Abstract
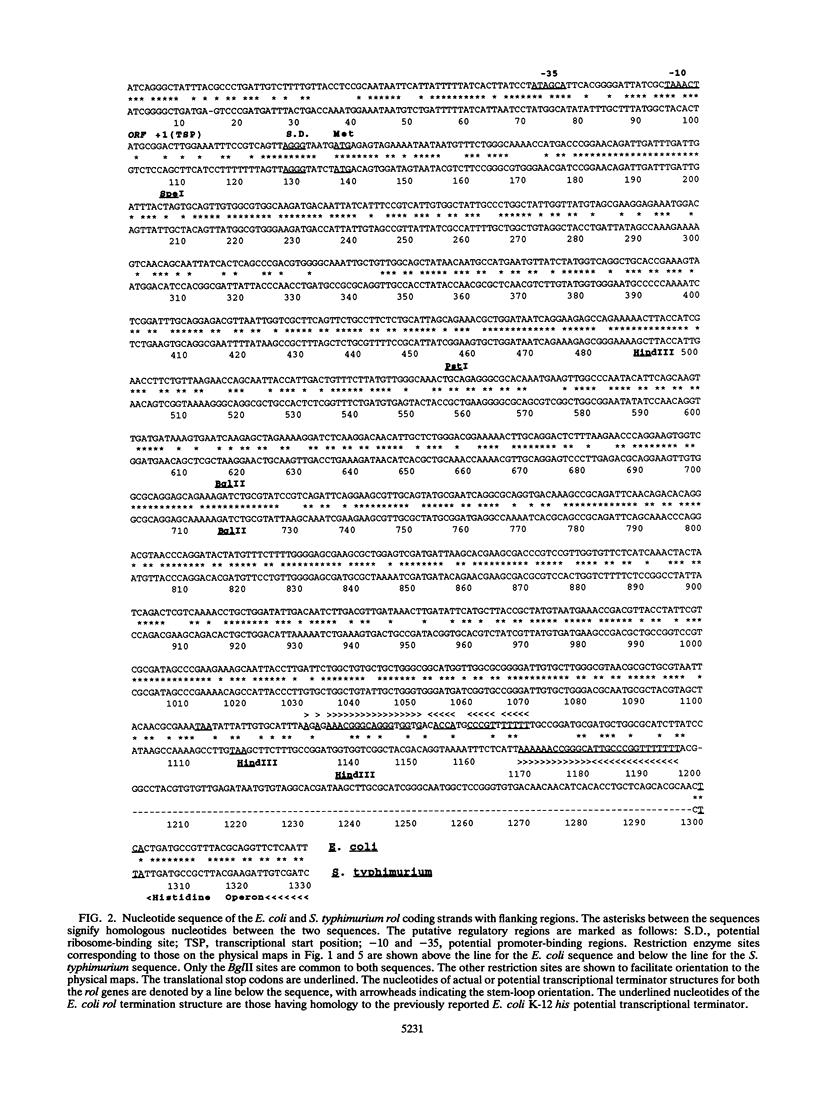
In this article, we report on the nucleotide sequences of the rol genes of Escherichia coli O75 and Salmonella typhimurium LT2. The rol gene in E. coli was previously shown to encode a 36-kDa protein that regulates size distribution of the O-antigen moiety of lipopolysaccharide. The E. coli and S. typhimurium rol gene sequences consist of 978 and 984 nucleotides, respectively. The homology between the nucleotide sequences of these two genes was found to be 68.9%. Both the E. coli rol and S. typhimurium rol genes are transcribed counter to the histidine operon and code for deduced polypeptides of 325 and 327 amino acids, respectively. The S. typhimurium rol gene was previously identified to encode a protein of unknown function and to share a transcription termination region with his. The homology between these deduced polypeptide sequences was observed to be 72%. A complementation test was performed in which the S. typhimurium rol gene was placed in trans with an E. coli plasmid (pRAB3) which encodes the O75 rfb gene cluster and not rol. The protein expressed from the S. typhimurium rol gene was found to regulate the distribution of the O75 O polysaccharide on the lipopolysaccharide of the host strain, E. coli S phi 874. The mechanism of Rol action may be independent of O antigen subunit structure, and its presence may be conserved in members of the family Enterobacteriaceae and other gram-negative bacilli that express O polysaccharides on their surface membrane.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Erickson B. W. Optimal sequence alignment using affine gap costs. Bull Math Biol. 1986;48(5-6):603–616. doi: 10.1007/BF02462326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 8. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jun;54(2):130–197. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.2.130-197.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barcak G. J., Wolf R. E., Jr Growth-rate-dependent expression and cloning of gnd alleles from natural isolates of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):365–371. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.365-371.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastin D. A., Romana L. K., Reeves P. R. Molecular cloning and expression in Escherichia coli K-12 of the rfb gene cluster determining the O antigen of an E. coli O111 strain. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Sep;5(9):2223–2231. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02152.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batchelor R. A., Haraguchi G. E., Hull R. A., Hull S. I. Regulation by a novel protein of the bimodal distribution of lipopolysaccharide in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(18):5699–5704. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5699-5704.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilofsky H. S., Burks C. The GenBank genetic sequence data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1861–1863. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlomagno M. S., Blasi F., Bruni C. B. Gene organization in the distal part of the Salmonella typhimurium histidine operon and determination and sequence of the operon transcription terminator. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(3):413–420. doi: 10.1007/BF00425756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlomagno M. S., Chiariotti L., Alifano P., Nappo A. G., Bruni C. B. Structure and function of the Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli K-12 histidine operons. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):585–606. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90194-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlomagno M. S., Riccio A., Bruni C. B. Convergently functional, Rho-independent terminator in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):362–368. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.362-368.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiariotti L., Alifano P., Carlomagno M. S., Bruni C. B. Nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli hisD gene and of the Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium hisIE region. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jun;203(3):382–388. doi: 10.1007/BF00422061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins L. V., Hackett J. Molecular cloning, characterization, and nucleotide sequence of the rfc gene, which encodes an O-antigen polymerase of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(8):2521–2529. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.8.2521-2529.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George D. G., Barker W. C., Hunt L. T. The protein identification resource (PIR). Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):11–15. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., Hunt F. Mechanism of O-antigen distribution in lipopolysaccharide. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5352–5359. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5352-5359.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., Joiner K., Leive L. Serum-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli O111 contain increased lipopolysaccharide, lack an O antigen-containing capsule, and cover more of their lipid A core with O antigen. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):877–882. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.877-882.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., Leive L. Heterogeneity of antigenic-side-chain length in lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli 0111 and Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):145–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman N., Schmetz M. A., Foulds J., Klima E. N., Jimenez-Lucho V. E., Leive L. L., Joiner K. A., Jiminez V. Lipopolysaccharide size and distribution determine serum resistance in Salmonella montevideo. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):856–863. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.856-863.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu M. C., Davidson N. Mapping transcription start points on cloned genomic DNA with T4 DNA polymerase: a precise and convenient technique. Gene. 1986;42(1):21–29. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jann B., Reske K., Jann K. Heterogeneity of lipopolysaccharides. Analysis of polysaccharide chain lengths by sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Dec 1;60(1):239–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb20996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang X. M., Neal B., Santiago F., Lee S. J., Romana L. K., Reeves P. R. Structure and sequence of the rfb (O antigen) gene cluster of Salmonella serovar typhimurium (strain LT2). Mol Microbiol. 1991 Mar;5(3):695–713. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00741.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Grossman N., Schmetz M., Leive L. C3 binds preferentially to long-chain lipopolysaccharide during alternative pathway activation by Salmonella montevideo. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):710–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence C. B., Goldman D. A. Definition and identification of homology domains. Comput Appl Biosci. 1988 Mar;4(1):25–33. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/4.1.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomberg H., Hellström M., Jodal U., Leffler H., Lincoln K., Svanborg Edén C. Virulence-associated traits in Escherichia coli causing first and recurrent episodes of urinary tract infection in children with or without vesicoureteral reflux. J Infect Dis. 1984 Oct;150(4):561–569. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.4.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacIntyre S., Lucken R., Owen P. Smooth lipopolysaccharide is the major protective antigen for mice in the surface extract from IATS serotype 6 contributing to the polyvalent Pseudomonas aeruginosa vaccine PEV. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):76–84. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.76-84.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLachlan P. R., Kadam S. K., Sanderson K. E. Cloning, characterization, and DNA sequence of the rfaLK region for lipopolysaccharide synthesis in Salmonella typhimurium LT2. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(22):7151–7163. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7151-7163.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macpherson D. F., Morona R., Beger D. W., Cheah K. C., Manning P. A. Genetic analysis of the rfb region of Shigella flexneri encoding the Y serotype O-antigen specificity. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jun;5(6):1491–1499. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00795.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCallum K. L., Schoenhals G., Laakso D., Clarke B., Whitfield C. A high-molecular-weight fraction of smooth lipopolysaccharide in Klebsiella serotype O1:K20 contains a unique O-antigen epitope and determines resistance to nonspecific serum killing. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3816–3822. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3816-3822.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath B. C., Osborn M. J. Localization of the terminal steps of O-antigen synthesis in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):649–654. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.649-654.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier-Dieter U., Barr K., Starman R., Hatch L., Rick P. D. Nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli rfe gene involved in the synthesis of enterobacterial common antigen. Molecular cloning of the rfe-rff gene cluster. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):746–753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munford R. S., Hall C. L., Rick P. D. Size heterogeneity of Salmonella typhimurium lipopolysaccharides in outer membranes and culture supernatant membrane fragments. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):630–640. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.630-640.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muschel L. H., Larsen L. J. The sensitivity of smooth and rough gram-negative bacteria to the immune bactericidal reaction. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Jan;133(1):345–348. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasoff M. S., Baker H. V., 2nd, Wolf R. E., Jr DNA sequence of the Escherichia coli gene, gnd, for 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase. Gene. 1984 Mar;27(3):253–264. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal B. L., Tsiolis G. C., Heuzenroeder M. W., Manning P. A., Reeves P. R. Molecular cloning and expression in Escherichia coli K-12 of chromosomal genes determining the O antigen of an E. coli O2: K1 strain. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Aug 15;66(3):345–351. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90286-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhard J., Thomassen E. Altered deoxyribonucleotide pools in P2 eductants of Escherichia coli K-12 due to deletion of the dcd gene. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):999–1001. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.999-1001.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nnalue N. A., Newton S., Stocker B. A. Lysogenization of Salmonella choleraesuis by phage 14 increases average length of O-antigen chains, serum resistance and intraperitoneal mouse virulence. Microb Pathog. 1990 Jun;8(6):393–402. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90026-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva E. T., Mäkelä P. H. Lipopolysaccharide heterogeneity in Salmonella typhimurium analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):137–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A. A., Haug A., McGroarty E. J. Physical properties of short- and long-O-antigen-containing fractions of lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli 0111:B4. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):116–122. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.116-122.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A. A., McGroarty E. J. High-molecular-weight components in lipopolysaccharides of Salmonella typhimurium, Salmonella minnesota, and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):738–745. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.738-745.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porat R., Johns M. A., McCabe W. R. Selective pressures and lipopolysaccharide subunits as determinants of resistance of clinical isolates of gram-negative bacilli to human serum. Infect Immun. 1987 Feb;55(2):320–328. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.2.320-328.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rana F. R., Macias E. A., Sultany C. M., Modzrakowski M. C., Blazyk J. Interactions between magainin 2 and Salmonella typhimurium outer membranes: effect of lipopolysaccharide structure. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 18;30(24):5858–5866. doi: 10.1021/bi00238a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves P., Stevenson G. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the Salmonella typhimurium LT2 gnd gene and its homology with the corresponding sequence of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 May;217(1):182–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00330960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Roth J. R. Linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium, edition VII. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Dec;52(4):485–532. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.4.485-532.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., Dallas W. S., Falkow S. Characterization of an Escherichia coli plasmid encoding for synthesis of heat-labile toxin: molecular cloning of the toxin determinant. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):405–411. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.405-411.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T., Kido N., Komatsu T., Ohta M., Kato N. Expression of the cloned Escherichia coli O9 rfb gene in various mutant strains of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):55–58. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.55-58.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomás J. M., Ciurana B., Benedí V. J., Juarez A. Role of lipopolysaccharide and complement in susceptibility of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium to non-immune serum. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Apr;134(4):1009–1016. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-4-1009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Beckerdite-Quagliata S., Elsbach P. Resistance of gram-negative bacteria to purified bactericidal leukocyte proteins: relation to binding and bacterial lipopolysaccharide structure. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):619–628. doi: 10.1172/JCI109707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh H. Y., Jacobs D. M. Characterization of lipopolysaccharide fractions and their interactions with cells and model membranes. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):336–341. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.336-341.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]