Abstract
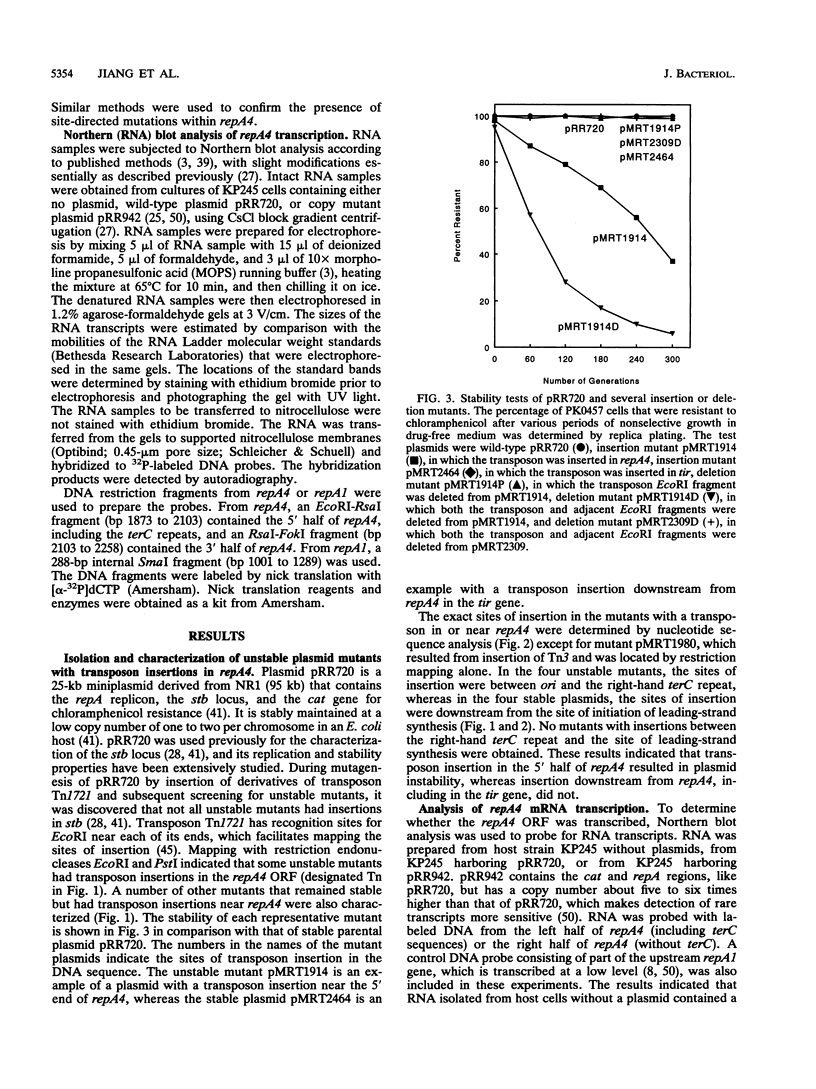
Mutants of IncFII plasmid NR1 that have transposons inserted in the repA4 open reading frame (ORF) are not inherited stably. The repA4 ORF is located immediately downstream from the replication origin (ori). The repA4 coding region contains inverted-repeat sequences that are homologous to the terC inverted repeats located in the replication terminus of the Escherichia coli chromosome. The site of initiation of leading-strand synthesis for replication of NR1 is also located in repA4 near its 3' end. Transposon insertions between ori and the right-hand terC repeat resulted in plasmid instability, whereas transposon insertions farther downstream did not. Derivatives that contained a 35-bp frameshift insertion in the repA4 ORF were all stable, even when the frameshift was located very near the 5' end of the coding region. This finding indicates that repA4 does not specify a protein product that is essential for plasmid stability. Examination of mutants having a nest of deletions with endpoints in or near repA4 indicated that the 3' end of the repA4 coding region and the site of leading-strand initiation could be deleted without appreciable effect on plasmid stability. Deletion of the pemI and pemK genes, located farther downstream from repA4 and reported to affect plasmid stability, also had no detectable effect. In contrast, mutants from which the right-hand terC repeat, or both right- and left-hand repeats, had been deleted were unstable. None of the insertion or deletion mutations in or near repA4 affected plasmid copy number. Alteration of the terC repeats by site-directed mutagenesis had little effect on plasmid stability. Plasmid stability was not affected by a fus mutation known to inactivate the termination function. Therefore, it appears that the overall integrity of the repA4 region is more important for stable maintenance of plasmid NR1 than are any of the individual known features found in this region.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong K. A., Ohtsubo H., Bauer W. R., Yoshioka Y., Miyazaki C., Maeda Y., Ohtsubo E. Characterization of the gene products produced in minicells by pSM1, a derivative of R100. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Oct;205(1):56–65. doi: 10.1007/BF02428032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin S. J. Plasmid partition. Plasmid. 1988 Jul;20(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(88)90001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernander R., Krabbe M., Nordström K. Mapping of the in vivo start site for leading strand DNA synthesis in plasmid R1. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4481–4487. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05549.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo A., Ortega S., de Torrontegui G., Díaz R. Killing of Escherichia coli cells modulated by components of the stability system ParD of plasmid R1. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Dec;215(1):146–151. doi: 10.1007/BF00331316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo A., de Torrontegui G., Díaz R. Identification of components of a new stability system of plasmid R1, ParD, that is close to the origin of replication of this plasmid. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Nov;210(1):101–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00337764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H., Luttropp L. K., Falkow S. Molecular cloning of replication and incompatibility regions from the R-plasmid R6K. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 25;124(3):443–468. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90181-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong X. N., Womble D. D., Rownd R. H. In-vivo studies on the cis-acting replication initiator protein of IncFII plasmid NR1. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 5;202(3):495–509. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90281-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong X. N., Womble D. D., Rownd R. H. Transcriptional pausing in a region important for plasmid NR1 replication control. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5353–5363. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5353-5363.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong X., Womble D. D., Luckow V. A., Rownd R. H. Regulation of transcription of the repA1 gene in the replication control region of IncFII plasmid NR1 by gene dosage of the repA2 transcription repressor protein. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):544–551. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.544-551.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easton A. M., Rownd R. H. The incompatibility product of IncFII R plasmid NR1 controls gene expression in the plasmid replication region. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):829–839. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.829-839.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka M., Akiyama M., Horiuchi T. A consensus sequence of three DNA replication terminus sites on the E. coli chromosome is highly homologous to the terR sites of the R6K plasmid. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):467–475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. M., Marians K. J. Escherichia coli Tus protein acts to arrest the progression of DNA replication forks in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2481–2485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. M., Pelletier A. J., Tecklenburg M. L., Kuempel P. L. Identification of the DNA sequence from the E. coli terminus region that halts replication forks. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):459–466. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. M., Tecklenburg M. L., Pelletier A. J., Kuempel P. L. tus, the trans-acting gene required for termination of DNA replication in Escherichia coli, encodes a DNA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1593–1597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi T., Hidaka M. Core sequence of two separable terminus sites of the R6K plasmid that exhibit polar inhibition of replication is a 20 bp inverted repeat. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):515–523. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light J., Molin S. Post-transcriptional control of expression of the repA gene of plasmid R1 mediated by a small RNA molecule. EMBO J. 1983;2(1):93–98. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01387.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light J., Riise E., Molin S. Transcription and its regulation in the basic replicon region of plasmid R1. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;198(3):503–508. doi: 10.1007/BF00332947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacAllister T., Khatri G. S., Bastia D. Sequence-specific and polarized replication termination in vitro: complementation of extracts of tus- Escherichia coli by purified Ter protein and analysis of termination intermediates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2828–2832. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masai H., Arai K. RepA and DnaA proteins are required for initiation of R1 plasmid replication in vitro and interact with the oriR sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4781–4785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki T., Easton A. M., Rownd R. H. Cloning of replication, incompatibility, and stability functions of R plasmid NR1. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):87–99. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.87-99.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min Y. N., Tabuchi A., Fan Y. L., Womble D. D., Rownd R. H. Complementation of mutants of the stability locus of IncFII plasmid NR1. Essential functions of the trans-acting stbA and stbB gene products. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 20;204(2):345–356. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90581-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min Y. N., Tabuchi A., Womble D. D., Rownd R. H. Transcription of the stability operon of IncFII plasmid NR1. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(7):2378–2384. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.7.2378-2384.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki C., Kawai Y., Ohtsubo H., Ohtsubo E. Unidirectional replication of plasmid R100. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 20;204(2):331–343. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90580-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordström K., Austin S. J. Mechanisms that contribute to the stable segregation of plasmids. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:37–69. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.000345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordström K., Molin S., Light J. Control of replication of bacterial plasmids: genetics, molecular biology, and physiology of the plasmid R1 system. Plasmid. 1984 Sep;12(2):71–90. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(84)90054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsubo H., Ryder T. B., Maeda Y., Armstrong K., Ohtsubo E. DNA replication of the resistance plasmid R100 and its control. Adv Biophys. 1986;21:115–133. doi: 10.1016/0065-227x(86)90018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor G. N., Rownd R. H. Rosanilins: indicator dyes for chloramphenicol-resistant enterobacteria containing chloramphenicol acetyltransferase. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1375–1382. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1375-1382.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen J., Ryder T., Inokuchi H., Ohtsubo H., Ohtsubo E. Genes and sites involved in replication and incompatibility of an R100 plasmid derivative based on nucleotide sequence analysis. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;179(3):527–537. doi: 10.1007/BF00271742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen J., Ryder T., Ohtsubo H., Ohtsubo E. Role of RNA transcripts in replication incompatibility and copy number control in antibiotic resistance plasmid derivatives. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):794–797. doi: 10.1038/290794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rownd R. H., Womble D. D., Dong X. N., Luckow V. A., Wu R. P. Incompatibility and IncFII plasmid replication control. Basic Life Sci. 1985;30:335–354. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-2447-8_26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder T. B., Davidson D. B., Rosen J. I., Ohtsubo E., Ohtsubo H. Analysis of plasmid genome evolution based on nucleotide-sequence comparison of two related plasmids of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):299–310. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90146-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sista P. R., Mukherjee S., Patel P., Khatri G. S., Bastia D. A host-encoded DNA-binding protein promotes termination of plasmid replication at a sequence-specific replication terminus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3026–3030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabuchi A., Min Y. N., Kim C. K., Fan Y. L., Womble D. D., Rownd R. H. Genetic organization and nucleotide sequence of the stability locus of IncFII plasmid NR1. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 5;202(3):511–525. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90282-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabuchi A., Min Y. N., Womble D. D., Rownd R. H. Autoregulation of the stability operon of IncFII plasmid NR1. J Bacteriol. 1992 Dec;174(23):7629–7634. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.23.7629-7634.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanimoto K., Iino T., Ohtsubo H., Ohtsubo E. Identification of a gene, tir of R100, functionally homologous to the F3 gene of F in the inhibition of RP4 transfer. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;198(2):356–357. doi: 10.1007/BF00383019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ubben D., Schmitt R. Tn1721 derivatives for transposon mutagenesis, restriction mapping and nucleotide sequence analysis. Gene. 1986;41(2-3):145–152. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Womble D. D., Dong X., Wu R. P., Luckow V. A., Martinez A. F., Rownd R. H. IncFII plasmid incompatibility product and its target are both RNA transcripts. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):28–35. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.28-35.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Womble D. D., Rownd R. H. Genetic and physical map of plasmid NR1: comparison with other IncFII antibiotic resistance plasmids. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Dec;52(4):433–451. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.4.433-451.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Womble D. D., Rownd R. H. Regulation of IncFII plasmid DNA replication. A quantitative model for control of plasmid NR1 replication in the bacterial cell division cycle. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 5;192(3):529–547. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90274-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Womble D. D., Sampathkumar P., Easton A. M., Luckow V. A., Rownd R. H. Transcription of the replication control region of the IncFII R-plasmid NR1 in vitro and in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1985 Feb 5;181(3):395–410. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90228-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


