Abstract
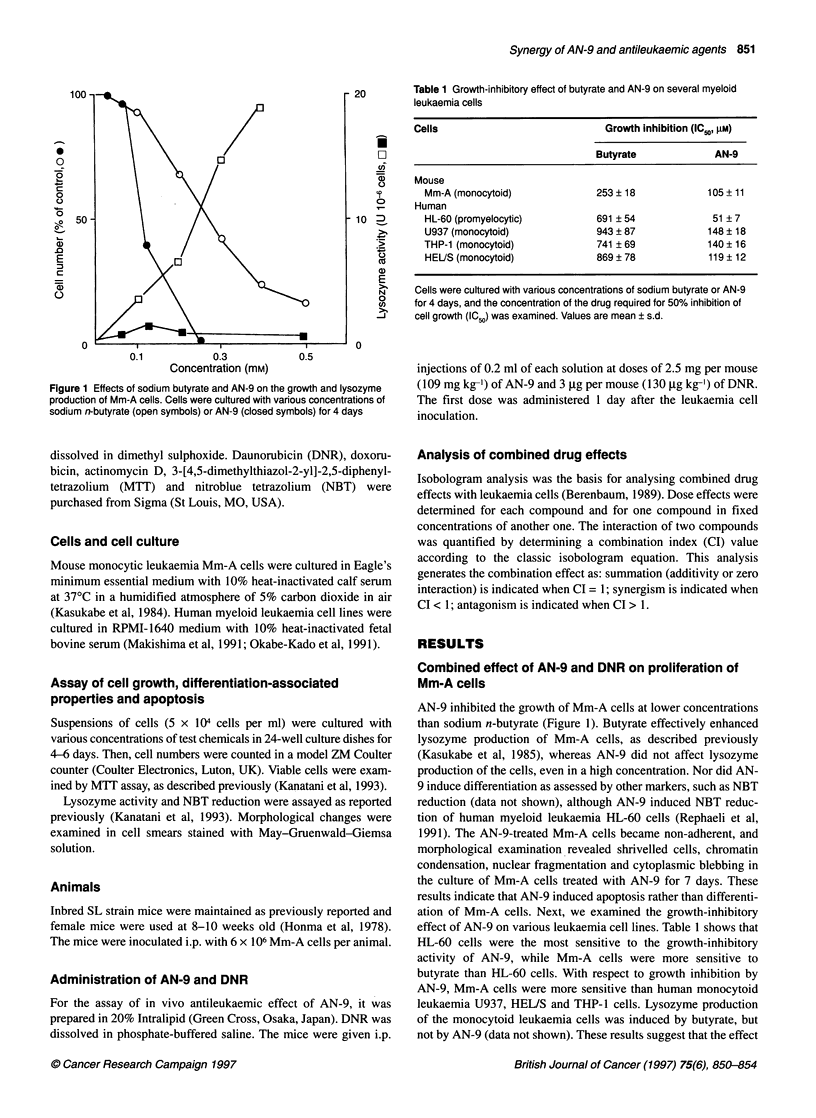
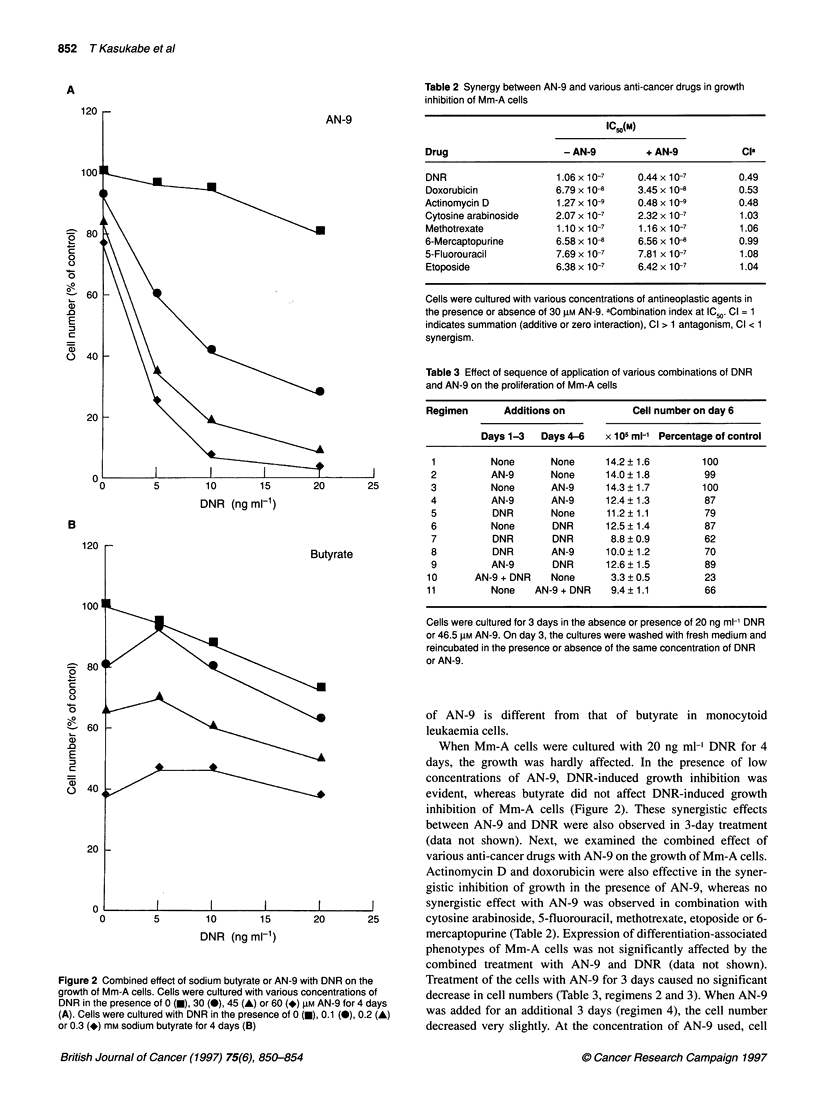
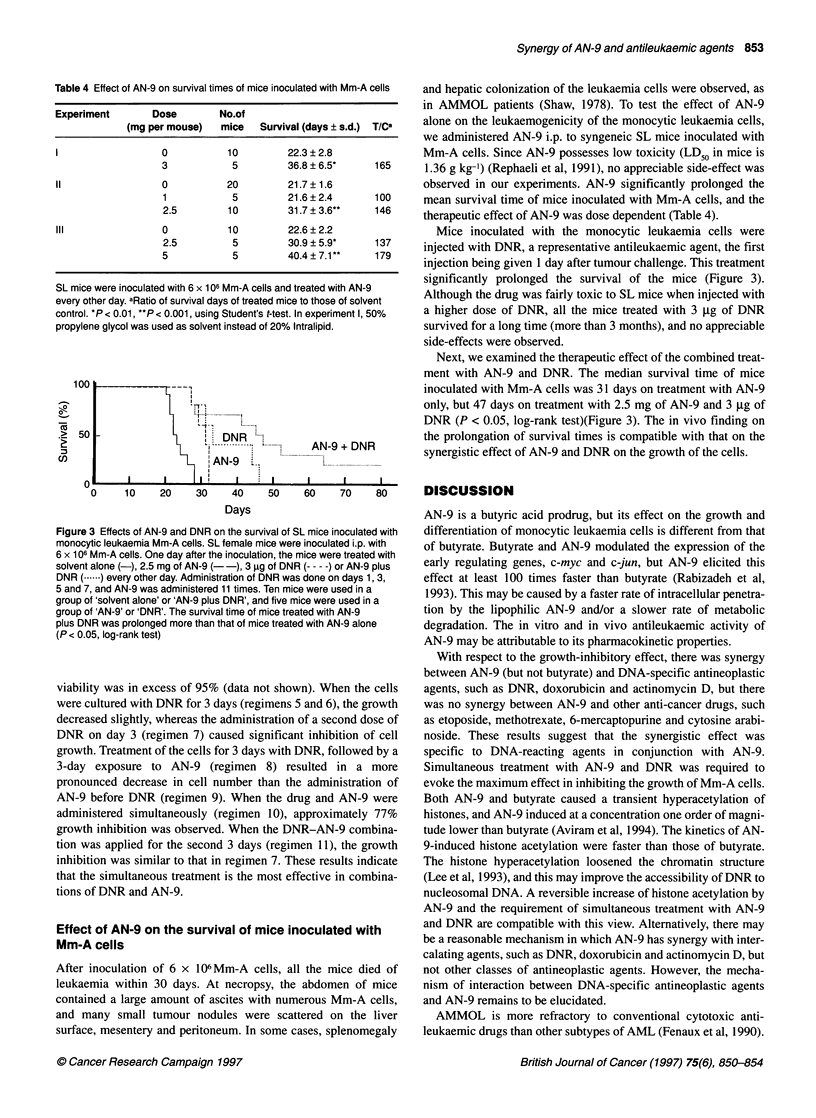
A derivative of butyric acid, pivalyloxymethyl butyrate (AN-9), inhibited the proliferation and induced apoptosis of mouse monocytic leukaemia Mm-A cells, although sodium butyrate, but not AN-9, induced differentiation of the cells. AN-9 and DNA-specific antineoplastic agents synergistically inhibited the growth of Mm-A cells, and the simultaneous treatment was required to evoke the maximum growth-inhibitory effect. On the other hand, there was no synergy between butyrate and the drugs, or AN-9 and anti-metabolic agents in inhibiting the growth of the cells, suggesting that the synergistic effect is specific to AN-9 and DNA-reacting agents. AN-9 as a single agent prolonged the survival of mice inoculated with Mm-A cells in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, administration of AN-9 plus daunorubicin (DNR) markedly prolonged their survival. These results suggest that combination with AN-9 and DNR entails an obvious therapeutic potential.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviram A., Zimrah Y., Shaklai M., Nudelman A., Rephaeli A. Comparison between the effect of butyric acid and its prodrug pivaloyloxymethylbutyrate on histones hyperacetylation in an HL-60 leukemic cell line. Int J Cancer. 1994 Mar 15;56(6):906–909. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910560625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berenbaum M. C. What is synergy? Pharmacol Rev. 1989 Jun;41(2):93–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenaux P., Vanhaesbroucke C., Estienne M. H., Preud'homme C., Pagniez D., Facon T., Millot F., Bauters F. Acute monocytic leukaemia in adults: treatment and prognosis in 99 cases. Br J Haematol. 1990 May;75(1):41–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb02614.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honma Y., Fujita Y., Kasukabe T., Hozumi M., Sampi K., Sakurai M., Tsushima S., Nomura H. Induction of differentiation of human acute non-lymphocytic leukemia cells in primary culture by inducers of differentiation of human myeloid leukemia cell line HL-60. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1983 Feb;19(2):251–261. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(83)90424-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honma Y., Honma C., Bloch A. Mechanism of interaction between antineoplastic agents and natural differentiation factors in the induction of human leukemic cell maturation. Cancer Res. 1986 Dec;46(12 Pt 1):6311–6315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honma Y., Kasukabe T., Hozumi M. Relationship between leukemogenicity and in vivo inducibility of normal differentiation in mouse myeloid leukemia cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1978 Sep;61(3):837–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanatani Y., Kasukabe T., Hozumi M., Motoyoshi K., Nagata N., Honma Y. Genistein exhibits preferential cytotoxicity to a leukemogenic variant but induces differentiation of a non-leukemogenic variant of the mouse monocytic leukemia Mm cell line. Leuk Res. 1993 Oct;17(10):847–853. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(93)90150-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasukabe T., Honma Y., Hozumi M. Induction of differentiation of cultured mouse monocytic leukemia cells (Mm-A) by inducers different from those of parent myeloblastic leukemia cells (M1). Jpn J Cancer Res. 1985 Nov;76(11):1056–1063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasukabe T., Honma Y., Hozumi M. Selection of mouse macrophage-like sublines that differ in leukemogenic potential and characterization. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Feb;118(2):105–112. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041180202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. Y., Hayes J. J., Pruss D., Wolffe A. P. A positive role for histone acetylation in transcription factor access to nucleosomal DNA. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):73–84. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90051-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makishima M., Honma Y., Hozumi M., Sampi K., Hattori M., Motoyoshi K. Induction of differentiation of human leukemia cells by inhibitors of myosin light chain kinase. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 5;287(1-2):175–177. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80044-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. A., Kurschel E., Osieka R., Schmidt C. G. Clinical pharmacology of sodium butyrate in patients with acute leukemia. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1987 Sep;23(9):1283–1287. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(87)90109-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novogrodsky A., Dvir A., Ravid A., Shkolnik T., Stenzel K. H., Rubin A. L., Zaizov R. Effect of polar organic compounds on leukemic cells. Butyrate-induced partial remission of acute myelogenous leukemia in a child. Cancer. 1983 Jan 1;51(1):9–14. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19830101)51:1<9::aid-cncr2820510104>3.0.co;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudelman A., Ruse M., Aviram A., Rabizadeh E., Shaklai M., Zimrah Y., Rephaeli A. Novel anticancer prodrugs of butyric acid. 2. J Med Chem. 1992 Feb 21;35(4):687–694. doi: 10.1021/jm00082a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okabe-Kado J., Honma Y., Hayashi M., Hozumi M. Effects of transforming growth factor-beta and activin A on vitamin D3-induced monocytic differentiation of myeloid leukemia cells. Anticancer Res. 1991 Jan-Feb;11(1):181–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okabe J., Honma Y., Hayashi M., Hozumi M. Actinomycin D restores in vivo sensitivity to differentiation induction of non-differentiating mouse myeloid leukemia cells. Int J Cancer. 1979 Jul 15;24(1):87–91. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910240115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad K. N. Butyric acid: a small fatty acid with diverse biological functions. Life Sci. 1980 Oct 13;27(15):1351–1358. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90397-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabizadeh E., Shaklai M., Nudelman A., Eisenbach L., Rephaeli A. Rapid alteration of c-myc and c-jun expression in leukemic cells induced to differentiate by a butyric acid prodrug. FEBS Lett. 1993 Aug 16;328(3):225–229. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80932-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rephaeli A., Rabizadeh E., Aviram A., Shaklai M., Ruse M., Nudelman A. Derivatives of butyric acid as potential anti-neoplastic agents. Int J Cancer. 1991 Aug 19;49(1):66–72. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910490113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw M. T. The distinctive features of acute monocytic leukemia. Am J Hematol. 1978;4(1):97–103. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830040113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


