Abstract
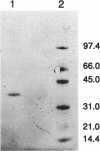
Malate dehydrogenase (MDH; EC 1.1.1.37) from strain NCIB 8327 of the green sulfur bacterium Chlorobium vibrioforme was purified to homogeneity by triazine dye affinity chromatography followed by gel filtration. Purification of MDH gave an approximately 1,000-fold increase in specific activity and recoveries of typically 15 to 20%. The criteria of purity were single bands on sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and nondenaturing polyacrylamide electrophoresis (PAGE) and the detection of a single N terminus in an Edman degradation analysis. MDH activity was detected in purified preparations by activity staining of gels in the direction of malate oxidation. PAGE and gel filtration (Sephadex G-100) analyses showed the native enzyme to be a dimer composed of identical subunits both at room temperature and at 4 degrees C. The molecular weight of the native enzyme as estimated by gel filtration was 77,000 and by gradient PAGE was 74,000. The subunit molecular weight as estimated by SDS-gradient PAGE was 37,500. N-terminal sequences of MDHs from C. vibrioforme, Chlorobium tepidum, and Heliobacterium gestii are presented. There are obvious key sequence similarities in MDHs from the phototrophic green bacteria. The sequences presented probably possess a stretch of amino acids involved in dinucleotide binding which is similar to that of Chloroflexus aurantiacus MDH and other classes of dehydrogenase enzymes but unique among MDHs.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birktoft J. J., Banaszak L. J. The presence of a histidine-aspartic acid pair in the active site of 2-hydroxyacid dehydrogenases. X-ray refinement of cytoplasmic malate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):472–482. doi: 10.2210/pdb2mdh/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birktoft J. J., Rhodes G., Banaszak L. J. Refined crystal structure of cytoplasmic malate dehydrogenase at 2.5-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 11;28(14):6065–6081. doi: 10.1021/bi00440a051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
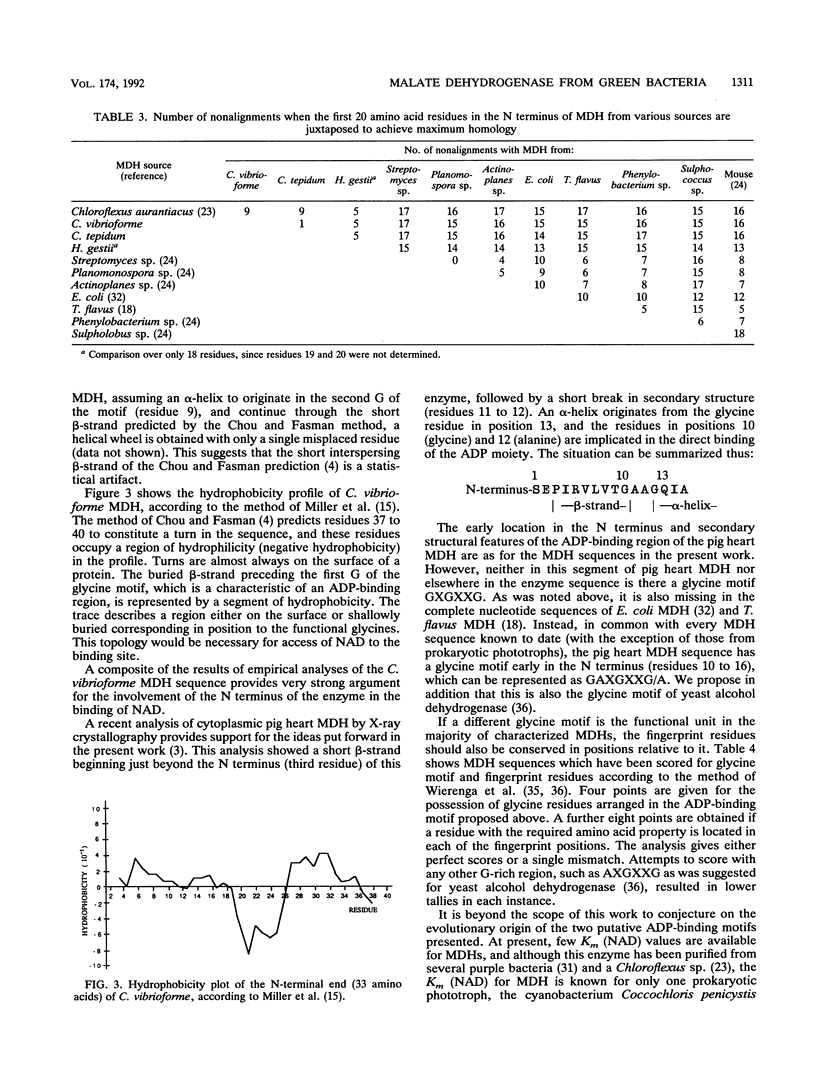
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duhamel R. C., Meezan E., Brendel K. Metachromatic staining with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 of the proline-rich calf thymus histone, H1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 16;626(2):432–442. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90139-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRIMM F. C., DOHERTY D. G. Properties of the two forms of malic dehydrogenase from beef heart. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jul;236:1980–1985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopetzki E., Entian K. D., Lottspeich F., Mecke D. Purification procedure and N-terminal amino acid sequence of yeast malate dehydrogenase isoenzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Apr 30;912(3):398–403. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(87)90044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles W. R. The olfactory sense and infrared radiation in the large American cockroach. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1420–1423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S., Janin J., Lesk A. M., Chothia C. Interior and surface of monomeric proteins. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 5;196(3):641–656. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90038-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphey W. H., Barnaby C., Lin F. J., Kaplan N. O. Malate dehydrogenases. II. Purification and properties of Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus stearothermophilus, and Escherichia coli malate dehydrogenases. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 10;242(7):1548–1559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphey W. H., Kitto G. B., Everse J., Kaplan N. Malate dehydrogenases. I. A survey of molecular size measured by gel filtration. Biochemistry. 1967 Feb;6(2):603–610. doi: 10.1021/bi00854a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama M., Matsubara N., Yamamoto K., Iijima S., Uozumi T., Beppu T. Nucleotide sequence of the malate dehydrogenase gene of Thermus flavus and its mutation directing an increase in enzyme activity. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14178–14183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolstad A. K., Howland E., Sirevåg R. Malate dehydrogenase from the thermophilic green bacterium Chloroflexus aurantiacus: purification, molecular weight, amino acid composition, and partial amino acid sequence. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):2947–2953. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.2947-2953.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommel T. O., Hund H. K., Speth A. R., Lingens F. Purification and N-terminal amino-acid sequences of bacterial malate dehydrogenases from six actinomycetales strains and from Phenylobacterium immobile, strain E. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1989 Jul;370(7):763–768. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1989.370.2.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffer M., Edmundson A. B. Correlation of amino acid sequence and conformation in tobacco mosaic virus. Biophys J. 1968 Jan;8(1):29–39. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(68)86472-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirevåg R., Ormerod J. G. Carbon dioxide fixation in green sulphur bacteria. Biochem J. 1970 Nov;120(2):399–408. doi: 10.1042/bj1200399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaram T. K., Wright I. P., Wilkinson A. E. Malate dehydrogenase from thermophilic and mesophilic bacteria. Molecular size, subunit structure, amino acid composition, immunochemical homology, and catalytic activity. Biochemistry. 1980 May 13;19(10):2017–2022. doi: 10.1021/bi00551a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tayeh M. A., Madigan M. T. Malate dehydrogenase in phototrophic purple bacteria: purification, molecular weight, and quaternary structure. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4196–4202. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4196-4202.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel R. F., Entian K. D., Mecke D. Cloning and sequence of the mdh structural gene of Escherichia coli coding for malate dehydrogenase. Arch Microbiol. 1987;149(1):36–42. doi: 10.1007/BF00423133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierenga R. K., Hol W. G. Predicted nucleotide-binding properties of p21 protein and its cancer-associated variant. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):842–844. doi: 10.1038/302842a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierenga R. K., Terpstra P., Hol W. G. Prediction of the occurrence of the ADP-binding beta alpha beta-fold in proteins, using an amino acid sequence fingerprint. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 5;187(1):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90409-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- You K. S., Kaplan N. O. Purification and properties of malate dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas testosteroni. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):704–716. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.704-716.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young P. R. An improved method for the detection of peroxidase-conjugated antibodies on immunoblots. J Virol Methods. 1989 Apr-May;24(1-2):227–235. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(89)90025-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yueh A. Y., Chung C. S., Lai Y. K. Purification and molecular properties of malate dehydrogenase from the marine diatom Nitzschia alba. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 15;258(1):221–228. doi: 10.1042/bj2580221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]