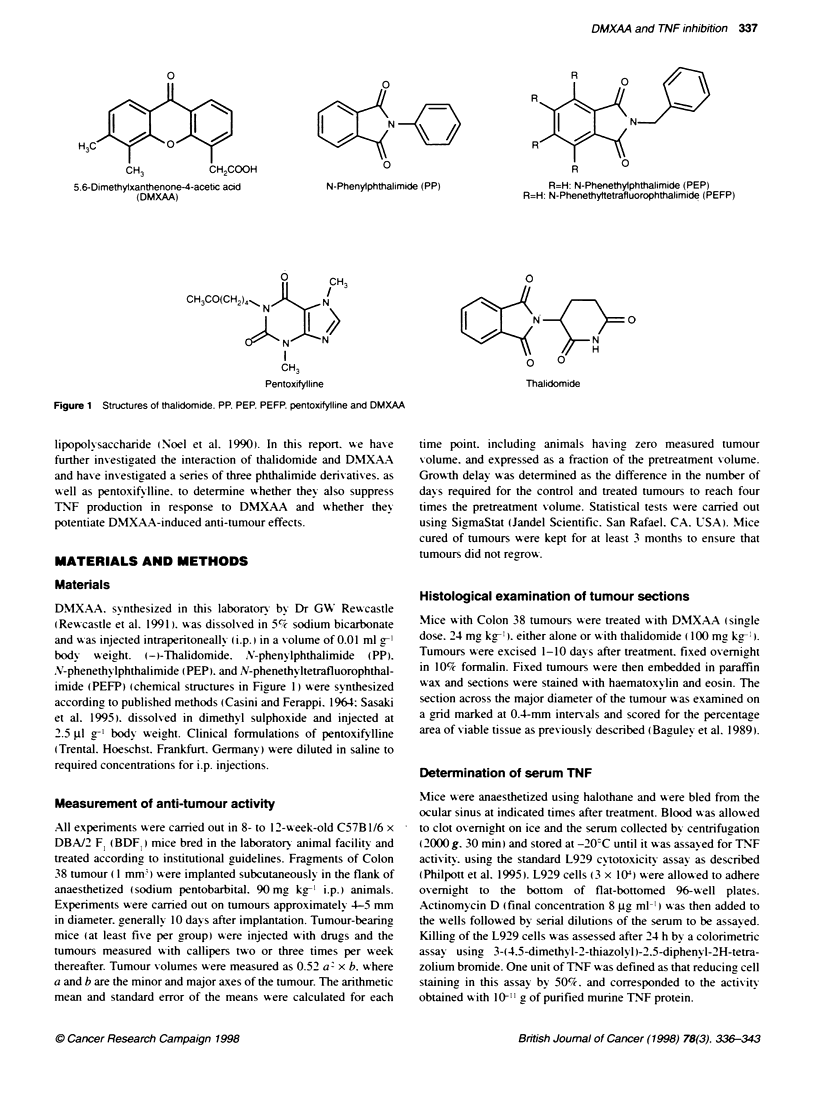
- CASINI G., FERAPPI M. PREPARAZIONE DI UNO DEGLI ANTIPODI OTTICI DELLA 2-FTALIMMIDOGLUTARIMMIDE. Farmaco Sci. 1964 Jun;19:563–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ching L. M., Baguley B. C. Induction of natural killer cell activity by the antitumour compound flavone acetic acid (NSC 347 512). Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1987 Jul;23(7):1047–1050. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(87)90357-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ching L. M., Joseph W. R., Zhuang L., Atwell G. J., Rewcastle G. W., Denny W. A., Baguley B. C. Induction of natural killer activity by xanthenone analogues of flavone acetic acid: relation with antitumour activity. Eur J Cancer. 1991;27(1):79–83. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(91)90067-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ching L. M., Xu Z. F., Gummer B. H., Palmer B. D., Joseph W. R., Baguley B. C. Effect of thalidomide on tumour necrosis factor production and anti-tumour activity induced by 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid. Br J Cancer. 1995 Aug;72(2):339–343. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amato R. J., Loughnan M. S., Flynn E., Folkman J. Thalidomide is an inhibitor of angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):4082–4085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.4082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabro S., Smith R. L., Williams R. T. Toxicity and teratogenicity of optical isomers of thalidomide. Nature. 1967 Jul 15;215(5098):296–296. doi: 10.1038/215296a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futami H., Eader L., Back T. T., Gruys E., Young H. A., Wiltrout R. H., Baguley B. C. Cytokine induction and therapeutic synergy with interleukin-2 against murine renal and colon cancers by xanthenone-4-acetic acid derivatives. J Immunother (1991) 1992 Nov;12(4):247–255. doi: 10.1097/00002371-199211000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J., Thompson P., Beutler B. Dexamethasone and pentoxifylline inhibit endotoxin-induced cachectin/tumor necrosis factor synthesis at separate points in the signaling pathway. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):391–394. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mace K. F., Hornung R. L., Wiltrout R. H., Young H. A. Correlation between in vivo induction of cytokine gene expression by flavone acetic acid and strict dose dependency and therapeutic efficacy against murine renal cancer. Cancer Res. 1990 Mar 15;50(6):1742–1747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan V., Malik S. T., Meager A., Fiers W., Lewis G. P., Hart I. R. Role of tumor necrosis factor in flavone acetic acid-induced tumor vasculature shutdown. Cancer Res. 1990 Sep 1;50(17):5537–5542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreira A. L., Sampaio E. P., Zmuidzinas A., Frindt P., Smith K. A., Kaplan G. Thalidomide exerts its inhibitory action on tumor necrosis factor alpha by enhancing mRNA degradation. J Exp Med. 1993 Jun 1;177(6):1675–1680. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.6.1675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura K., Hashimoto Y., Iwasaki S. Enhancement of phorbol ester-induced production of tumor necrosis factor alpha by thalidomide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Mar 15;199(2):455–460. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel P., Nelson S., Bokulic R., Bagby G., Lippton H., Lipscomb G., Summer W. Pentoxifylline inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced serum tumor necrosis factor and mortality. Life Sci. 1990;47(12):1023–1029. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(90)90474-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philpott M., Baguley B. C., Ching L. M. Induction of tumour necrosis factor-alpha by single and repeated doses of the antitumour agent 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1995;36(2):143–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00689199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratesi G., Rodolfo M., Rovetta G., Parmiani G. Role of T cells and tumour necrosis factor in antitumour activity and toxicity of flavone acetic acid. Eur J Cancer. 1990;26(10):1079–1083. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(90)90056-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rewcastle G. W., Atwell G. J., Baguley B. C., Calveley S. B., Denny W. A. Potential antitumor agents. 58. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of substituted xanthenone-4-acetic acids active against the colon 38 tumor in vivo. J Med Chem. 1989 Apr;32(4):793–799. doi: 10.1021/jm00124a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rewcastle G. W., Atwell G. J., Li Z. A., Baguley B. C., Denny W. A. Potential antitumor agents. 61. Structure-activity relationships for in vivo colon 38 activity among disubstituted 9-oxo-9H-xanthene-4-acetic acids. J Med Chem. 1991 Jan;34(1):217–222. doi: 10.1021/jm00105a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampaio E. P., Sarno E. N., Galilly R., Cohn Z. A., Kaplan G. Thalidomide selectively inhibits tumor necrosis factor alpha production by stimulated human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):699–703. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki K., Shibata Y., Hashimoto Y., Iwasaki S. Benzylphthalimides and phenethylphthalimides with thalidomide-like activity on the production of tumor necrosis factor alpha. Biol Pharm Bull. 1995 Sep;18(9):1228–1233. doi: 10.1248/bpb.18.1228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon E. J., Sandoval F. Thalidomide can be either agonistic or antagonistic to LPS evoked synthesis of TNF-alpha by mononuclear cells. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 1996 Feb;18(1):59–72. doi: 10.3109/08923979609007110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teicher B. A., Holden S. A., Ara G., Northey D. Response of the FSaII fibrosarcoma to antiangiogenic modulators plus cytotoxic agents. Anticancer Res. 1993 Nov-Dec;13(6A):2101–2106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwi L. J., Baguley B. C., Gavin J. B., Wilson W. R. Blood flow failure as a major determinant in the antitumor action of flavone acetic acid. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1989 Jul 5;81(13):1005–1013. doi: 10.1093/jnci/81.13.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwi L. J., Baguley B. C., Gavin J. B., Wilson W. R. Correlation between immune and vascular activities of xanthenone acetic acid antitumor agents. Oncol Res. 1994;6(2):79–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


