Abstract
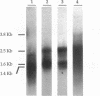
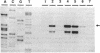
The sequencing of the EcoRI-HindIII fragment complementing mutations in the structural genes of the L-rhamnose regulon of Escherichia coli has permitted identification of the open reading frames corresponding to rhaB, rhaA, and rhaD. The deduced amino acid sequences gave a 425-amino-acid polypeptide corresponding to rhamnulose kinase for rhaB, a 400-amino-acid polypeptide corresponding to rhamnose isomerase for rhaA, and a 274-amino-acid polypeptide corresponding to rhamnulose-1-phosphate aldolase for rhaD. Transcriptional fusions of the three putative promoter regions to lacZ showed that only the rhaB leader region acted as a promoter, as indicated by the high beta-galactosidase activity induced by rhamnose, while no significant activity from the rhaA and rhaD constructions was detected. The rhaB transcription start site was mapped to -24 relative to the start of translation. Mutations in the catabolic genes were used to show that L-rhamnose may directly induce rhaBAD transcription.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Zarban S., Heffernan L., Nishitani J., Ransone L., Wilcox G. Positive control of the L-rhamnose genetic system in Salmonella typhimurium LT2. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):603–608. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.603-608.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 8. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jun;54(2):130–197. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.2.130-197.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backman K., Chen Y. M., Magasanik B. Physical and genetic characterization of the glnA--glnG region of the Escherichia coli chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3743–3747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badía J., Baldomà L., Aguilar J., Boronat A. Identification of the rhaA, rhaB and rhaD gene products from Escherichia coli K-12. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Dec;53(3):253–257. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90226-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belasco J. G., Beatty J. T., Adams C. W., von Gabain A., Cohen S. N. Differential expression of photosynthesis genes in R. capsulata results from segmental differences in stability within the polycistronic rxcA transcript. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):171–181. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90320-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boronat A., Aguilar J. Rhamnose-induced propanediol oxidoreductase in Escherichia coli: purification, properties, and comparison with the fucose-induced enzyme. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):320–326. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.320-326.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. K., Romana L. K., Reeves P. R. Molecular analysis of the rfb gene cluster of Salmonella serovar muenchen (strain M67): the genetic basis of the polymorphism between groups C2 and B. Mol Microbiol. 1992 May;6(10):1385–1394. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00859.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. Y., Beatty J. T., Cohen S. N., Belasco J. G. An intercistronic stem-loop structure functions as an mRNA decay terminator necessary but insufficient for puf mRNA stability. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):609–619. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90473-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. M., Lin E. C. Dual control of a common L-1,2-propanediol oxidoreductase by L-fucose and L-rhamnose in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):828–832. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.828-832.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. M., Lu Z., Lin E. C. Constitutive activation of the fucAO operon and silencing of the divergently transcribed fucPIK operon by an IS5 element in Escherichia coli mutants selected for growth on L-1,2-propanediol. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6097–6105. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6097-6105.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. M., Tobin J. F., Zhu Y., Schleif R. F., Lin E. C. Cross-induction of the L-fucose system by L-rhamnose in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3712–3719. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3712-3719.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. M., Zhu Y., Lin E. C. The organization of the fuc regulon specifying L-fucose dissimilation in Escherichia coli K12 as determined by gene cloning. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Dec;210(2):331–337. doi: 10.1007/BF00325702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimri G. P., Rudd K. E., Morgan M. K., Bayat H., Ames G. F. Physical mapping of repetitive extragenic palindromic sequences in Escherichia coli and phylogenetic distribution among Escherichia coli strains and other enteric bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(14):4583–4593. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.14.4583-4593.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway J. L., Platt T. Signals sufficient for rho-dependent transcription termination at trp t' span a region centered 60 base pairs upstream of the earliest 3' end point. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1761–1767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Martin C., Baldomà L., Badía J., Aguilar J. Nucleotide sequence of the rhaR-sodA interval specifying rhaT in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Jun;138(6):1109–1116. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-6-1109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson E., Saurin W., Perrin D., Bachellier S., Hofnung M. Palindromic units are part of a new bacterial interspersed mosaic element (BIME). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1375–1383. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.7.1375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson E., Saurin W., Perrin D., Bachellier S., Hofnung M. The BIME family of bacterial highly repetitive sequences. Res Microbiol. 1991 Feb-Apr;142(2-3):217–222. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo E., Chen Y. M., Lin E. C., Aguilar J. Molecular cloning and DNA sequencing of the Escherichia coli K-12 ald gene encoding aldehyde dehydrogenase. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):6118–6123. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.6118-6123.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes: a proposal for a synonymous codon choice that is optimal for the E. coli translational system. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):389–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang X. M., Neal B., Santiago F., Lee S. J., Romana L. K., Reeves P. R. Structure and sequence of the rfb (O antigen) gene cluster of Salmonella serovar typhimurium (strain LT2). Mol Microbiol. 1991 Mar;5(3):695–713. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00741.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Z., Lin E. C. The nucleotide sequence of Escherichia coli genes for L-fucose dissimilation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4883–4884. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupski J. R., Weinstock G. M. Short, interspersed repetitive DNA sequences in prokaryotic genomes. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(14):4525–4529. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.14.4525-4529.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick J. R., Zengel J. M., Lindahl L. Intermediates in the degradation of mRNA from the lactose operon of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 25;19(10):2767–2776. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.10.2767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. D., Bear D. G., Litchman B. L., von Hippel P. H. RNA sequence and secondary structure requirements for rho-dependent transcription termination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 24;13(10):3739–3754. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.10.3739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newbury S. F., Smith N. H., Higgins C. F. Differential mRNA stability controls relative gene expression within a polycistronic operon. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1131–1143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90599-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishitani J., Wilcox G. Cloning and characterization of the L-rhamnose regulon in Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Gene. 1991 Aug 30;105(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90511-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Power J. The L-rhamnose genetic system in Escherichia coli K-12. Genetics. 1967 Mar;55(3):557–568. doi: 10.1093/genetics/55.3.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder T., Schleif R. AraC protein can activate transcription from only one position and when pointed in only one direction. J Mol Biol. 1993 May 20;231(2):205–218. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander C., Schneider R. Database of homology-derived protein structures and the structural meaning of sequence alignment. Proteins. 1991;9(1):56–68. doi: 10.1002/prot.340090107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Houman F., Kleckner N. Improved single and multicopy lac-based cloning vectors for protein and operon fusions. Gene. 1987;53(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. J., Ames G. F., Smith N. H., Robinson E. C., Higgins C. F. Repetitive extragenic palindromic sequences: a major component of the bacterial genome. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1015–1026. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90436-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate C. G., Muiry J. A., Henderson P. J. Mapping, cloning, expression, and sequencing of the rhaT gene, which encodes a novel L-rhamnose-H+ transport protein in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6923–6932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin J. F., Schleif R. F. Positive regulation of the Escherichia coli L-rhamnose operon is mediated by the products of tandemly repeated regulatory genes. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):789–799. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90405-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin J. F., Schleif R. F. Purification and properties of RhaR, the positive regulator of the L-rhamnose operons of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jan 5;211(1):75–89. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90012-B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziemke P., McCarthy J. E. The control of mRNA stability in Escherichia coli: manipulation of the degradation pathway of the polycistronic atp mRNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Apr 6;1130(3):297–306. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90442-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- d'Aubenton Carafa Y., Brody E., Thermes C. Prediction of rho-independent Escherichia coli transcription terminators. A statistical analysis of their RNA stem-loop structures. J Mol Biol. 1990 Dec 20;216(4):835–858. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(99)80005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]