Abstract
We have studied the relationship between expression of genes implicated in mediating resistance to cleavable complex-forming topoisomerase II (topo II) inhibitors and cellular sensitivity to ICRF-159, a 'catalytic' inhibitor of topo II. Overexpression of the membrane transporters, P-glycoprotein and multidrug resistance-related protein (MRP), or down-regulation of topo IIalpha and/or -beta, did not confer ICRF-159 resistance. Indeed, marked topo IIalpha down-regulation appeared to be associated with collateral sensitivity to ICRF-159. Our results indicate that the resistance mechanisms that pertain to cleavable complex-forming topo II inhibitors and ICRF-159 are distinct. The evidence presented here suggests that topo IIalpha, not topo IIbeta, is more likely to be the major in vivo target for ICRF-159.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batist G., Tulpule A., Sinha B. K., Katki A. G., Myers C. E., Cowan K. H. Overexpression of a novel anionic glutathione transferase in multidrug-resistant human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15544–15549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck W. T., Danks M. K., Wolverton J. S., Kim R., Chen M. Drug resistance associated with altered DNA topoisomerase II. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1993;33:113–127. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(93)90012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley G., Ling V. P-glycoprotein, multidrug resistance and tumor progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1994 Jun;13(2):223–233. doi: 10.1007/BF00689638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M., Beck W. T. Differences in inhibition of chromosome separation and G2 arrest by DNA topoisomerase II inhibitors merbarone and VM-26. Cancer Res. 1995 Apr 1;55(7):1509–1516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole S. P., Bhardwaj G., Gerlach J. H., Mackie J. E., Grant C. E., Almquist K. C., Stewart A. J., Kurz E. U., Duncan A. M., Deeley R. G. Overexpression of a transporter gene in a multidrug-resistant human lung cancer cell line. Science. 1992 Dec 4;258(5088):1650–1654. doi: 10.1126/science.1360704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danks M. K., Warmoth M. R., Friche E., Granzen B., Bugg B. Y., Harker W. G., Zwelling L. A., Futscher B. W., Suttle D. P., Beck W. T. Single-strand conformational polymorphism analysis of the M(r) 170,000 isozyme of DNA topoisomerase II in human tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1993 Mar 15;53(6):1373–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
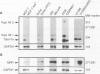
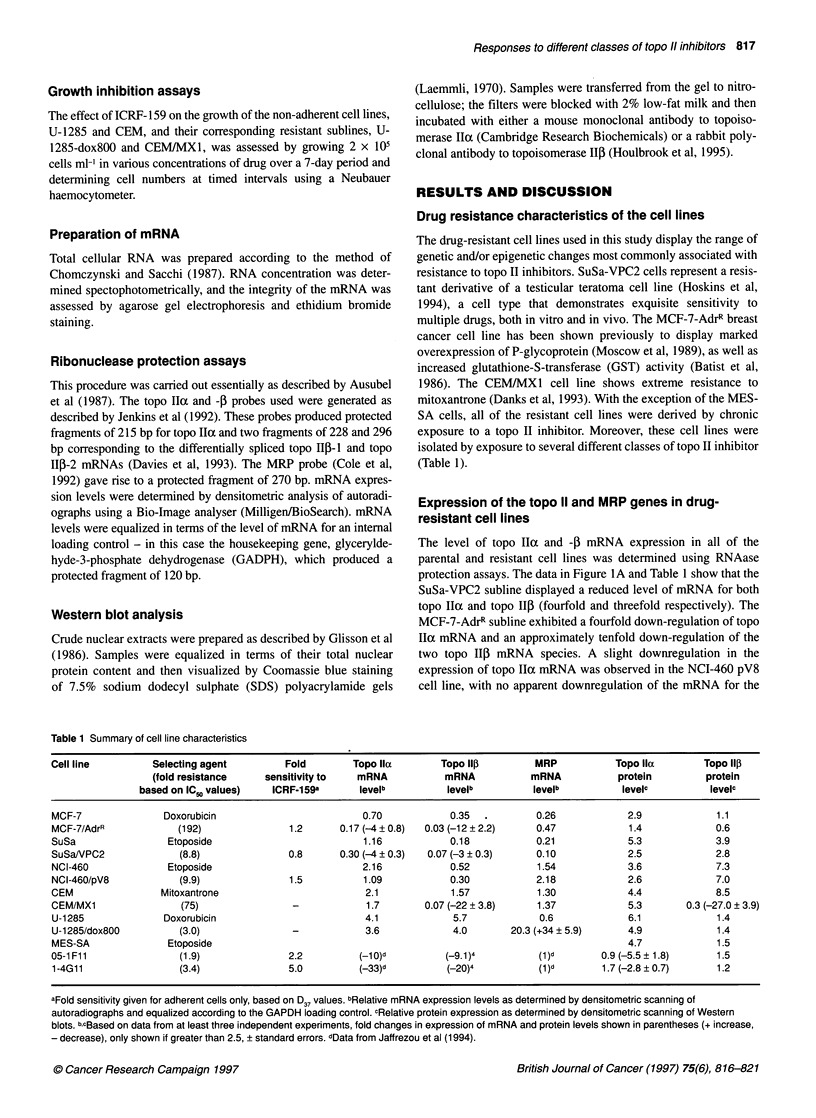
- Davies S. L., Jenkins J. R., Hickson I. D. Human cells express two differentially spliced forms of topoisomerase II beta mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Aug 11;21(16):3719–3723. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.16.3719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
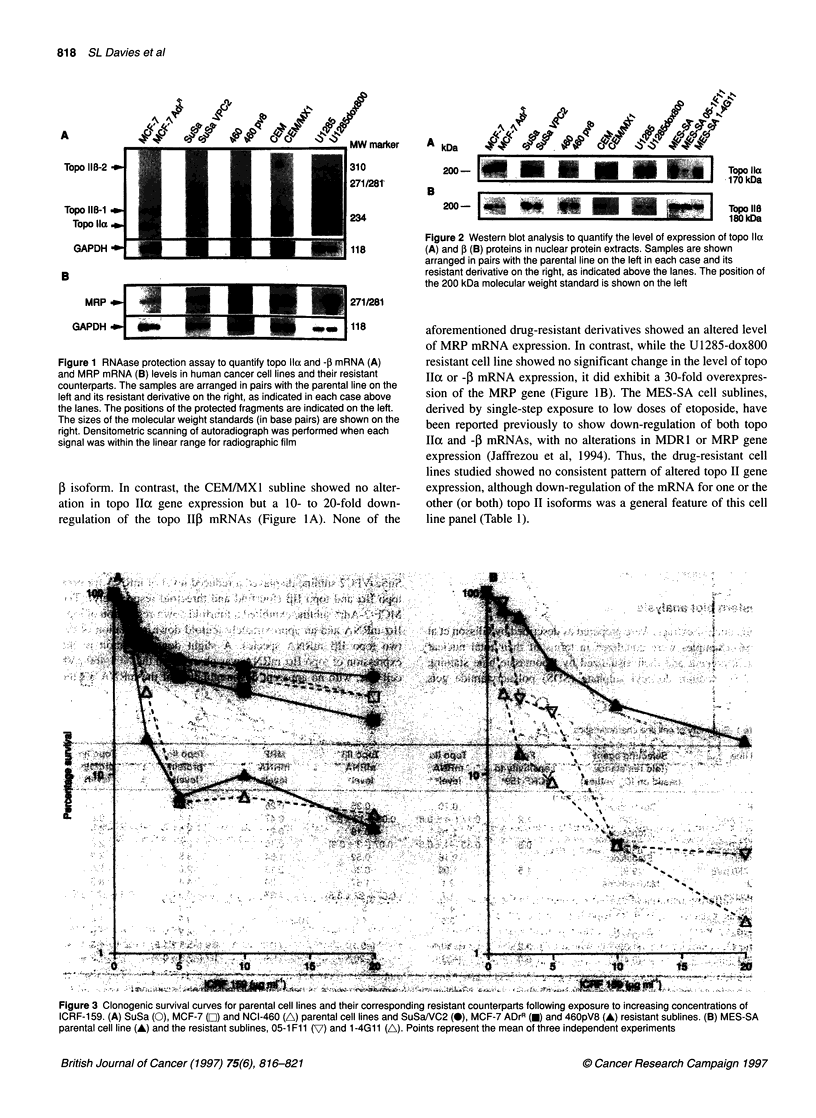
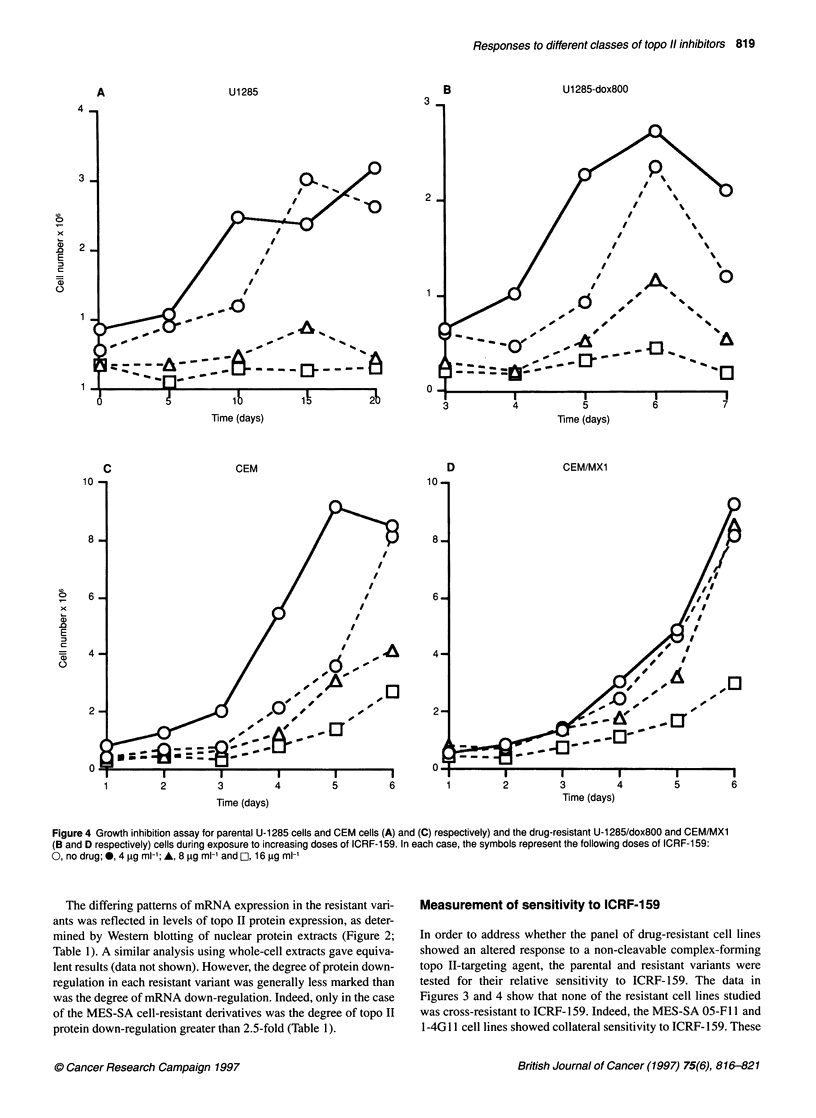
- Davies S. M., Robson C. N., Davies S. L., Hickson I. D. Nuclear topoisomerase II levels correlate with the sensitivity of mammalian cells to intercalating agents and epipodophyllotoxins. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17724–17729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemantle S. J., Jackman A. L., Kelland L. R., Calvert A. H., Lunec J. Molecular characterisation of two cell lines selected for resistance to the folate-based thymidylate synthase inhibitor, ZD1694. Br J Cancer. 1995 May;71(5):925–930. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froelich-Ammon S. J., Osheroff N. Topoisomerase poisons: harnessing the dark side of enzyme mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 15;270(37):21429–21432. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.37.21429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry A. M., Chresta C. M., Davies S. M., Walker M. C., Harris A. L., Hartley J. A., Masters J. R., Hickson I. D. Relationship between topoisomerase II level and chemosensitivity in human tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 15;51(24):6592–6595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisson B., Gupta R., Smallwood-Kentro S., Ross W. Characterization of acquired epipodophyllotoxin resistance in a Chinese hamster ovary cell line: loss of drug-stimulated DNA cleavage activity. Cancer Res. 1986 Apr;46(4 Pt 2):1934–1938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosking L. K., Whelan R. D., Shellard S. A., Davies S. L., Hickson I. D., Danks M. K., Hill B. T. Multiple mechanisms of resistance in a series of human testicular teratoma cell lines selected for increasing resistance to etoposide. Int J Cancer. 1994 Apr 15;57(2):259–267. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910570222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houlbrook S., Addison C. M., Davies S. L., Carmichael J., Stratford I. J., Harris A. L., Hickson I. D. Relationship between expression of topoisomerase II isoforms and intrinsic sensitivity to topoisomerase II inhibitors in breast cancer cell lines. Br J Cancer. 1995 Dec;72(6):1454–1461. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffrézou J. P., Chen G., Durán G. E., Kühl J. S., Sikic B. I. Mutation rates and mechanisms of resistance to etoposide determined from fluctuation analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994 Aug 3;86(15):1152–1158. doi: 10.1093/jnci/86.15.1152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. R., Ayton P., Jones T., Davies S. L., Simmons D. L., Harris A. L., Sheer D., Hickson I. D. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding the beta isozyme of human DNA topoisomerase II and localisation of the gene to chromosome 3p24. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 11;20(21):5587–5592. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.21.5587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Rowe T. C., Yang L., Tewey K. M., Chen G. L. Cleavage of DNA by mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15365–15370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscow J. A., Fairchild C. R., Madden M. J., Ransom D. T., Wieand H. S., O'Brien E. E., Poplack D. G., Cossman J., Myers C. E., Cowan K. H. Expression of anionic glutathione-S-transferase and P-glycoprotein genes in human tissues and tumors. Cancer Res. 1989 Mar 15;49(6):1422–1428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pommier Y. DNA topoisomerase I and II in cancer chemotherapy: update and perspectives. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1993;32(2):103–108. doi: 10.1007/BF00685611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roca J., Ishida R., Berger J. M., Andoh T., Wang J. C. Antitumor bisdioxopiperazines inhibit yeast DNA topoisomerase II by trapping the enzyme in the form of a closed protein clamp. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 1;91(5):1781–1785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.5.1781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe K., Ikegami Y., Ishida R., Andoh T. Inhibition of topoisomerase II by antitumor agents bis(2,6-dioxopiperazine) derivatives. Cancer Res. 1991 Sep 15;51(18):4903–4908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]