Abstract
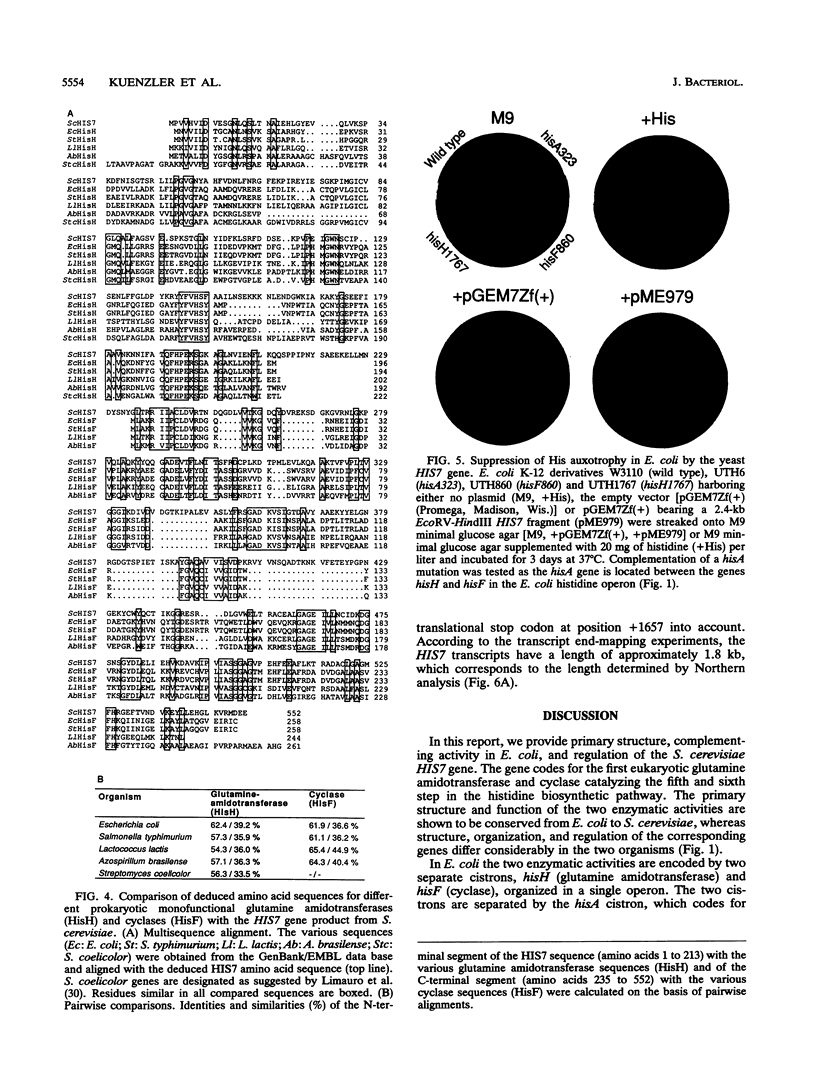
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae HIS7 gene was cloned by its location immediately downstream of the previously isolated and characterized ARO4 gene. The two genes have the same orientation with a distance of only 416 bp between the two open reading frames. The yeast HIS7 gene represents the first isolated eukaryotic gene encoding the enzymatic activities which catalyze the fifth and sixth step in histidine biosynthesis. The open reading frame of the HIS7 gene has a length of 1,656 bp resulting in a gene product of 552 amino acids with a calculated molecular weight of 61,082. Two findings implicate a bifunctional nature of the HIS7 gene product. First, the N-terminal and C-terminal segments of the deduced HIS7 amino acid sequence show significant homology to prokaryotic monofunctional glutamine amidotransferases and cyclases, respectively, involved in histidine biosynthesis. Second, the yeast HIS7 gene is able to suppress His auxotrophy of corresponding Escherichia coli hisH and hisF mutants. HIS7 gene expression is regulated by the general control system of amino acid biosynthesis. GCN4-dependent and GCN4-independent (basal) transcription use different initiator elements in the HIS7 promoter.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AHMED A., CASE M. E., GILES N. H. THE NATURE OF COMPLEMENTATION AMONG MUTANTS IN THE HISTIDINE-3 REGION OF NEUROSPORA CRASSA. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1964 Dec;17:53–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altboum Z., Gottlieb S., Lebens G. A., Polacheck I., Segal E. Isolation of the Candida albicans histidinol dehydrogenase (HIS4) gene and characterization of a histidine auxotroph. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3898–3904. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3898-3904.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndt K. T., Styles C., Fink G. R. Multiple global regulators control HIS4 transcription in yeast. Science. 1987 Aug 21;237(4817):874–880. doi: 10.1126/science.3303332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndt K., Fink G. R. GCN4 protein, a positive transcription factor in yeast, binds general control promoters at all 5' TGACTC 3' sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8516–8520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckler G. S., Reeve J. N. Conservation of primary structure in the hisI gene of the archaebacterium, Methanococcus vannielii, the eubacterium Escherichia coli, and the eucaryote Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jul;204(1):133–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00330200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. The primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene for alcohol dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3018–3025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braus G., Mösch H. U., Vogel K., Hinnen A., Hütter R. Interpathway regulation of the TRP4 gene of yeast. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):939–945. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03455.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlomagno M. S., Chiariotti L., Alifano P., Nappo A. G., Bruni C. B. Structure and function of the Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli K-12 histidine operons. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):585–606. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90194-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Martinez-Arias A., Shapira S. K., Chou J. Beta-galactosidase gene fusions for analyzing gene expression in escherichia coli and yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:293–308. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daignan-Fornier B., Fink G. R. Coregulation of purine and histidine biosynthesis by the transcriptional activators BAS1 and BAS2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6746–6750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delorme C., Ehrlich S. D., Renault P. Histidine biosynthesis genes in Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(20):6571–6579. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.20.6571-6579.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue T. F., Farabaugh P. J., Fink G. R. The nucleotide sequence of the HIS4 region of yeast. Gene. 1982 Apr;18(1):47–59. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90055-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINK G. R. GENE-ENZYME RELATIONS IN HISTIDINE BIOSYNTHESIS IN YEAST. Science. 1964 Oct 23;146(3643):525–527. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3643.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fani R., Bazzicalupo M., Damiani G., Bianchi A., Schipani C., Sgaramella V., Polsinelli M. Cloning of histidine genes of Azospirillum brasilense: organization of the ABFH gene cluster and nucleotide sequence of the hisB gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Apr;216(2-3):224–229. doi: 10.1007/BF00334360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furter R., Paravicini G., Aebi M., Braus G., Prantl F., Niederberger P., Hütter R. The TRP4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: isolation and structural analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6357–6373. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. E., Hope I. A., Macke J. P., Struhl K. Saturation mutagenesis of the yeast his3 regulatory site: requirements for transcriptional induction and for binding by GCN4 activator protein. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):451–457. doi: 10.1126/science.3532321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G. A hierarchy of trans-acting factors modulates translation of an activator of amino acid biosynthetic genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2349–2360. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G., Fink G. R. Repeated DNA sequences upstream from HIS1 also occur at several other co-regulated genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5238–5247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G. Mechanisms of gene regulation in the general control of amino acid biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jun;52(2):248–273. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.2.248-273.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. Bacteriophage T4 late promoters: mapping 5' ends of T4 gene 23 mRNAs. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):107–114. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01132.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Künzler M., Paravicini G., Egli C. M., Irniger S., Braus G. H. Cloning, primary structure and regulation of the ARO4 gene, encoding the tyrosine-inhibited 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1992 Apr 1;113(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90670-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legerton T. L., Yanofsky C. Cloning and characterization of the multifunctional his-3 gene of Neurospora crassa. Gene. 1985;39(2-3):129–140. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limauro D., Avitabile A., Cappellano C., Puglia A. M., Bruni C. B. Cloning and characterization of the histidine biosynthetic gene cluster of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Gene. 1990 May 31;90(1):31–41. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90436-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minton N. P. Improved plasmid vectors for the isolation of translational lac gene fusions. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):269–273. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90220-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miozzari G., Niederberger P., Hütter R. Tryptophan biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: control of the flux through the pathway. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):48–59. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.48-59.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer R. K., Contopoulou C. R., King J. S. Genetic and physical maps of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Edition 11. Yeast. 1992 Oct;8(10):817–902. doi: 10.1002/yea.320081002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mösch H. U., Graf R., Braus G. H. Sequence-specific initiator elements focus initiation of transcription to distinct sites in the yeast TRP4 promoter. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4583–4590. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05560.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai A., Ward E., Beck J., Tada S., Chang J. Y., Scheidegger A., Ryals J. Structural and functional conservation of histidinol dehydrogenase between plants and microbes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4133–4137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagawa F., Fink G. R. The relationship between the "TATA" sequence and transcription initiation sites at the HIS4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8557–8561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederberger P., Aebi M., Hütter R. Identification and characterization of four new GCD genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet. 1986;10(9):657–664. doi: 10.1007/BF00410913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiwaki K., Hayashi N., Irie S., Chung D. H., Harashima S., Oshima Y. Structure of the yeast HIS5 gene responsive to general control of amino acid biosynthesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jun;208(1-2):159–167. doi: 10.1007/BF00330437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver S. G., van der Aart Q. J., Agostoni-Carbone M. L., Aigle M., Alberghina L., Alexandraki D., Antoine G., Anwar R., Ballesta J. P., Benit P. The complete DNA sequence of yeast chromosome III. Nature. 1992 May 7;357(6373):38–46. doi: 10.1038/357038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paravicini G., Braus G., Hütter R. Structure of the ARO3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Sep;214(1):165–169. doi: 10.1007/BF00340197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellman D., McLaughlin M. E., Fink G. R. TATA-dependent and TATA-independent transcription at the HIS4 gene of yeast. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):82–85. doi: 10.1038/348082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggot P. J., Hoch J. A. Revised genetic linkage map of Bacillus subtilis. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Jun;49(2):158–179. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.2.158-179.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratzkin B., Carbon J. Functional expression of cloned yeast DNA in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):487–491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Cameron J. R., Davis R. W. Functional genetic expression of eukaryotic DNA in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1471–1475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Chen W., Hill D. E., Hope I. A., Oettinger M. A. Constitutive and coordinately regulated transcription of yeast genes: promoter elements, positive and negative regulatory sites, and DNA binding proteins. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:489–503. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tice-Baldwin K., Fink G. R., Arndt K. T. BAS1 has a Myb motif and activates HIS4 transcription only in combination with BAS2. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):931–935. doi: 10.1126/science.2683089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel K., Hörz W., Hinnen A. The two positively acting regulatory proteins PHO2 and PHO4 physically interact with PHO5 upstream activation regions. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2050–2057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wobbe C. R., Struhl K. Yeast and human TATA-binding proteins have nearly identical DNA sequence requirements for transcription in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3859–3867. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]